Question
The table shows some measurable quantities.
Which row gives the correct order of magnitude of the measurable quantity in the stated unit?
| measurable quantity | order of magnitude | unit | |
A B C D | mass of a coin thickness of a sheet of paper weight of an apple temperature of a person’s body | 10–4 10–2 100 101 | kg m N K |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
A byte (b) comprises 8 bits.
How many bits are there in 1 terabyte (1Tb)?
A 1 × 109 B 8 × 109 C 1 × 1012 D 8 × 1012
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
Which pair of quantities contains both a scalar and a vector?
A acceleration and momentum
B charge and resistance
C kinetic energy and mass
D temperature and velocity
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
A transmitter emits a pulse of electromagnetic waves towards a reflector. The pulse is reflected and returns to the transmitter.
A detector is located at the transmitter. The emitted pulse and the reflected pulse are displayed on a cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO) as shown.
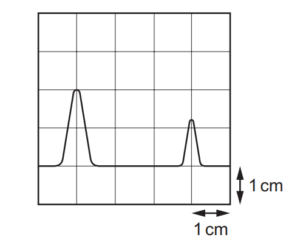
The pulse takes 6.3 µs to travel from the transmitter to the reflector.
What is the time-base setting of the CRO?
A 2.1µs cm–1 B 3.2µs cm–1 C 4.2µs cm–1 D 6.3µs cm–1
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
A micrometer is used to measure the diameters of two cylinders.
diameter of first cylinder = (12.78 ± 0.02) mm
diameter of second cylinder = (16.24 ± 0.03) mm
The difference in the diameters is calculated.
What is the uncertainty in this difference?
A 0.01 mm B 0.02 mm C 0.03 mm D 0.05 mm
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
A stone is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff and falls into the sea below. Air resistance is negligible. The path of the stone is shown.
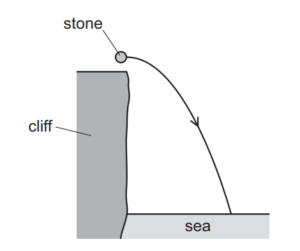
In which direction does the resultant force on the stone act during its fall?
A horizontally to the right
B parallel to its velocity
C perpendicular to its velocity
D vertically downwards
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
A car moves with uniform acceleration along a straight road. Oil leaks from the car at the rate of one drop every two seconds. The diagram shows the distances between three successive oil drops on the road.
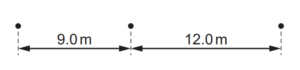
What is the acceleration of the car?
A 0.75 m s–2 B 1.5 m s–2 C 3.0 m s–2 D 6.0 m s–2
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
A person of mass 60 kg stands on accurate bathroom scales, placed on the floor of an elevator (lift) which operates in a tall building.
At a certain instant the bathroom scales read 58kg.
Which row could give the person’s direction of movement and type of motion?
| direction | motion | |
A B C D | downwards downwards upwards upwards | constant speed slowing down constant speed slowing down |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
The diagram shows graphs of various quantities plotted against time for an object dropped from a stationary balloon high in the atmosphere.
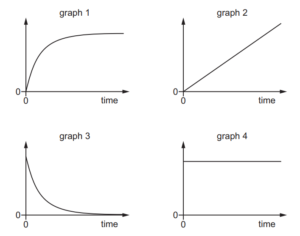
Which statement could be correct?
A Graph 1 is acceleration against time and graph 3 is resultant force against time.
B Graph 1 is acceleration against time and graph 4 is resultant force against time.
C Graph 3 is acceleration against time and graph 1 is velocity against time.
D Graph 3 is acceleration against time and graph 2 is velocity against time.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
The diagram shows a particle P, travelling at speed v, about to collide with a stationary particle Q of the same mass. The collision is perfectly elastic.

Which statement describes the motion of P and of Q immediately after the collision?
A P and Q both travel in the same direction with speed \(\frac{1}{2}V\) .
B P comes to rest and Q acquires speed V.
C P rebounds with speed \(\frac{1}{2}V\) and Q acquires speed \(\frac{1}{2}V\) .
D P rebounds with speed v and Q remains stationary.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
A particle is in a uniform field. The particle experiences a force in the opposite direction to the field.
In which type of field is the particle, and on which property of the particle is the field acting?
| type of field | property of particle on which the field acts | |
A B C D | electric electric gravitational gravitational | charge current mass weight |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
A uniform rod of weight 20 N and length 2.0 m is acted upon by two vertical forces, as shown.

What are the resultant force acting on the rod and the resultant moment about the centre of gravity of the rod?
| resultant force /N | resultant moment /N m | |
A B C D | 0 0 20 20 | 10 20 10 20 |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
Three coplanar forces act on a block.
Which diagram shows the directions of the forces such that the block could be in equilibrium?
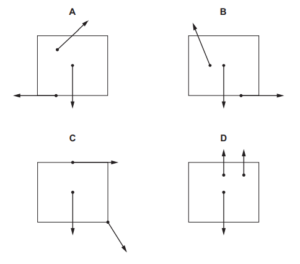
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
A cylinder contains a volume of 0.012 m3
of gas at a pressure of 1.0 × 105Pa.
400 J of work is done on this gas, with its pressure remaining constant throughout.
What is the final volume of the gas?
A 0.0040 m3 B 0.0080 m3 C 0.016 m3 D 0.020 m3
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the surface of the Earth.
Which statement describes the energy of the ball as it rises through the air?
A The kinetic energy of the ball decreases as the gravitational potential energy decreases.
B The kinetic energy of the ball decreases as the gravitational potential energy increases.
C The kinetic energy of the ball increases as the gravitational potential energy decreases.
D The total energy of the ball increases.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
A sledge of mass 50 kg sits on a snowy surface. It is pulled horizontally for 10 m against a
frictional force of 200N, then it is pulled horizontally across ice for 10 m. There is no friction
between the ice and the sledge. It is lifted up vertically by 1 m and finally carried back at a
constant speed to where it started.
During which stage of its journey is most work done on the sledge?
A being carried back 20 m at constant speed
B being lifted up 1 m
C being pulled 10 m across ice
D being pulled 10 m across snow
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
An object is moved in a vertical plane from X to Y, and then from Y to Z, as shown in the diagram.
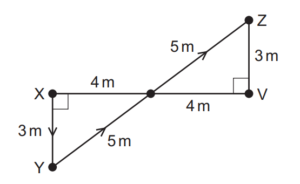
The distances between various points are indicated on the diagram.
Lines XY and VZ are vertical.
The object weighs 20 N.
How much gravitational potential energy does the object gain by moving from X to Z?
A 60 J B 120 J C 140 J D 260 J
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
A car travels at a constant speed of 25 m s–1 up a slope. The wheels driven by the engine exert a
forward force of 3000N. The total force due to air resistance and friction is 2100N. The weight of
the car has a component down the slope of 900N.
What is the rate at which thermal energy is dissipated?
A zero B 2.3 × 104W C 5.3 × 104W D 7.5 × 104W
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
A composite rod is made by attaching a glass-reinforced plastic rod and a nylon rod end to end, as shown.
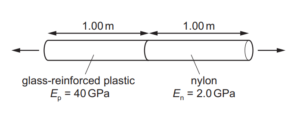
The rods have the same cross-sectional area and each rod is 1.00 m in length. The Young modulus Ep of the plastic is 40GPa and the Young modulus En of the nylon is 2.0GPa.
The composite rod will break when its total extension reaches 3.0 mm.
What is the greatest tensile stress that can be applied to the composite rod before it breaks?
A 2.9 × 106Pa
B 5.7 × 106Pa
C 2.9 × 109Pa
D 5.7 × 109Pa
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
The graph shows the non-linear force–extension curve for a wire made from a new composite material.
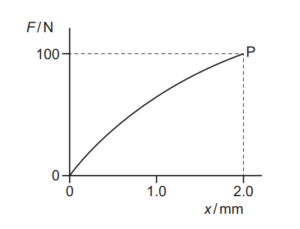
What is the best estimate of the work done in stretching the wire to point P?
A 0.09 J B 0.10 J C 0.11 J D 0.20 J
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
A wave of frequency 15Hz travels at 24 m s–1 through a medium.
What is the phase difference between two points 2.0 m apart?
A There is no phase difference.
B They are out of phase by a quarter of a cycle.
C They are out of phase by half a cycle.
D They are out of phase by 0.80 of a cycle.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
Which row describes a longitudinal wave and a medium through which it can travel?
| direction of oscillation of the medium compared with the direction of propagation of wave energy | medium | |
A B C D | parallel parallel perpendicular perpendicular | air vacuum air vacuum |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
A sound wave is displayed on the screen of a cathode-ray oscilloscope, as shown.
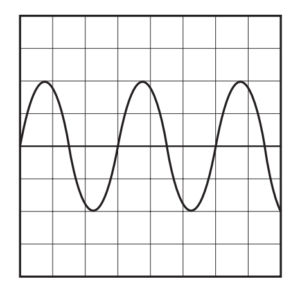
The time-base setting is 0.50 ms per division.
What is the frequency of the sound wave?
A 500Hz B 670Hz C 1000Hz D 1300Hz
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
An observer is situated at the top of a tall tower. An aeroplane emitting sound at a frequency of 1000Hz approaches the observer at a speed of 165 m s–1.
The speed of sound is 330 m s–1.
What is the frequency of the sound received by the observer?
A 330Hz B 667Hz C 1000Hz D 2000Hz
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
What is the order of magnitude of the wavelengths of microwaves and X-rays?
| wavelength of microwaves / m | wavelength of X-rays / m | |
A B C D | 10–6 10–2 10–6 10–2 | 103 103 10–10 10–10 |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
A musical instrument is made using a long tube with a mouthpiece at one end. The other end is open and flared, as shown.
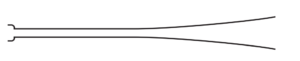
A musician maintains stationary sound waves with a node at the mouthpiece and an antinode at the other end. The lowest frequency of sound that the instrument can produce is 92Hz.
Which different frequencies of sound can be produced by the instrument?
A 92Hz, 138Hz, 184Hz, 230Hz
B 92Hz, 184Hz, 276Hz, 368Hz
C 92Hz, 276Hz, 460Hz, 644Hz
D 92Hz, 276Hz, 828Hz, 1288Hz
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
A water wave passes through a gap between two barriers. The wavefronts spread out as shown.

What is the name of this phenomenon?
A coherence
B diffraction
C interference
D superposition
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
The table shows four possible combinations of values for the laser wavelength, slit separation and slit-screen distance in a two-slit interference experiment to show the interference of visible light on a white screen.
Which combination will result in visible fringes being observed?
| aser wavelength / nm | slit separation / mm | slit-screen distance/ m | |
A B C D | 200 200 600 600 | 0.10 100 0.10 100 | 5.0 1.0 5.0 1.0 |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
Light of wavelength λ is incident normally on a diffraction grating, as shown.
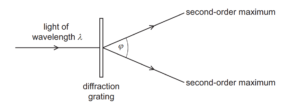
The angle between the two second-order maxima is ϕ.
Which expression gives the spacing of the lines on the diffraction grating?
A \(\frac{\lambda }{sin\theta }\) B \(\frac{\lambda }{\left ( sin\theta /2 \right )}\) C \(\frac{2\lambda }{sin\theta }\) D \(\frac{2\lambda }{sin\left ( \theta /2 \right )}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
Two positive charges and one negative charge, all of equal magnitude, are set at the corners of an equilateral triangle.
Which diagram represents the electric field surrounding the charges?

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
A negatively charged oil drop is held stationary, equidistant between two plates connected to a high voltage supply, as shown.

Which change would not increase the upward electrical force on the drop?
A decreasing the distance between the plates whilst keeping the drop equidistant from them
B increasing the amount of negative charge on the drop
C increasing the supply voltage
D moving the drop closer to the positive plate
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
Electrons move in a vacuum from one metal plate to another metal plate. As a result of this, there is an electric current of 48 µA between the two plates.
How many electrons are emitted by the first plate in a time of 5.0 minutes?
A 1.4 × 104 B 1.5 × 1015 C 1.8 × 1016 D 9.0 × 1016
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
A battery is connected to three resistors of resistances 12Ω, 6Ω and 2Ω, as shown.
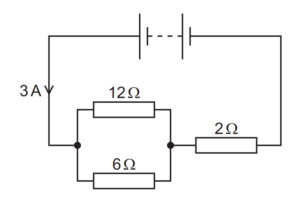
The current from the battery is 3A.
What is the value of the ratio \(\frac{power dissipated in the resistor of resistance 6\Omega }{power dissipated in the resistor of resistance 6\Omega }\)
A \(\frac{1}{3}\) B \(\frac{4}{3}\) C \(\frac{2}{1}\) D \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
A manufacturer recommends that the longer the extension cord you use with an electric drill, the bigger the cross-sectional area of the cord should be.
What is a reason for this recommendation?
A Resistance is inversely proportional to both the length and the cross-sectional area.
B Resistance is inversely proportional to the length and directly proportional to the cross-sectional area.
C Resistance is proportional to both the length and the cross-sectional area.
D Resistance is proportional to the length and inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
Two batteries are connected together, as shown.
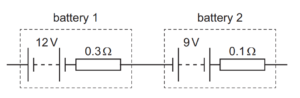
Battery 1 has electromotive force (e.m.f.) 12V and internal resistance 0.3Ω.
Battery 2 has e.m.f. 9V and internal resistance 0.1Ω.
What are the e.m.f. and the internal resistance of a single battery that has the same effect as the combination?
| e.m.f. /V | internal resistance/Ω | |
A B C D | 3 3 21 21 | 0.2 0.4 0.2 0.4 |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
The diagram shows a circuit.
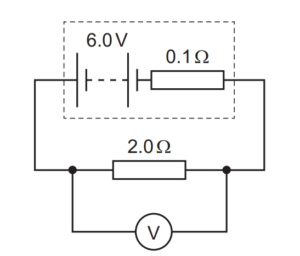
What is the reading on the voltmeter?
A 0.3V B 5.7V C 6.0V D 6.3V
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
In the circuits shown, the cell has negligible internal resistance.
Which diagram shows a potential divider circuit that can vary the potential difference (p.d.) across the lamp?

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
Two alpha-particles with the same kinetic energy are moving towards, and are then deflected by, a gold nucleus.

Which diagram could show the paths of the two alpha-particles?

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
The equation represents the decay of a nucleus X to a nucleus Y.
\(_{Z}^{A}\textrm{X}\rightarrow _{Z-1}^{A}\textrm{X}+p+q\)
What are particles p and q?
| p | q | |
A B C D | β–particle β–particle β+particle β+particle | neutron proton antineutrino neutrino |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
Which row gives the correct type and quark composition for the named particle?
| particle | type | quark composition | |
A B C D | neutron neutron proton proton | hadron lepton hadron lepton | u u d u d d u u d u d d |
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
