Questions 1
Topic – 1.2
Which row shows a physical quantity and its base unit in the SI system?
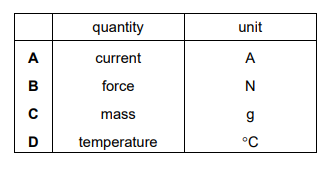
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans A
Questions 2
Topic – 2.1
A car of mass 850 kg is travelling in a horizontal straight line. The diagram shows the two horizontal forces acting on the car in opposite directions.

One force has magnitude 1200 N, and the other force has magnitude 1600 N. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the car?
A \(0.47 m s^{–2}\)
B \(1.4 m s^{–2}\)
C \(1.9 m s^{–2}\)
D \(3.3 m s^{–2}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans A
Questions 3
Topic – 6.1
An object of mass m is suspended by a spring from a fixed point.

The spring has spring constant k. The object is set into vertical oscillations of period T. Which equation for T is homogeneous with respect to base units?
A \(T=2\pi (\frac{k}{m})\)
B \(T=2\pi (\frac{m}{k})\)
C \(T=2\pi \sqrt{\frac{k}{m}}\)
D \(T=2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 4
Topic – 3.1
An object of fixed mass is initially at rest at point P. The object then moves away from point P with uniform acceleration. Which statement describes the resultant force acting on the object when it is moving?
A It increases uniformly with respect to time.
B It is constant but not zero.
C It is proportional to the displacement from point P.
D It is zero.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 5
Topic – 2.1
A projectile is launched at an angle of \(25 \circ \) to the horizontal with a horizontal component of velocity of \(13 m s^{–1}\). What is the vertical component of the velocity of the projectile when it is launched?
A \(5.5 m s^{–1}\)
B \(6.1 m s^{–1}\)
C \(12 m s^{–1}\)
D \(14 m s^{–1}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 6
Topic – 2.1
A ball is released from rest at position X at time zero. At 1.0 s, it bounces inelastically from a horizontal surface and rebounds, reaching the top of its first bounce at 1.5 s.
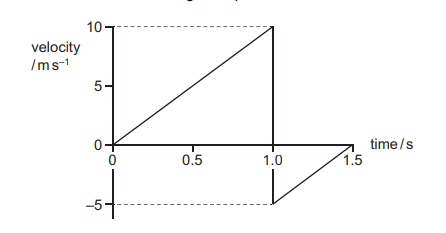
What is the total displacement of the ball from its original position X at 1.5 s?
A 1.25 m
B 3.75 m
C 5.00 m
D 6.25 m
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 7
Topic – 2.1
What is the definition of acceleration?
A change in velocity per unit time
B rate of change of speed per unit time
C rate of change of velocity per unit time
D resultant force per unit mass
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans A
Questions 8
Topic – 2.1
Two balls P and Q, of equal mass, move along a straight line directly towards each other as shown.
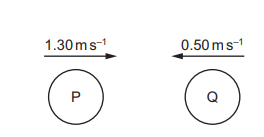
Ball P has velocity \(1.30 m s^{–1}\) to the right. Ball Q has velocity \(0.50 m s{–1}\) to the left. P and Q collide with one another. The collision is perfectly elastic and the total momentum is conserved. Which diagram correctly shows the motion of P and Q after the collision? 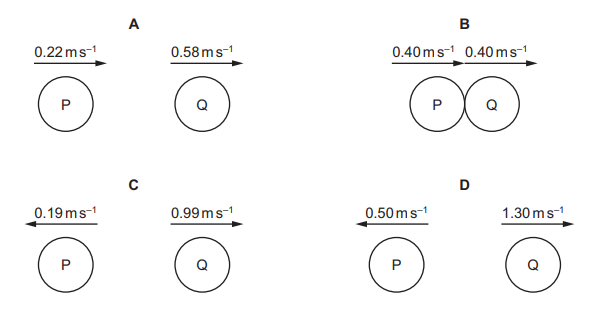
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 9
Topic – 2.1
A basketball player hits a ball vertically downwards with a speed of \(2.4 m s^{–1}\) from a height of 0.90 m. Air resistance is negligible. What is the speed of the ball as it hits the ground?
A \(4.2 m s^{–1}\)
B \(4.8 m s^{–1}\)
C \(18 m s^{–1}\)
D \(23 m s^{–1}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 10
Topic – 4.3
A ball falls through a liquid at a constant speed. It is acted upon by three forces: an upthrust, a drag force and its weight. The liquid has a uniform density. Which statement is correct?
A The drag force increases with increasing depth.
B The drag force is equal to the sum of the upthrust and weight.
C The upthrust is constant with increasing depth.
D The weight is greater than the sum of the drag force and the upthrust.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 11
Topic – 4.1
Some small solid cubes each have mass 1.0 kg and sides of length 5.0 cm. These small cubes are stacked together to form a large solid cube with sides of length 2.0 m. What is the weight of the large cube?
A 0.39 kN
B 0.39 MN
C 0.63 MN
D 0.63GN
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 12
Topic – 4.1
A borehole of depth 2000 m contains both oil and water, as shown. The pressure due to the liquids at the bottom of the borehole is 17.5 MPa. The density of the oil is \(830 kgm^{–3}\) and the density of the water is \(1000 kgm^{–3}\).
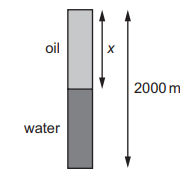
What is the depth x of the oil?
A 907 m
B 1000 m
C 1090 m
D 1270 m
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 13
Topic – 4.2
A rod is pivoted at one end. Initially the angle \(\Theta\) of the rod to the horizontal is \(0\circ \) . The weight of the rod causes a moment M about the pivot. The rod is then rotated in the vertical plane so that the angle \(\Theta\) of the rod increases from \(0\circ \) to \(180\circ \) . Which graph shows the variation of M with \(\Theta\) ?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 14
Topic – 4.1
A hinged trapdoor is held closed in the horizontal position by a cable. Three forces act on the trapdoor: the weight W of the door, the tension T in the cable and the force H at the hinge.
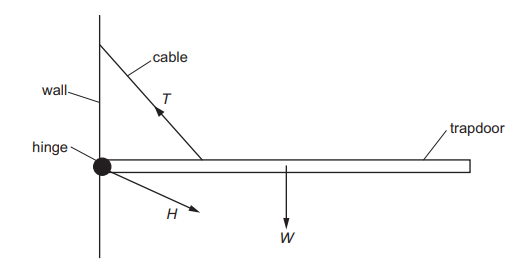
Which list gives the three forces in increasing order of magnitude?
A H, T, W
B T, H, W
C W, H, T
D W, T, H
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 15
Topic – 4.1
What is the definition of force?
A the product of mass and acceleration
B the product of mass and velocity
C the rate of change of momentum
D the rate of transfer of energy
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 16
Topic – 5.1
A boat moves at a constant velocity v through still water. A constant drag force F acts on the boat. What is the power used by the boat to move through the water?
A \(\frac{1}{2}Fv\)
B Fv
C \(\frac{1}{2}Fv^2\)
D \(Fv^2\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 17
Topic – 4.1
The diagram shows four forces acting on a circular disc.
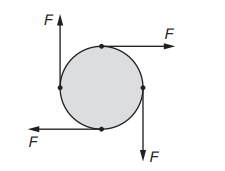
Each force has magnitude F. Two of the forces act vertically and the other two forces act horizontally. All four forces act in the same plane as the disc. No other forces act on the disc. The disc has diameter d. Which statement is correct?
A The disc is in equilibrium because the resultant force is zero.
B The disc is not in equilibrium because the resultant force is 4F.
C The disc is in equilibrium because the resultant torque is zero.
D The disc is not in equilibrium because the resultant torque is 2Fd.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 18
Topic – 5.2
A ball is projected into the air from horizontal ground and follows the path shown in the diagram.
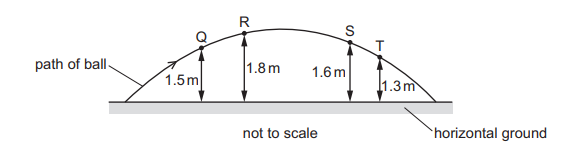
At points Q, R, S and T, the ball has kinetic energies \(E_Q\), \(E_R\), \(E_S\) and \(E_T\) respectively. The heights above the ground of these four points are shown. Air resistance is negligible. Which difference in kinetic energies is the smallest?
A \(E_Q – E_S\)
B \(E_S – E_R\)
C \(E_T – E_Q\)
D \(E_T – E_R\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans A
Questions 19
Topic – 5.1
The battery of a small tablet computer is initially uncharged. It is connected to a constant 10W power supply for 2.0 hours to charge the battery. The efficiency of the charging process is 80%. What is the total energy stored in the battery?
A \(1.6 × 10^1 J\)
B \(1.6 × 10^3 J\)
C \(5.8 × 10^4 J\)
D \(5.8 × 10^6 J\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 20
Topic – 5.2
An initially stationary firework explodes and splits into two fragments that move horizontally in opposite directions. The total kinetic energy transferred to the fragments by the explosion is E. One fragment has mass m and the other one has mass 2m. What is the speed of the fragment of mass m immediately after the explosion?
A \(\sqrt{\frac{E}{m}}\)
B \(\sqrt{\frac{2E}{m}}\)
C \(\sqrt{\frac{2E}{3m}}\)
D \(\sqrt{\frac{4E}{3m}}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 21
Topic – 6.2
A spring is fixed at one end and extended by applying force F to the other end. The spring has extension x and elastic potential energy \(E_P\). The spring constant is k. The spring obeys Hooke’s law. Which relationship is correct for this spring?
A \(E_P \alpha F\)
B \(E_P \alpha x\)
C \(E_P \alpha k\)
D \(E_P \alpha x^2\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 22
Topic – 6.2
A force–extension graph is produced for a metal wire. What must describe the limit of proportionality of the wire?
A the point at which the wire breaks
B the point beyond which Hooke’s law is not obeyed
C the point beyond which the wire cannot return to its original length
D the point beyond which the wire starts to deform plastically
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 23
Topic – 6.1
A spring has a spring constant of 6.0 \(Ncm^{–1}\). It is joined to another spring whose spring constant is 4.0 \(Ncm^{–1}\). A load of 80 N is suspended from this composite spring.
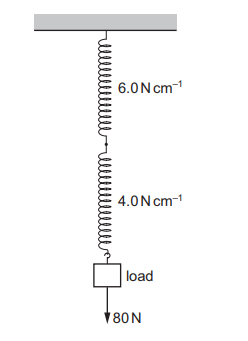
What is the extension of this composite spring?
A 8.0 cm
B 16 cm
C 17 cm
D 33 cm
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 24
Topic – 7.3
The range of frequencies of sound waves emitted by blue whales is 10Hz to 40 Hz. The speed of sound in seawater is approximately 1.5 \(km s^{–1}\). What is the approximate range of wavelengths of the sound waves emitted by blue whales?
A 6.7 mm to 27 mm
B 3.8 cm to 15 cm
C 6.7 m to 27 m
D 38 m to 150 m
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 25
Topic – 7.1
A sound wave is detected by a microphone and displayed on the screen of a cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO).

The frequency of the wave is 2.5 kHz. What is the setting on the time-base of the CRO?
A 0.1 \(ms cm^{–1}\)
B 0.4 \(ms cm^{–1}\)
C 0.1 \(s cm^{–1}\)
D 0.4 \(s cm^{–1}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans A
Questions 26
Topic – 7.3
A source of sound waves with constant frequency moves towards a stationary observer. The observer compares the sound waves arriving at the observer’s position with the waves emitted by the source of sound. What is detected by the observer?
A a decreased frequency of the sound waves
B no change in frequency of the sound waves
C a decreased wavelength of the sound waves
D no change in wavelength of the sound waves
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 27
Topic – 7.1
Which type of waves cannot be polarised?
A radio waves
B sound waves
C ultraviolet waves
D X-rays
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 28
Topic – 8.3
A beam of light with power P has an area of cross-section A. The amplitude of the light waves in the beam is X. The beam of light is then changed to one with the same frequency but with an increased amplitude of 4X and an area of cross-section reduced to \(\frac{A}{3 }\). What is the power of the new beam?
A 1.3P
B 5.3P
C 12P
D 48P
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 29
Topic – 7.1
Two loudspeakers are connected to the same signal generator. The signal generator produces a single frequency. The loudspeakers face each other so that a stationary sound wave is set up in the region between the loudspeakers.
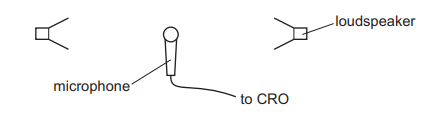
A microphone is connected to a cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO) and positioned between the two loudspeakers. The microphone is moved along a line joining the two loudspeakers. The signal on the CRO shows 5 maximum amplitudes as the microphone moves. The microphone moves a distance of 2.0 m from the position that gives the first maximum to the position that gives the fifth maximum. What is the wavelength of the sound wave?
A 0.40 m
B 0.50 m
C 0.80 m
D 1.0 m
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans D
Questions 30
Topic – 7.4
Two wave sources emit coherent waves. Which condition must be correct for the coherent waves?
A The waves are emitted in phase.
B The waves are emitted and move in opposite directions.
C The waves are emitted with a constant phase difference.
D The waves are emitted with the same amplitude.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 31
Topic – 7.4
A student sets up an experiment to investigate double-slit interference. The student uses light of a single wavelength from a laser to illuminate a double slit so that a pattern of interference fringes is observed on the screen.
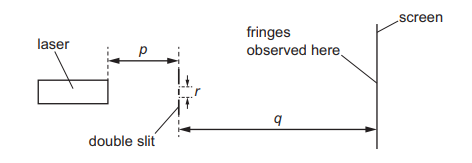
The student finds that the fringes are very close together. What could the student decrease in order to increase the separation of the fringes on the screen?
A the distance p from the laser to the double slit
B the distance q from the double slit to the screen
C the separation r of the slits
D the wavelength of the light from the laser
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 32
Topic – 9.2
What are the definitions of potential difference (p.d.) and electromotive force (e.m.f.), in terms of energy transfer W and charge q?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans A
Questions 33
Topic – 10.2
The diagram shows a network consisting of three resistors.

What is the combined resistance of the network between terminal X and terminal Y?
A 0.67 \( k\Omega \)
B 1.6 \( k\Omega \)
C 3.2 \( k\Omega \)
D 8.1 \( k\Omega \)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 34
Topic – 9.3
A resistor dissipates 25W of power when there is a potential difference (p.d.) of 4.0V across it. What is the resistance of the resistor?
A 0.16\( \Omega \)
B 0.64\( \Omega \)
C 100\( \Omega \)
D 400\( \Omega \)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 35
Topic – 9.1
The diagram shows a cell with internal resistance connected in parallel with a fixed resistor and a variable resistor.

The resistance of the variable resistor is decreased. What happens to the potential difference V across the variable resistor and the current I in the variable resistor? 
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 36
Topic – 11.1
A radioactive source produces a beam of \( \alpha \)-particles in a vacuum. The average current caused by the \( \alpha \)-particles in the beam is \(1.5 × 10^{–9}\)A. The beam is incident on a metal target. What is the average number of \( \alpha \)-particles hitting the metal target in a time of 3.0 s?
A \(4.7 × 10^9\)
B \(9.4 × 10^9\)
C \(1.4 × 10^{10}\)
D \(2.8 × 10^{10}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 37
Topic – 10.1
The charge carriers in a metal wire are free electrons. Which statement about the charge of each free electron is correct?
A The magnitude of the charge increases with the potential difference across the wire.
B The magnitude of the charge is zero unless there is a potential difference across the wire.
C The sign and magnitude of the charge do not depend on the potential difference across the wire.
D The sign of the charge depends on the potential difference across the wire.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Questions 38
Topic – 11.2
Which flavours of quark have charge \(+\frac{2}{3}e ?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans A
Questions 39
Topic – 11.1
An unstable nucleus of an element decays by emitting an \(\alpha \)-particle or a \(\beta ^-\)– particle to become a nucleus of a different element. This nucleus is also unstable and emits an \(\alpha \)-particle or a \(\beta ^-\)– particle. The process continues until an isotope of the original element is produced. What is the minimum possible number of these particles emitted?
A 2
B 3
C 4
D 5
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Questions 40
Topic – 11.1
A nucleus of carbon-10, \(_{6}^{10}\textrm{C} \), decays by beta-emission to form a nucleus of boron-10, \(_{5}^{10}\textrm{B} \). For this decay process, what is the change to a nucleon and what is the change in the quark composition of the nucleon?
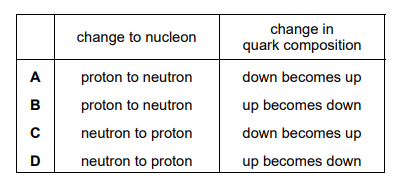
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
