Question
What is a reasonable estimate of the kinetic energy of a car travelling at a speed of 30 m \(s^{–1}\)?
A \(10^2\) J B \(10^4\) J C \(10^6\) J D \(10^8\) J
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
The frequency f of vibration of a mass m supported by a spring with spring constant k is given by the equation
\(f = Cm^pk^q\)
where C is a constant with no units.
What are the values of p and q?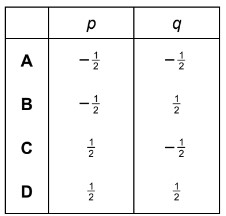
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The power produced by a force moving an object is given by the equation shown.
power = \(\frac{work}{time} = \frac{force \times displacement}{time}\)
Which quantities are scalars and which are vectors?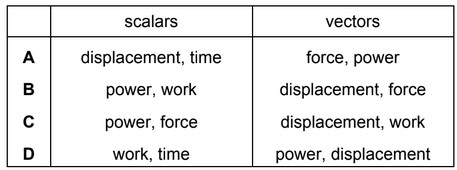
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A cathode-ray oscilloscope displays a square wave, as shown.
The time-base setting is 0.20 ms per division.
What is the frequency of the square wave?
A 0.83Hz B 830Hz C 1300Hz D 1700Hz
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A measurement is taken correctly but with a ruler at a significantly higher temperature than that at
which the ruler was calibrated. The higher temperature causes the ruler to expand.
What describes the effect on the measurement caused by the higher temperature and how the
measurement may be improved?
A The measurement will be subject to a random error. The measurement can be made more
accurate by taking the average of several repeated measurements.
B The measurement will be subject to a random error. The measurement can be made more
precise by taking the average of several repeated measurements.
C The measurement will be subject to a systematic error. The measurement can be made more
accurate by taking the average of several repeated measurements.
D The measurement will be subject to a systematic error. The measurement can be made more
precise by taking the average of several repeated measurements.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
The velocity of an electric car changes as shown.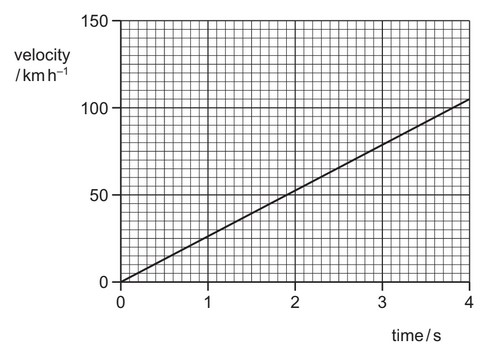
What is the acceleration of the car?
A 210 m \(s^{–2}\) B 58 m \(s^{–2}\) C 26 m \(s^{–2}\) D 7.3 m \(s^{–2}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A projectile is fired from point P with velocity V at an angle θ to the horizontal. It lands at point Q,
a horizontal distance R from P, after time T.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
A car accelerates from rest in a straight line with constant acceleration.
Which graph best represents the variation of the momentum p of the car with the distance s
travelled by the car?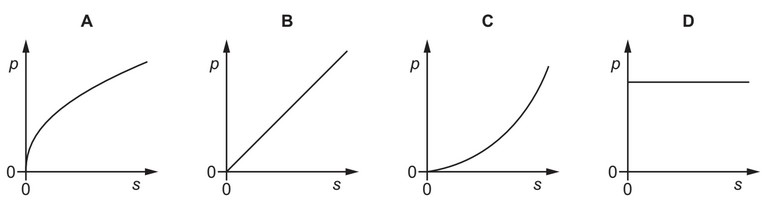
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The resultant force F on a raindrop of mass m falling with velocity v is given by the equation
F = mg – \(kv^2\)
where k is a constant and g is the acceleration of free fall.
What is the velocity of the raindrop when it reaches a constant (terminal) velocity?
A \(\sqrt{\frac{k}{mg}}\) B \(\frac{k}{mg}\) C \(\sqrt{\frac{mg}{k}}\) D \(\frac{mg}{k}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A stationary toy gun fires a bullet.
Which statement about the bullet and the gun, immediately after firing, is not correct?
A The force exerted on the bullet by the gun has the same magnitude as the force exerted on
the gun by the bullet.
B The force exerted on the bullet by the gun is in the opposite direction to the force exerted on
the gun by the bullet.
C The gun and the bullet have the same magnitude of momentum.
D The kinetic energy of the gun must equal the kinetic energy of the bullet.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A wooden block rests on the rough surface of a board. One end of the board is then raised until
the block slides down the board at constant velocity v.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Which statement best describes a couple?
A a pair of forces of equal magnitude acting in opposite directions which produce rotational
motion but not translational motion
B a pair of forces of equal magnitude acting in opposite directions which produce translational
motion but not rotational motion
C a pair of forces of equal magnitude acting in the same direction which produce rotational
motion but not translational motion
D a pair of forces of equal magnitude acting in the same direction which produce translational
motion but not rotational motion
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
A uniform rod XY of weight 10.0N is freely hinged to a wall at X. It is held horizontal by a force F
acting from Y at an angle of 30° to the horizontal, as shown.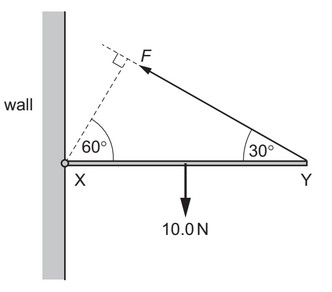
What is the value of F?
A 5.0N B 8.7N C 10.0N D 20.0N
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Four combinations of vectors are shown, each representing all the forces acting on an object.
The forces all act in the same plane.
The object is in equilibrium.
Which combination of vectors could represent the forces acting on the object?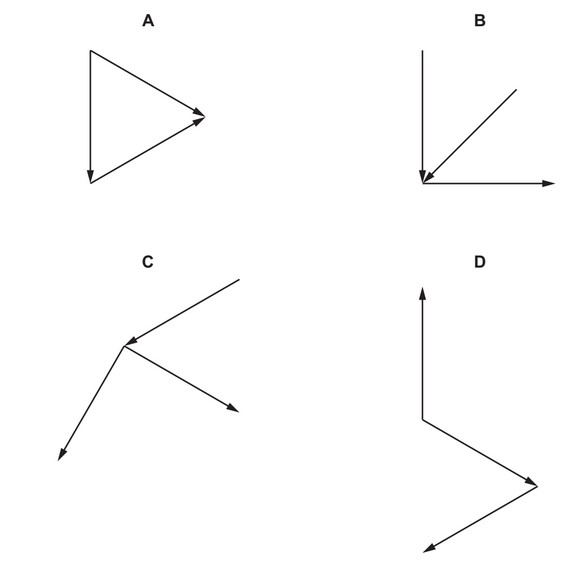
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A rectangular metal bar exerts a pressure of 15200Pa on the horizontal surface on which it rests.
The height of the metal bar is 80 cm.
What is the density of the metal?
A 190 kg\(m^{–3}\)
B 1900 kg\(m^{–3}\)
C 19 000kg \(m^{–3}\)
D 190 000kg\(m^{–3}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A mass attached to the lower end of a spring bounces up and down.
At which points in the path of the mass do the gravitational potential energy of the mass (GPE),
the elastic potential energy in the spring (EPE) and the kinetic energy of the mass (KE) have their
highest values?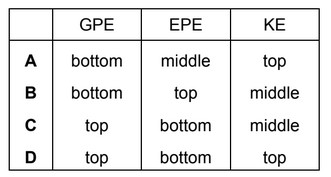
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A block of weight 80 N is pushed a distance of 60 cm up a slope inclined at 30° to the horizontal.
There is a frictional force of 25N between the block and the surface of the slope.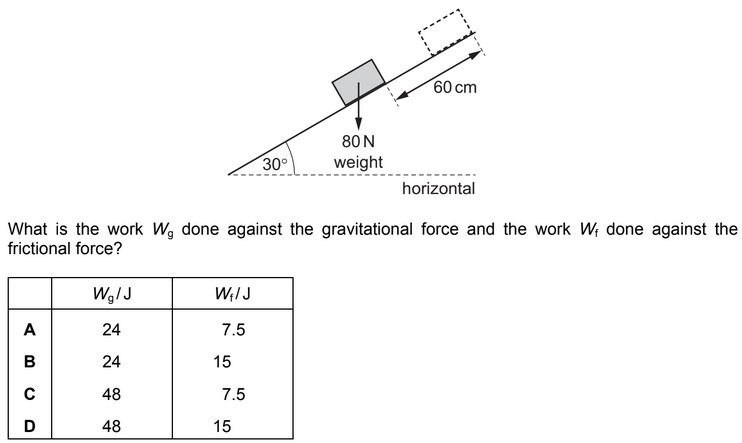
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A ball is dropped from rest and falls towards the ground. Air resistance is negligible.
Which graph shows the variation with speed of the height of the ball above the ground?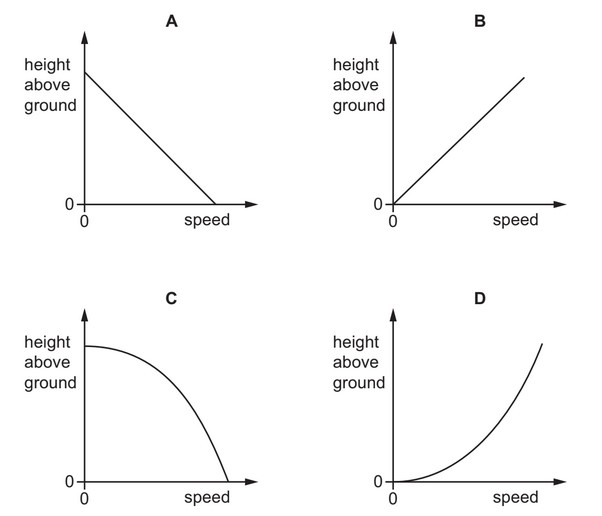
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Power is transferred through a machine as shown.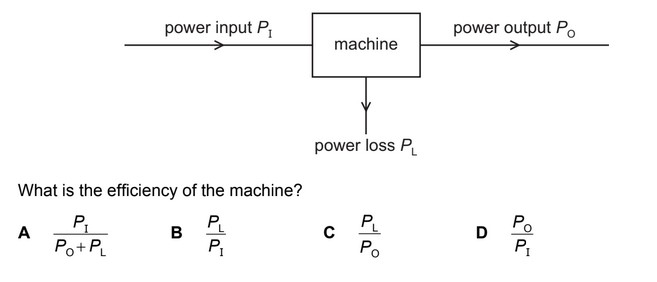
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A tensile force is used to extend a sample of a material. The force is then removed.
The variation with strain of the applied stress is shown on the graph.
Which point on the graph could represent the elastic limit for the material?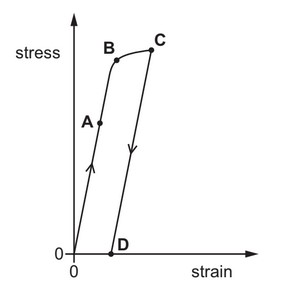
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A tensile force is applied to an unstretched rubber band, causing it to stretch. The tensile force is
then removed.
Which statement about the rubber band must be correct?
A If the rubber band stretches elastically and plastically, all the work done by the force is
converted to thermal energy in the rubber.
B If the rubber band stretches elastically, it obeys Hooke’s law.
C If the rubber band stretches elastically, the gradient of the force–extension graph represents
the work done by the force.
D If the rubber band stretches plastically, the rubber band will be longer after the force is
removed than it was before the force is applied.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A sound wave reduces in intensity but maintains a constant frequency as it travels through air.
Which statement is correct?
A The maximum displacement of the particles changes between one particle and the next
particle.
B The phase difference between adjacent particles is zero.
C The wavelength is the distance between two particles that have a phase difference of 180°.
D Two particles that have a phase difference of 360° have the same maximum displacement.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The graph shows the variation with time of the displacement of an electromagnetic wave at a
point.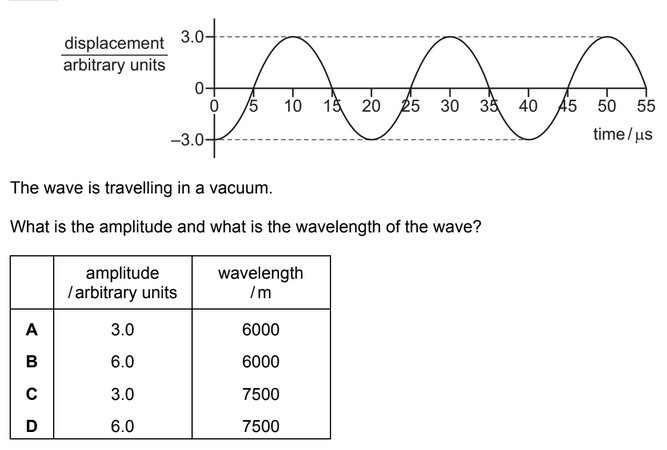
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
A long glass tube is almost completely immersed in a large tank of water. A tuning fork is struck
and held just above the open end of the tube as it is slowly raised.
A louder sound is first heard when the height h of the end of the tube above the water is 18.8 cm.
A louder sound is next heard when h is 56.4 cm. The speed of sound in air is 330 m \(s^{–1}\).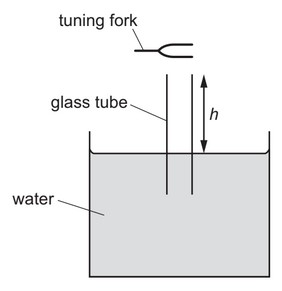
What is the frequency of the sound produced by the tuning fork?
A 220Hz B 440Hz C 660Hz D 880Hz
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A source emitting sound of a single frequency \(f_s\) travels at constant speed directly towards an
observer. The source then passes the observer and continues to move directly away from the
observer. The velocity of the source remains constant.
Which graph represents the variation with time of the frequency \(f_o\) of the sound heard by the
observer?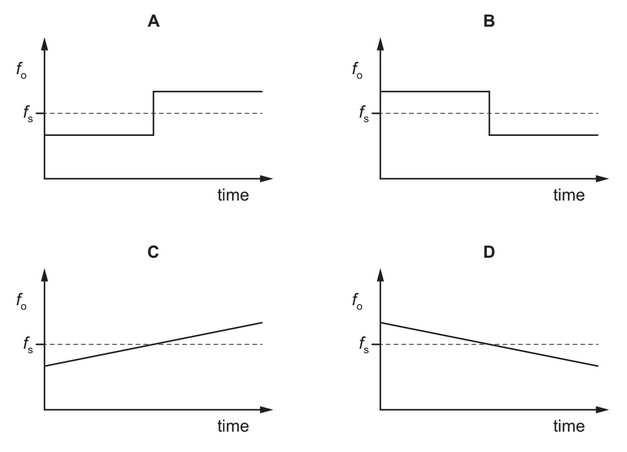
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
What are the names of the electromagnetic waves that have wavelengths in a vacuum of 100 pm
and of 100μm?
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
The diagram shows a string stretched between fixed points X and Y. There is a stationary wave
on the string.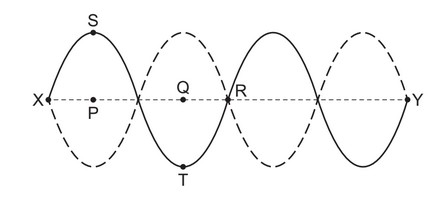
The solid curve shows the string at a position of maximum displacement. The dashed curve
shows the other position of maximum displacement. The straight central dashed line shows the
mean position of the string. Point S on the string is directly above point P. Point T on the string is
directly below Q.
Which statement is correct?
A A short time later, point R on the string will be displaced.
B Points S and T on the string move in opposite directions.
C The distance between P and Q is one wavelength.
D Two points on the string that are equal distances from point R vibrate in phase.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which statement must be true for diffraction to occur when a wave passes through a gap?
A The wave is able to travel in a vacuum.
B The wave is progressive.
C The wave has a large amplitude.
D The wave has a long wavelength.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Light of a single wavelength is incident normally on two slits that are 0.20 mm apart. Interference
fringes are observed on a screen that is 5.4m away from the slits. The distance between
successive bright fringes is 12mm.
What is the wavelength of the light?
A 440 nm B 540 nm C 650 nm D 900 nm
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
A diffraction grating and a screen are used to determine the single wavelength λ of the light from
a source.
What is an essential feature of this experiment?
A A curved screen must be used.
B The diffraction angle θ must be measured for at least two interference maxima.
C The light waves incident on the grating must be coherent.
D The third order intensity maximum must be produced.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A small charge q is placed in the electric field of a large charge Q.
Both charges experience a force F.
What is the electric field strength of the charge Q at the position of the charge q?
A \(\frac{F}{Qq}\) B \(\frac{F}{Q}\) C \(FqQ\) D \(\frac{F}{q}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A charged particle is in a vacuum between two horizontal metal plates as shown.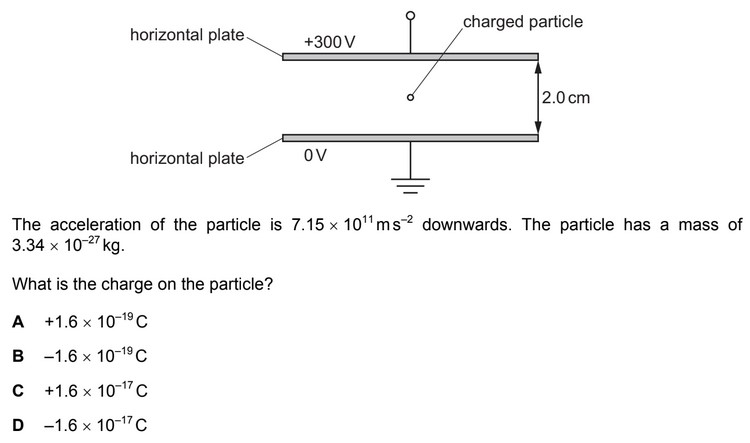
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The current in the circuit shown is 3.2 mA.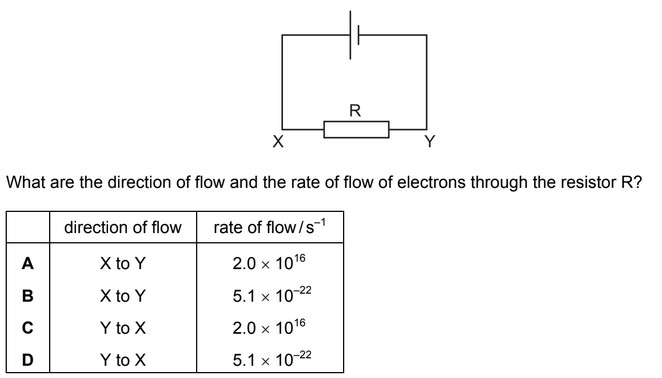
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Which graph best represents the way the current I through a filament lamp varies with the
potential difference V across it?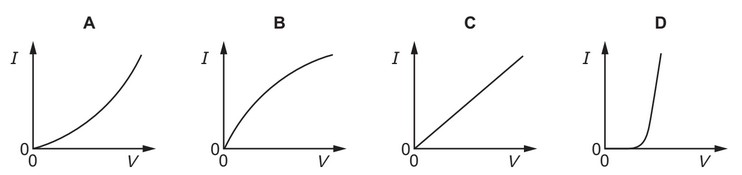
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A cylindrical metal wire X has resistance R. The same volume of the same metal is made into a
cylindrical wire Y of double the length.
What is the resistance of wire Y?
A R B 2R C 4R D 8R
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A cell of electromotive force (e.m.f.) E and internal resistance r is connected to a resistor of
resistance R.
A maximum power P can be dissipated by the resistor without overheating.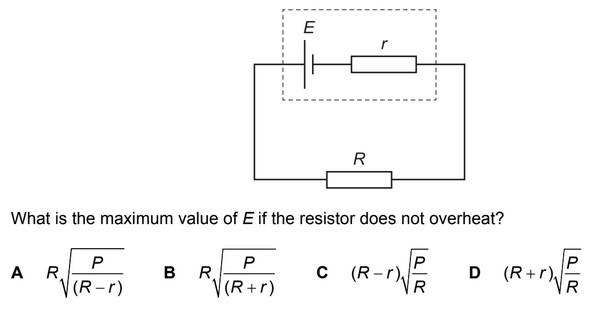
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Three identical resistors can be connected together in four different ways.
The resistances of two of these combinations are 4.0Ω and 9.0Ω.
What is the resistance of each individual resistor?
A 3.0Ω B 6.0Ω C 12Ω D 18Ω
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
In the circuit shown, a battery of negligible internal resistance is connected in series with a pair of fixed resistors \(R_1\) and \(R_2\).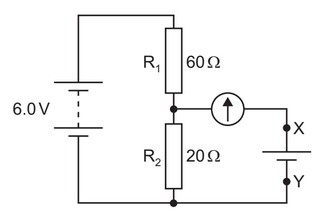
The circuit is to be used to test whether the electromotive force (e.m.f.) of a particular cell is 1.5V.
The cell is connected between terminals X and Y in parallel with \(R_2\) and in series with a
galvanometer.
Which statement about the test is correct?
A Any non-zero reading on the galvanometer means the cell has an e.m.f. of 1.5V.
B The battery does not need to have an e.m.f. of 6.0V.
C The cell may be connected either way round between X and Y.
D The galvanometer does not need a scale calibrated in amperes.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
An element has two isotopic forms.
What are the nuclear arrangements of these two isotopes?
A They have different nucleon numbers and different proton numbers.
B They have different nucleon numbers but the same proton number.
C They have the same nucleon number and the same proton number.
D They have the same nucleon number but different proton numbers.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A hadron has a charge +e, where e is the elementary charge.
Which combination of up (u) and down (d) quarks could form this hadron?
A ddd B udd C uud D uuu
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
