9702_w21_qp_11-loyola
Question
What is essential when recording a measurement of a physical quantity?
A the measurement has an SI unit
B the measurement has a unit and a number
C the measurement has a unit given as a base unit
D the measurement is from an analogue scale
Answer/Explanation
Ans
B
Question
The mobility µ of electrons travelling through a metal conductor can be calculated using the
equation
\(\mu =\left ( \frac{e}{m} \right )\tau \)
where e is the charge on an electron and m is its mass. The average time between the collisions
of an electron with the atoms in the metal is τ.
What are the SI base units of µ?
A Akg–1 B As2 kg–1 C As kg–1 D As–2 kg–1
Answer/Explanation
Ans
B
Question
An aircraft heads in a direction at an angle θ east of north with a horizontal velocity relative to the air of 800 km h–1. The wind blows with a horizontal velocity of 200 km h–1 from east to west, as shown.
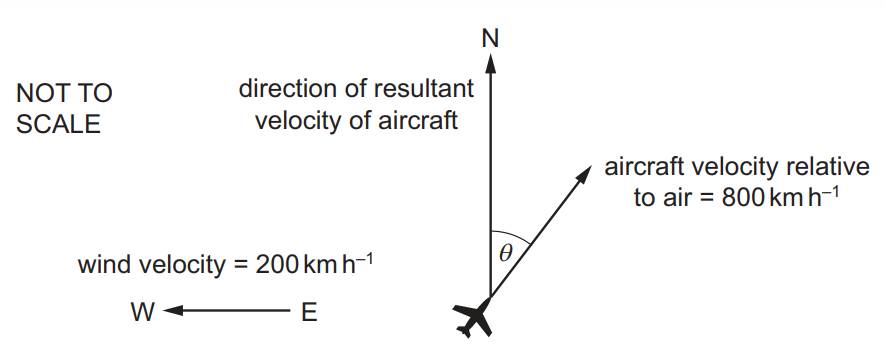
The resultant velocity of the aircraft is in a direction due north.
What is angle θ and what is the magnitude of the resultant velocity?
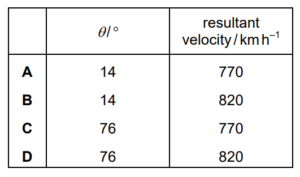
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
4 A cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO) is used to display a sound wave of frequency 2000 Hz.
The display of the CRO is shown.
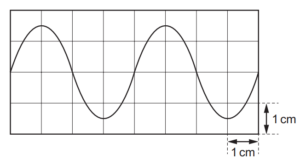
What is the time-base setting on the CRO?
A 125 µs cm–1 B 250 µs cm–1 C 500 µs cm–1 D 1000 µs cm–1
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
Four possible sources of error in a series of measurements are listed.
1 an analogue meter whose scale is read from different angles
2 a meter which always measures 5% too high
3 a meter with a needle that is not frictionless, so the needle sometimes sticks slightly
4 a meter with a zero error
Which errors are random and which are systematic?
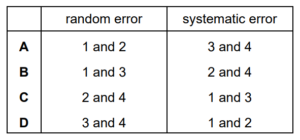
Answer/Explanation
Ans
B
Question
6 An archer shoots an arrow at a target. The diagram shows the path of the arrow.
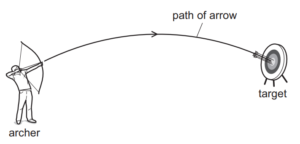
Air resistance is negligible.
The graphs show how three different quantities p, q and r vary with time.
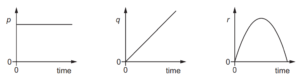
Which quantity could be the horizontal component of displacement and which quantity could be
the vertical component of displacement of the arrow?

Answer/Explanation
Ans
B
Question
7 Two cars X and Y are positioned as shown at time t = 0.
They are travelling in the same direction.
X is 50 m behind Y and has a constant velocity of 30 m s–1. Y has a constant velocity of 20 m s–1.
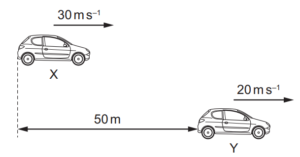
What is the value of t when X is level with Y?
A 1.0 s B 1.7 s C 2.5 s D 5.0 s
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
8 A constant resultant force acts on an object in the direction of the object’s velocity.
Which graph could show the variation with time t of the momentum p of the object?
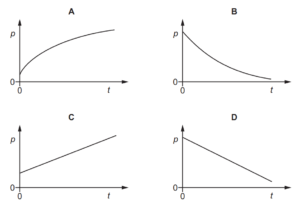
Answer/Explanation
Ans
C
Question
9 Which statement must be true for an object in a gravitational field?
A If the object has mass then the field causes it to accelerate.
B If the object has mass then the field causes it to have weight.
C If the object has weight then the field causes it to accelerate.
D If the object has weight then the field causes it to have mass.
Answer/Explanation
Ans
B
Question
10 A ball of mass 0.16 kg is travelling horizontally at a speed of 20 m s–1.
It collides with a wall and rebounds with a speed of 15 m s–1 along its original path. The ball is in
contact with the wall for a time of 1.0 ms.
What is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball?
A 800 N B 2400 N C 3200 N D 5600 N
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
11 A uniform solid block is fully submerged in a tank of water.
The dimensions of the block are x and y, as shown.
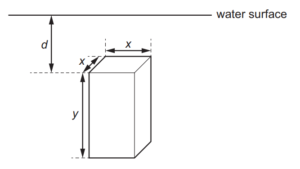
The block is held vertically in the position shown. The density of the block is the same as the
density of the water.
If the block is always held at the same depth d below the surface of the water, which single
change would increase the magnitude of the upthrust force on the block?
A decrease the density of the block
B hold the block horizontally
C increase dimension y
D increase the density of the block
Answer/Explanation
Ans
C
Question
12 A shelf XY is 0.40 m long and is attached to a wall at end X.
It is kept horizontal by a wire attached to Y and to the wall, as shown.
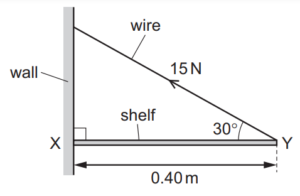
The tension force in the wire is 15 N at an angle of 30o to the horizontal.
What is the moment of this force about point X?
A 3.0 N m B 5.2 N m C 6.9 N m D 12N m
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
13 A statement about the principle of moments with some words omitted is shown.
‘For an object in a state of rotational equilibrium, the sum of the clockwise
moments about any point is equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments
about ………………… .’
Which words correctly complete the statement?
A any point
B the centre of gravity of the object
C the pivot
D the same point
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
14 A bird dives to a depth of 1.50 m below the surface of a lake. Atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa.
The density of water is 1000 kgm–3.
What is the pressure at this depth?
A 14.7 kPa B 86.3 kPa C 103 kPa D 116 kPa
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
15 Which statement about energy is not correct?
A Energy is never lost but it may be transferred between different forms.
B In an inelastic collision, the total energy is constant.
C The efficiency of a system is the ratio of the useful energy output to the total energy input.
D When a machine does work, friction reduces the total energy.
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
16 A pulley of radius 0.40 m supports weights of 20 N and 15N by means of a thin string, as shown.
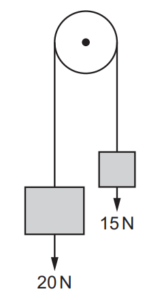
The weights are moved by slowly rotating the pulley clockwise through an angle of 60o.
What is the increase in the total gravitational potential energy of the weights?
A 0.33 J B 2.0 J C 2.1 J D 15 J
Answer/Explanation
Ans
C
Question
17 A car of mass 1500 kg accelerates from an initial speed of 15 m s–1. This acceleration causes the
car to gain 3.0 × 105 J of kinetic energy.
What is the change in the speed of the car?
A 5.4 m s–1 B 10 m s–1 C 20 m s–1 D 25 m s–1
Answer/Explanation
Ans
B
Question
18 A car of mass 1500 kg travels at a constant velocity of 30 m s–1 down a slope. The slope is at an
angle of 6.0o to the horizontal, as shown.
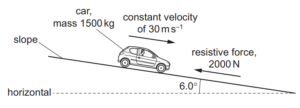
The magnitude of the total resistive force acting on the car is 2000 N.
What is the power output of the car’s engine?
A 14 kW B 60 kW C 110 kW D 380 kW
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
19 A metal wire, of cross-sectional area A and unstretched length l, is subjected to stress σ. As a
result it has strain ε.
Which expression gives the Young modulus of the metal?

Answer/Explanation
Ans
C
Question
20 Two identical springs are connected in parallel.
A weight of 8.0 N is hung from the combination, as shown.
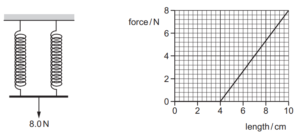
The graph shows the variation with length of the force applied to one of the springs.
What is the strain energy in one of the springs?
A 0.060J B 0.12 J C 0.14 J D 0.24 J
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
21 Two balls float on the surface of the sea. The balls are separated by a distance of 1.30 m.
A wave travels on the surface of the sea so that the balls move vertically up and down.
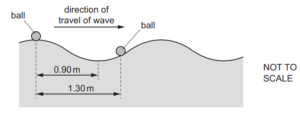
The distance between a crest and an adjacent trough of the wave is 0.90 m.
What is the phase difference between the two balls?
A 55o B 110o C 160o D 260o
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
22 Which statement about transverse or longitudinal waves is not correct?
A Longitudinal waves can be used to demonstrate diffraction.
B Longitudinal waves can travel in a vacuum.
C Transverse waves can form stationary waves.
D Transverse waves can transfer energy.
Answer/Explanation
Ans
B
Question
23 A glass tube is closed at one end and has a loudspeaker at the other end.

A stationary wave is formed with a node at the closed end of the tube when the sound has
frequency f0. There are no other nodes.
The frequency of the sound is then slowly increased.
What is the frequency of the sound that produces the next stationary wave?
A 1.25f0 B 1.50f0 C 2.00f0 D 3.00f0
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
24 With which waves can the Doppler effect be observed?
A all waves including sound and light
B light waves only
C sound and light waves only
D sound waves only
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
25 Which radiation could consist of waves of wavelength 0.5 nm?
A ϒ-rays
B ultraviolet
C visible light
D X-rays
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
26 A string is fixed between point P and an oscillator M. Another string is fixed between M and
point Q. M is midway between P and Q.
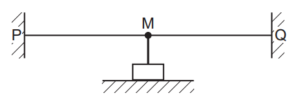
The frequency of the oscillator is adjusted until a stationary wave is formed on both strings. The
speed of the wave between P and M is twice the speed of the wave between M and Q.
Which diagram could represent the stationary wave pattern?
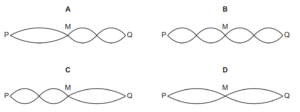
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
27 A water wave in a ripple tank is diffracted as it passes through a gap in a barrier.
Which two factors affect the angle of diffraction of the wave?
A the amplitude and frequency of the incident wave
B the amplitude of the incident wave and the width of the gap
C the wavelength and amplitude of the incident wave
D the wavelength of the incident wave and the width of the gap
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
28 Light of wavelength λ is incident normally on two narrow slits S1 and S2, a small distance apart.
Bright and dark fringes are observed on a screen a long distance away from the slits.
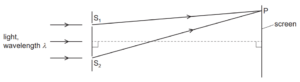
The n th dark fringe from the central bright fringe is observed at point P on the screen.
Which equation is correct for all positive values of n?
A \(S_{2}P-S_{1}P=\frac{n\lambda }{2}\)
B \(S_{2}P-S_{1}P=\frac{n\lambda }{2}\)
C \(S_{2}P-S_{1}P=(n-\frac{1}{2})\lambda \)
D \(S_{2}P-S_{1}P=(n+\frac{1}{2})\lambda \)
Answer/Explanation
Ans
C
Question
29 Green light is incident normally on a diffraction grating and forms a diffraction pattern on a distant
screen.

Which change, on its own, would decrease the separation of the diffraction maxima on the
screen?
A Increase the distance between the screen and the diffraction grating.
B Replace the diffraction grating with a grating that has a smaller separation between the slits.
C Replace the diffraction grating with a grating that has fewer slits per unit length.
D Replace the green light with red light
Answer/Explanation
Ans
C
Question
30 What is meant by electric field strength?
A force per unit charge acting on a small mass
B force per unit charge acting on a small positive charge
C force per unit mass acting on a small mass
D force per unit mass acting on a small positive charge
Answer/Explanation
Ans
B
Question
31 Three parallel metal plates of the same area are fixed with a separation of 2.0 cm between the top
plate and the middle plate, and 1.0 cm between the middle plate and the bottom plate. The top
plate is held at a potential of +500V, the middle plate at +200V and the bottom plate is earthed,
as shown.

What is the value of the ratio ![]()
A 0.75 B 1.00 C 1.25 D 1.50
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
32 The current I in a wire is given by the equation
I = nAvq
where n is the number density of the free electrons, A is the cross-sectional area of the wire, v is
the average drift velocity of the free electrons and q is the charge of an electron.
Which relationship is not used in the derivation of this equation?
A charge = current × time
B distance = speed × time
C number = number density × area
D volume = length × area
Answer/Explanation
Ans
C
Question
33 A circuit contains two resistors, P and Q, and a power supply of negligible internal resistance, as
shown.
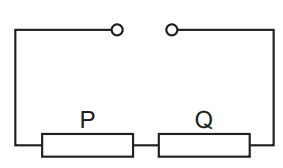
The current in resistor P is 2.0A and the power dissipated by resistor P is 18 W.
Resistor Q dissipates 240 J of energy when a charge of 40 C passes through it.
What is the electromotive force (e.m.f.) of the power supply?
A 3.0V B 6.0V C 9.0V D 15V
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
34 The I–V characteristics of two electrical components P and Q are shown.
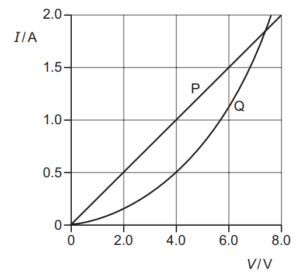
Which statement is correct?
A For a current of 0.5A, the power dissipated in Q is double that in P.
B For a current of 1.9A, the resistance of Q is approximately half that of P.
C The resistance of Q increases as the current in it increases.
D P is a fixed resistor and Q is a filament lamp
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
35 Two copper wires S and T, of equal length, are connected in parallel. Wire S has a diameter of
3.0 mm. Wire T has a diameter of 1.5 mm.
A potential difference is applied across the ends of this parallel arrangement.
What is the value of the ratio \(\frac{current \ in\ S}{current \ in \ T}\)
A \(\frac{1}{4}\) B \(\frac{1}{2}\) C 2 D 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans
D
Question
36 What is the circuit symbol for an oscilloscope?

Answer/Explanation
Ans
C
Question
37 Three identical cells, each of electromotive force (e.m.f.) E and internal resistance r, are
connected as shown.
What is the potential difference between points X and Y?
A 0 B E C 2E D 3E
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
38 Potential differences across two resistors of resistances R1 and R2 are compared using a
potentiometer wire (uniform resistance wire) in the electrical circuit shown.
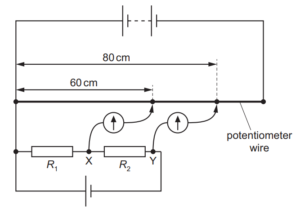
One terminal of a galvanometer is connected to point X. The galvanometer reads zero when its
other terminal is connected to a point that is a distance of 60 cm from one end of the
potentiometer wire.
One terminal of a second galvanometer is connected to point Y. This galvanometer reads zero
when its other terminal is connected to a point that is a distance of 80 cm from the same end of
the potentiometer wire.
What is the ratio \(\frac{R_{2}}{R_{1}}\)
A \(\frac{1}{3}\) B \(\frac{3}{4}\) C \(\frac{3}{1}\) D \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans
A
Question
39 A uranium-238 nucleus, ![]() undergoes a series of nuclear decays to form uranium-234,
undergoes a series of nuclear decays to form uranium-234, ![]()
Which series of decays could give this result?
A emission of four β–particles
B emission of four ϒ-rays
C emission of one a-particle and two β–particles
D emission of two a-particles and eight β–particles
Answer/Explanation
Ans
C
Question
40 Which combination of up (u) and down (d) quarks forms a proton?
A u u u B u u d C u d d D d d d
Answer/Explanation
Ans
B
