Before mitochondria are extracted from cells for microscopy, they are usually kept in a 0.25 mol dm-3 sucrose solution.
Why is the sucrose solution used?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The sucrose solution is isotonic (same water potential as mitochondria), preventing osmotic water movement that could shrink or swell the organelles. While it does act as a solvent (A), this isn’t its primary purpose. Sucrose isn’t metabolized by mitochondria (D), and concentration is too low for energy studies (B).
What describes a lysosome?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Lysosomes are single-membrane vesicles containing hydrolytic enzymes. They’re found in most animal cells (not just phagocytes) and can digest materials both inside the cell (autophagy) or outside (exocytosis). They’re formed from the Golgi apparatus, not ER.
The diagram shows a typical animal cell.
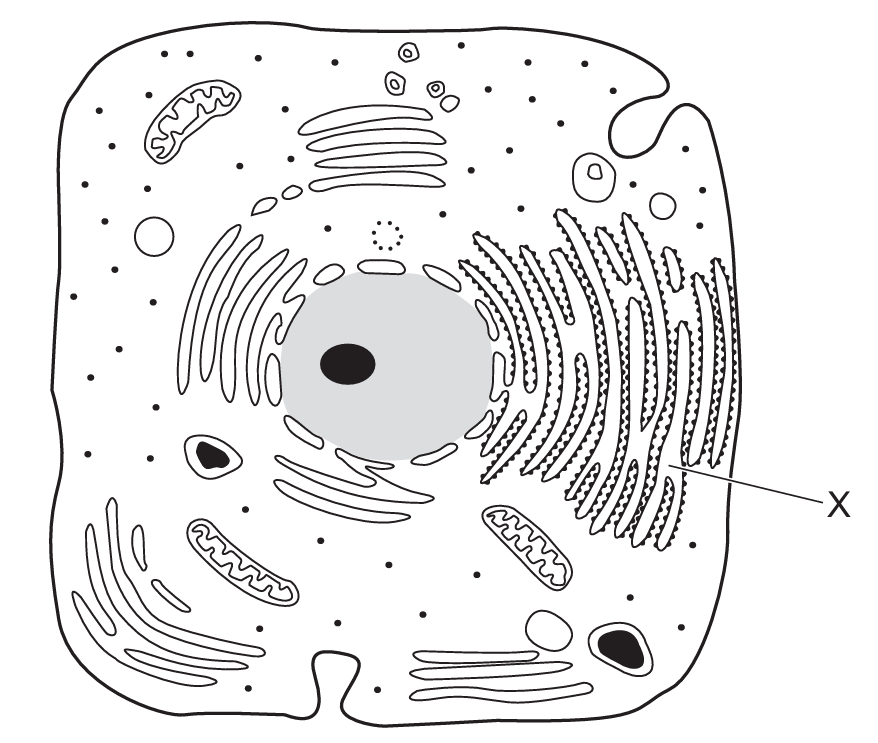
What is the function of the membrane system labelled X?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The membrane system X is the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). It has ribosomes for protein synthesis and channels for protein transport. While it’s involved in protein synthesis, it doesn’t work in isolation – synthesized proteins are transported through its membrane system.
Which statements are correct for a typical prokaryotic cell?
- It contains 70S ribosomes.
- It contains a cellulose cell wall.
- It contains circular DNA.
- It is up to 5 µm in diameter.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Prokaryotes have 70S ribosomes (1), circular DNA (3), and are typically 1-5µm in size (4). They have peptidoglycan cell walls, not cellulose (2 is incorrect). Therefore, the correct combination is 1, 3, and 4.
