Fig. 1.1 is a transmission electron micrograph of a cell from the stem of sago pondweed, Stuckenia pectinata.
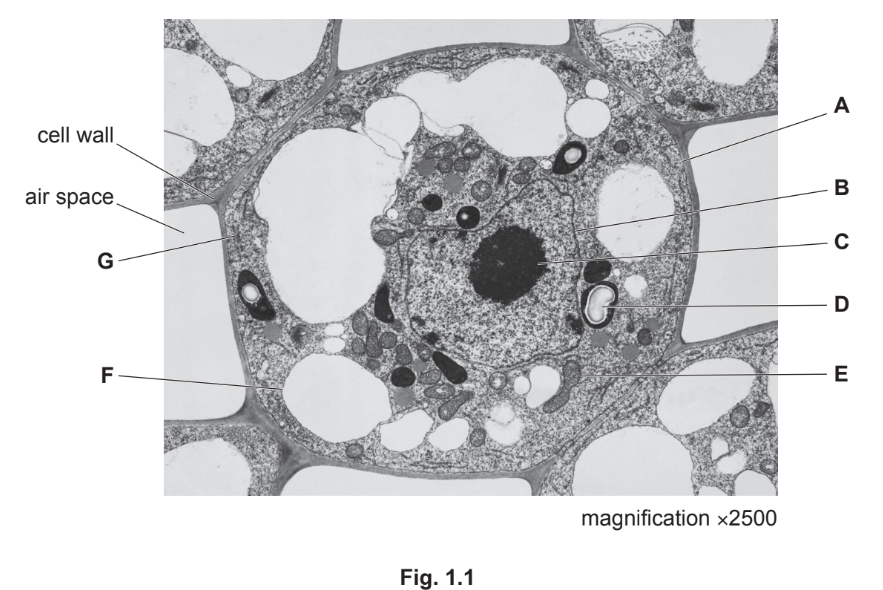
(a) (i) State the evidence from Fig. 1.1 that shows that the cell is from the stem of S. pectinata and not from the mesophyll of a leaf.
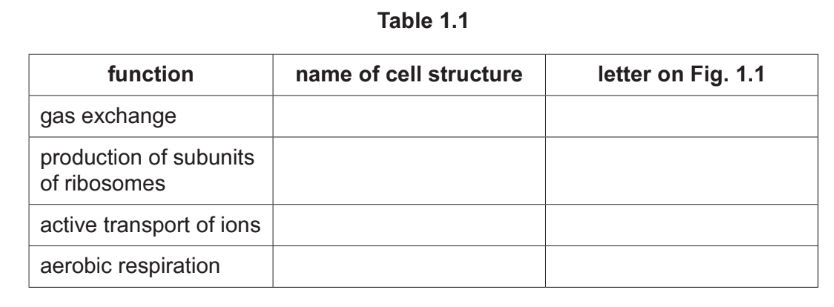
(ii) Complete each row in Table 1.1 to identify a cell structure shown in Fig. 1.1 that carries out the function listed.
(b) Plant vacuoles develop when vesicles fuse together. The vacuoles increase in size as more vesicles fuse.
Fig. 1.2 shows the movement of vesicles within a plant cell during the development of a vacuole.
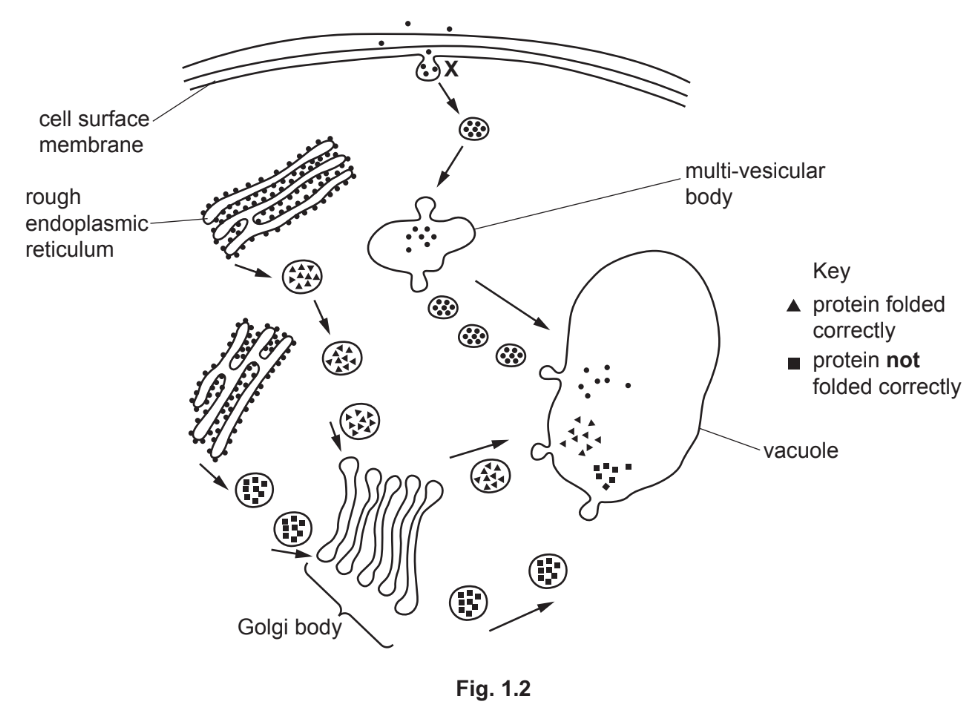
(i) Name the process that is occurring at X.
(ii) Some of the vesicles formed by the Golgi body pass to the vacuole. These vesicles contain proteins that have been folded correctly and some that have not folded into their correct shapes. The proteins that have not folded correctly pass to the vacuole where they are broken down.
Explain how proteins that have not folded correctly are broken down in the vacuole.
(c) Small vacuoles in S. pectinata may have roles similar to lysosomes in animal cells.
Describe the role of lysosomes in animal cells in defence against pathogens.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i)
Evidence: The cell lacks chloroplasts (which are present in mesophyll cells for photosynthesis) and contains many small vacuoles instead of a single large central vacuole. Additionally, the nucleus is centrally located, unlike in mesophyll cells where it is often pushed to the periphery.
(a)(ii)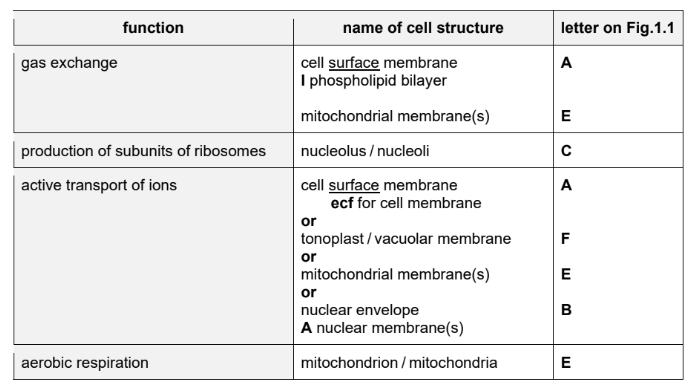
Explanation: The table is completed by identifying the correct cell structures: mitochondrion (ATP production), Golgi body (modification of proteins), rough endoplasmic reticulum (protein synthesis), and nucleus (DNA replication).
(b)(i) Endocytosis / Pinocytosis.
Explanation: The process at X is endocytosis, where the cell membrane engulfs extracellular material to form vesicles.
(b)(ii)
Explanation: Misfolded proteins are hydrolyzed in the vacuole by proteases, which break peptide bonds to form smaller peptides or amino acids. This process requires water and occurs in an acidic environment.
(c)
Explanation: Lysosomes defend against pathogens by fusing with phagocytic vesicles (forming phagolysosomes) and releasing hydrolytic enzymes (e.g., lysozyme, proteases) to digest the pathogen’s components (e.g., peptidoglycans, proteins). The breakdown products are harmless or reused by the cell.
