Question [Maximum marks: 14]
Fig. 2.1 shows a drawing made from an electron micrograph of two adjacent cells in a leaf.
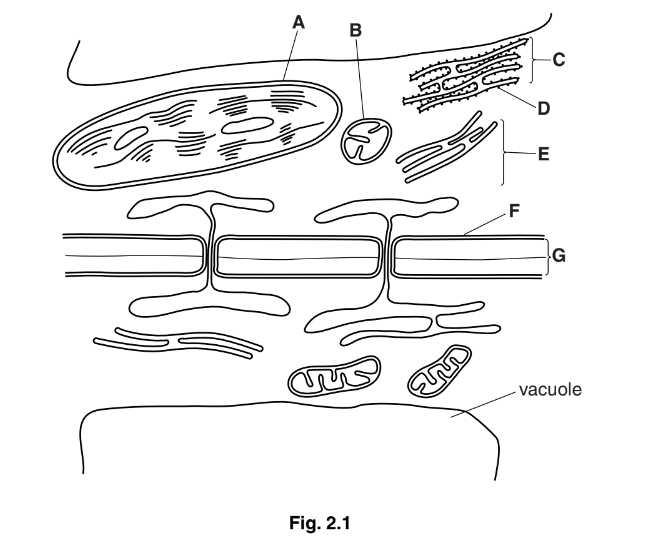
(a) Structures A and B are both visible using the light microscope, but the internal detail of
these organelles shown in Fig. 2.1 is only visible using the electron microscope.
Explain why the internal details of structures A and B are only visible when using the
electron microscope and not when using the light microscope.
(b) Name in full the structures labelled C, D and E.
(c) State one role of vacuoles in plant cells.
(d) Structures F and G have very different permeability properties.
Explain how the composition of structures F and G determines the permeability
properties of these structures.
(e) Fig. 2.1 shows two plasmodesmata connecting the adjacent cells.
Describe the roles of plasmodesmata in transport in plants.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: 2 (a) 1 electron microscope has, higher / AW, resolution (than LM) / ora ;
2 explanation of resolution as ability to differentiate between two points (close together) ;
3 ref. to (internal) membranes (of A and B) which cannot be seen in LM ;
A named membranes e.g. cristae, grana
4 AVP ; e.g.
(resolution of) EM is 0.5 nm (0.0005μm) and LM is 200 nm (0.2μm)
A 0.5 to 1 nm (0.001μm)
resolution is equal to half the wavelength (of medium used)
ref. to shorter / AW, wavelength (of electrons) / ora (must have a comparison)
ref. to, width of membranes / distance apart of membranes, e.g. width of membranes
in A and B is 7 nm (+/– 1)
2(b) C – rough endoplasmic reticulum ; penalise once only for ER instead of endoplasmic
reticulum
D – ribosome ; A ribosomes ignore 70S
E – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ; A smooth ER if full term used for C
award one mark if E = rough endoplasmic reticulum and
C = smooth endoplasmic reticulum
2(c) any one relevant e.g.
store of / holds, cell sap ; R if contains organelles
store of / holds, water / ions / named ion(s) / minerals / salts / pigments / (named) sugars ;
R substances / molecules
R storage unqualified
pushes chloroplast to edge of cell ;
gives, turgidity / turgor pressure / hydrostatic pressure / support / AW ;
A makes, firm / rigid
A controls / maintains, turgidity
R gives shape / strengthen
store of / holds, waste (products)
R reactions occur in vacuole, unqualified
2(d) no marks for identifying F and G
if only F or G described max 3
if F and G incorrectly identified, accept mark points correctly linked to membrane and wall
to max 3
1 F partially permeable A selectively permeable
and G (fully / freely / AW), permeable / porous ;
F is partially permeable cell surface membrane
2 phospholipid (bilayer);
3 permeable to, lipid-soluble molecules / oxygen ;
A other terms for lipid-soluble
treat reference to water as neutral
4 impermeable to, water-soluble / AW, molecules / ions / AW ;
A other terms for water-soluble
treat reference to water as neutral
5 aquaporins / proteins, provide (increased) permeability to water ;
6 transport proteins provide permeability to, ions / polar molecules ;
A channel / pore / carrier, proteins
G is permeable cell wall
7 cellulose ;
8 fibres ;
9 ref. to, spaces / gaps / holes / pores, (between, fibres / other cell wall
components) ; [max 4]
2(e) 1 allows transport of, water / sucrose / amino acids / organic substances / ions /minerals /
salts / lipids / hormones / ATP, (from cell to cell / between cells) ; R if linked to an incorrect transport mechanism e.g. sucrose moves by osmosis
2 without crossing, membranes / walls ; A without going through protein channels
3 this is movement through the symplast ;
4 any e.g. ; companion cell to (phloem) sieve tube (element / cell)
between mesophyll cells
mesophyll cell to companion cell
cortical cell to cortical cell / across cells of the cortex
cortical cell to endodermal cell
endodermal cell to, pericycle cell / xylem / phloem
ignore between sieve tube elements
5 allows, communication / signalling, between cells ; [max 3]
Question
Capillaries are known as exchange vessels. Substances are exchanged between blood and tissue fluid as the blood flows through the capillaries.
Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of a section through a capillary with two red blood cells.
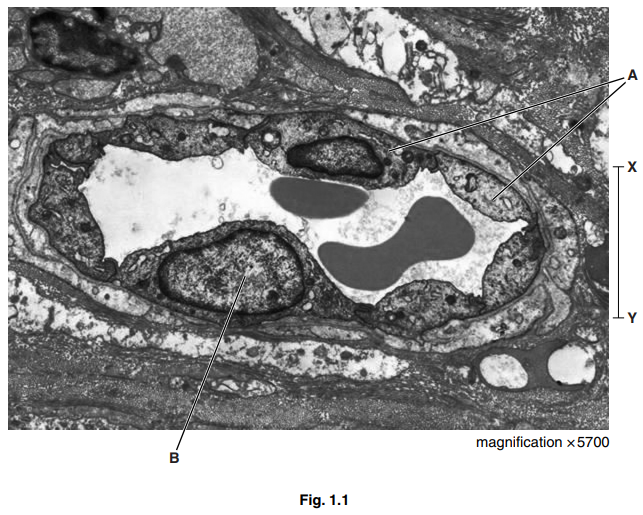
(a) (i) Name the cells labelled A and the structure labelled B.[2]
A
B
(ii) Calculate the actual distance X – Y on Fig. 1.1.
Show your working and give your answer to the nearest micrometre (μm).
answer μm [2]
(iii) Explain how capillaries are adapted for their function as exchange vessels.[2]
(b) Table 1.1 shows the composition of blood, tissue fluid and lymph.
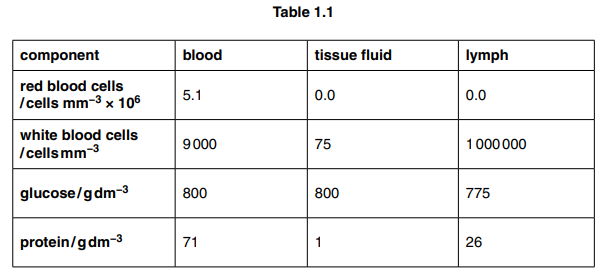
Explain the differences between the composition of blood, tissue fluid and lymph as shown in Table 1.1, for white blood cells, glucose and protein.[5]
white blood cells
glucose
protein
(c) Outline how red blood cells are involved in the transport of carbon dioxide.[3] [Total: 14]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1 (a) (i) A – endothelial/ squamous / epithelial (cell) ;
B – nucleus ;
(ii) 7 (µm) ;;
award two marks if correct answer given
award one mark if not rounded to nearest whole number
award one mark if given incorrect unit
if no answer given, award one mark if correct measurement
(38–41/ 3.8–4.1/38000–41000) is divided by 5700
(iii) for two marks – one structure and one function
only two functions = 1 mark
only two structures = 1 mark
1 (capillary) wall is, thin/ single layer of cells / one cell thick ;
A endothelium/ epithelium for wall
2 short diffusion, pathway / distance/AW ;
R ‘easy’ diffusion
3 (many have) endothelial pores / fenestrations / gaps / spaces / openings ;
4 to allow named, substance/ cell, to leave the blood ;
A idea of separation/ selection, of named substance(s) by size
5 small diameter/ small lumen/ diameter of red blood cells ;
6 slows down flow of red blood cells /(capillary / blood) close to cells ;
7 (capillaries have) large, surface area/ surface area to volume ratio ;
8 idea that allows more exchange ;
Ignore faster exchange
(b) white blood cells
1 (named) white blood cells can, leave capillaries / enter tissue fluid ;
A diapedesis /(suggestion that some) too large to leave the, blood/ capillaries
2 high number in, lymph nodes / thymus / bone marrow/ spleen ;
A stored/ produced
glucose
3 small (molecule) ;
4 filtered/ diffuses /leaves / leaks, from blood/ from capillaries / into tissue fluid ;
5 taken up / used, by cells in respiration ;
Ignore supply
protein
6 too large to, leave capillaries / enter lymph/ enter tissue fluid ;
7 (in lymph / tissue fluid) antibodies / proteins, from/ secreted by, lymphocytes / other cells ;
(c) accept hydrogen carbonate (ions)/ bicarbonate (ions)/HCO3– penalise HCO3 once only
1 carbon dioxide, reacts / combines, with (terminal amine/N terminal, of) haemoglobin ;
R carried by /reacts with, haem
2 to form carbaminohaemoglobin ;
3 carbonic anhydrase catalyses, formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3)/reverse reaction described (in the lungs) ;
4 (carbonic acid dissociates to) HCO3– /CHO3– / hydrogen carbonate (and H+) ;
5 hydrogen carbonate/HCO3–, diffuses /moves /AW, out (into plasma) ;
Question
Vibrio cholerae is a prokaryotic organism.
Fig. 1.1 shows the structure of a cell of V. cholerae.
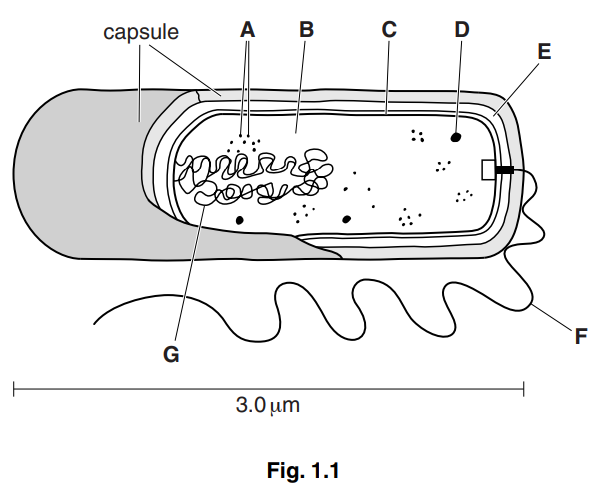
(a) Calculate the magnification of Fig. 1.1.
Show your working and give your answer to the nearest whole number.
magnification × [2]
(b) Locate the structures in Fig. 1.1 that apply to each of the features shown in Table 1.1. Complete Table 1.1 by writing the appropriate letter and the name of the structure. You must only give one letter in each case. You may use each letter once, more than once or
not at all. The first answer has been completed for you.[4]
(c) State three structural features that are present in a mesophyll cell in a leaf that are not present in a prokaryotic cell such as that of V. cholerae.[3]
1
2
3
(d) Describe how V. cholerae is transmitted from an infected person to an uninfected person.[2]
(e) It is important to know how pathogens are transmitted in order to develop effective control methods.
Explain how this knowledge is used to control the spread of V. cholerae in the human population.[3] [Total: 14]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1 (a) award two marks if correct answer within range 29000 to 31000 is given
allow ±3 mm in reading the line, e.g
\(\frac{90000}{3.0}\) \(\frac{90×10^{3}}{3.0×10^{-6}}\) \(\frac{9.0×10^{-2}}{3.0×10^{-9}}\)
(×) 30000/3 × 104 ;;
one mark if not rounded to nearest whole number
one mark if a unit (mm, µm) is given
one mark if line is measured and given in mm or cm within accepted range and divided by
3.0µm but incorrect conversion factor used for the line measurement or 3.0µm
(b) 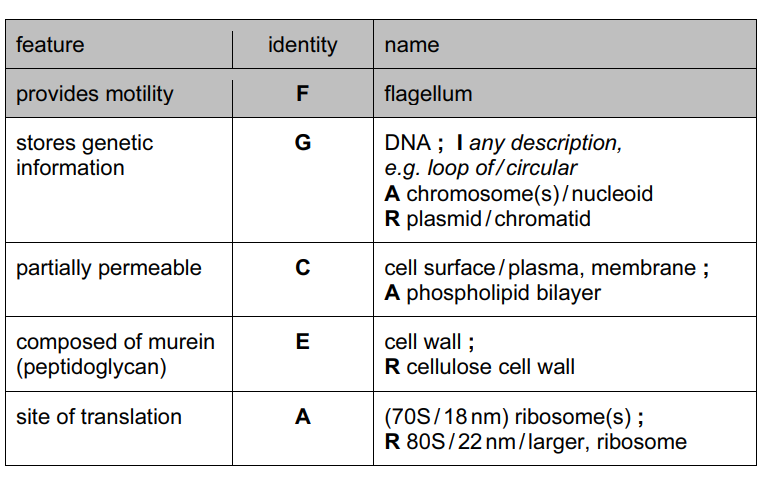
(c) A (double) membrane-bound organelles only if no examples given (true)
nucleus / nuclear envelope ; A nuclear membrane I well-defined
chloroplast ; A grana/ thylakoid(s) A plastid
(permanent) vacuole/tonoplast ; R vesicles unqualified A lysosome
mitochondrion/mitochondria ; A cristae
Golgi (body / apparatus / complex)/ dictyosome ; A Golgi vesicle(s)
rough endoplasmic reticulum/rough (ER)/RER ;
smooth endoplasmic reticulum/ smooth ER/SER ; A endoplasmic reticulum, if RER and SER not given
nucleolus ;
linear/AW, chromosomes ; A DNA + histones
cellulose cell wall ;
starch grain/ amyloplast ;
plasmodesma(ta) ;
larger/ 80S/ 22nm, ribosomes ;
(d) one mark for infected person with contaminated faeces, e.g.
faeces / sewage, contaminates (drinking)water/ cooking utensils / vegetable plots / crops / food ;
A diarrhoea for faeces
R (human) waste unqualified
A ref. to houseflies landing on contaminated faeces
one mark for uninfected person
eating contaminated food/using contaminated utensils / drinking contaminated water ;
A bacteria enters water in context of drinking
R infected food or water
I handling contaminated food
A faecal-oral route for two marks
(e) pathogen is at most vulnerable when in transfer between hosts /AW ;
A idea of breaking the transmission cycle
2 max for the following control methods:
sewage treatment/(effective) sanitation/ correct ref. to positioning of latrines ;
do not use human faeces for fertiliser ;
piped/ treated/ boiled/ chlorinated/ purified, (drinking) water ;
A sanitised / clean, water
I cooking refs.
A water treatment with UV/ ozone
bottled water ;
water treatment plants upstream of sewage disposal ;
(to reduce pool of infected people) antibiotics or oral/ intravenous, rehydration (therapy) ; A ORT
