The diagram shows the structure of part of a peptidoglycan molecule.
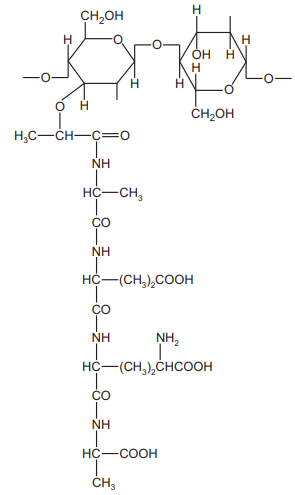
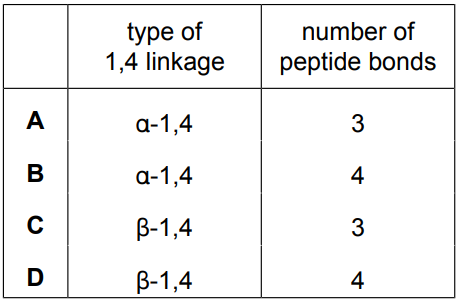
Which type of 1,4 linkage and how many peptide bonds are shown in this part of the molecule?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Peptidoglycan consists of repeating units of N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) linked by β 1,4-glycosidic bonds. In the given structure, two peptide bonds are visible: one between NAM and the first amino acid (L-alanine) and another between the last amino acids (D-alanine and another residue). Thus, the correct answer is β 1,4 linkage with 2 peptide bonds (Option D).
Some stains can be used to identify cell structures in living cells.
A dilute solution of one stain causes the whole cell to appear blue.
The blue colour rapidly disappears from most cell structures. Those cell structures that release
energy stay blue.
Which type of cell structure is likely to stay blue?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The stain remains blue in cell structures that release energy. The mitochondrion is the organelle responsible for energy production (ATP) through cellular respiration. Other options (Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, lysosome) do not primarily function in energy release, making D the correct answer.
Which type of cell will have the highest proportion of its volume taken up with cell structures bound by a single membrane?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Goblet cells (option B) are specialized secretory cells that produce large amounts of mucus, which is stored in membrane-bound vesicles before secretion. These vesicles occupy a significant portion of the cell’s volume. In contrast, red blood cells (C) lack membrane-bound organelles, ciliated epithelial cells (A) have mostly double-membrane organelles, and companion cells (D) have typical plant cell structures.
Which features are found in typical eukaryotes and also in typical bacteria?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Both eukaryotes and bacteria share certain cellular features. The correct option is C because it includes cytoplasm, cell membrane, and ribosomes, which are common to both cell types. Eukaryotes have membrane-bound organelles (e.g., nucleus), while bacteria lack them, ruling out other options.
