Question
(a) Define the term disease.[1]
Fig. 2.1 is a flow chart that shows the four different ways that a person can become immune to an infectious disease.
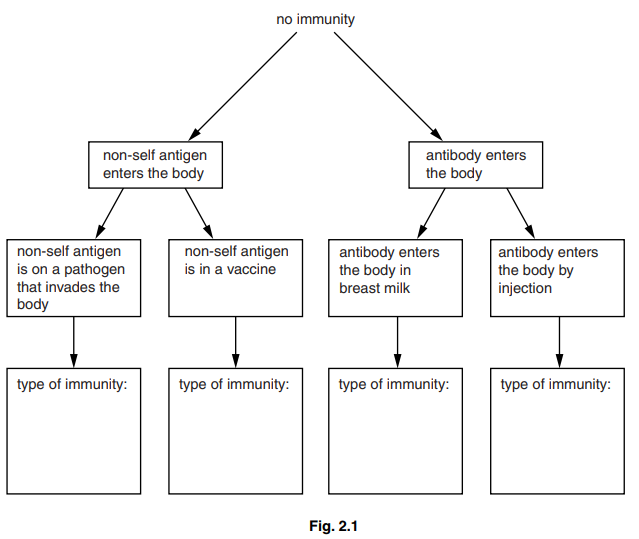
(b) Complete Fig. 2.1 by writing in the boxes provided the four types of immunity described. [4]
Fig. 2.2 shows the number of cases of smallpox from 1950 to 1980:
- in all the countries of the world
- in India.
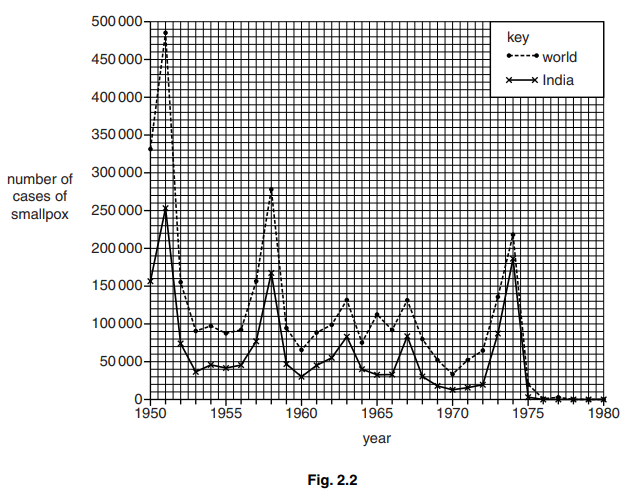
(c) Describe the changes in number of cases of smallpox as shown in Fig. 2.2.[3]
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the world to be free of smallpox in 1980.
(d) Outline some of the factors that led to the successful eradication of smallpox from the world population.[4] [Total: 12]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
2 (a) abnormal condition/abnormal state/disorder/ill-health/AW, qualified
e.g. having an adverse effect (on an organism)
reduces the effectiveness of functions
produces (specific) signs/symptoms
infectious and non-infectious causes ;
(b) natural active ; artificial active ; natural passive ; artificial passive ;
Allow one mark for active and passive correct
(c) number of cases fluctuates ; A description of increases and decreases over time
(overall trend) number of cases decreases (over time) ;
overall decrease, data quote to support ;
e.g. (India) 155000/160000 cases in 1950 to 0 in 1980
(all countries) 330000 cases in 1950 to 0 in 1980
(India) 250000/160000 cases in 1951 to 0 in 1980
(all countries) 485000 cases in 1951 to 0 in 1980
India/all countries, three major peaks ;
data quote to support ; e.g. 1951, 1958, 1974
eradication, no cases from 1975/1976, for India or 1978 for world ;
A (almost zero) from 1976 for world
(d) 1 smallpox virus was stable/did not mutate ;
2 same vaccine was used for whole programme/vaccine did not need to be changed ;
3 vaccine was live/gave a strong immune response ; A effective
4 one dose was enough to give life-long immunity/no boosters required ;
5 heat stable/freeze dried vaccine ;
6 suitable for hot countries/isolated areas/rural areas ;
7 bifurcated/steel, needle, could be re-used/easier delivery/AW ;
8 herd/mass, vaccination/immunity ; A (many countries) mandatory vaccination
9 ring vaccination/ref. to contact tracing ;
10 few/no symptomless carriers ;
11 no animal reservoir/only in humans ;
12 infected people easy to identify ;
13 isolation of cases to prevent spread ;
14 AVP ; e.g. comparatively low cost, qualified; many volunteers became vaccinators/AW ;
Question
B-lymphocytes respond to the presence of a non-self antigen by dividing as shown in Fig. 4.1.
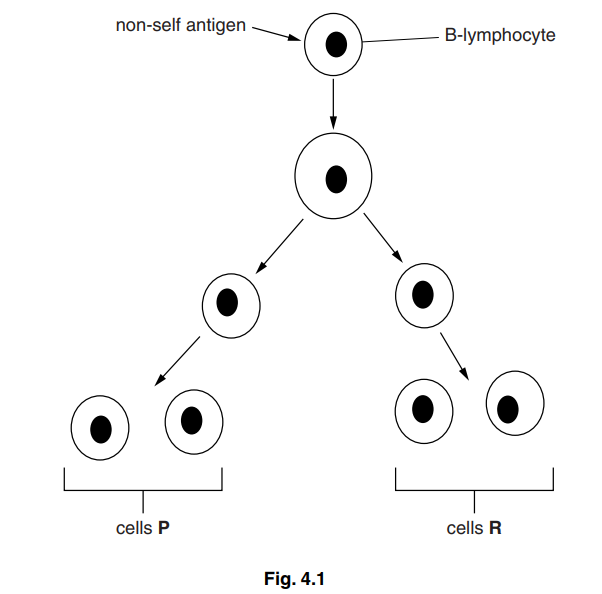
(a) (i) Explain what is meant by the term non-self antigen.[2]
(ii) Outline how B-lymphocytes recognise non-self antigens.[2]
The cells labelled P on Fig. 4.1 continue to divide to give rise to many cells that differentiate into short-lived plasma cells. The plasma cells release antibody molecules.
(b) (i) Outline how plasma cells produce antibody molecules.[4]
(ii) Describe how antibody molecules are released from the plasma cell.[2]
(c) The cells labelled R on Fig. 4.1 divide to give more cells that do not differentiate into plasma cells. These cells have an important role in the immune system.
Explain the role of these cells.[3]
The mass of DNA in the cells shown in Fig. 4.1 was determined. The results are shown in Fig. 4.2.
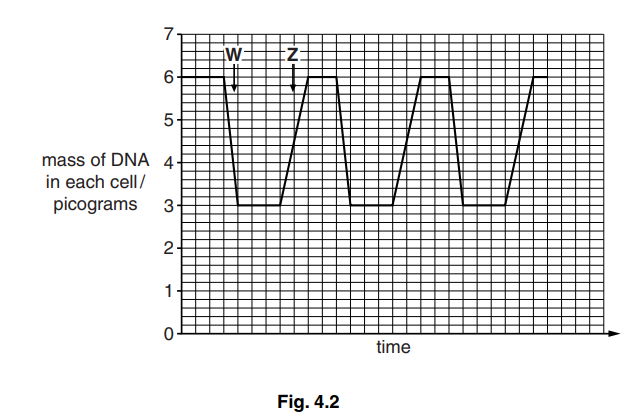
(d) State what happens at W and Z to change the mass of DNA in each cell.[2]
W
Z
(e) Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is a cancer of B-lymphocytes. It is very rare in adults, but more common in children. A study in 2009 found that exposure to tobacco smoke in the home may put children at risk of developing ALL.
Suggest how smoking by adults in the home may put their children at risk of cancers, such as ALL.[3] [Total: 18]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
4 (a) (i) non-self
foreign/AW ; A ref. to epitope(s) I pathogen/organism
antigen
macromolecule/(glyco)protein/ carbohydrate/ polysaccharide/ oligosaccharide ;
stimulates /AW, an immune response/production of antibodies ;
A results in formation of antigen-antibody complexes
A other described events in an immune response
(ii) antibody / immunoglobulin/ IgG, on cell surface/on cell membrane ; (act as) receptors ;
ref. to antigen-binding/AW ;
(shape) specific / complementary, to antigen ;
(b) (i) DNA/ gene transcribed/ mRNA using DNA as template/AW ;
A transcription unqualified
idea of mRNA associating with ribosome(s) ;
ref. to tRNA with specific amino acid (carried to ribosome) ;
pairing/AW of codons on mRNA with anticodons on tRNA ;
formation of peptide bonds (between adjacent amino acids) ;
antibody /protein/ polypeptide(s), enters RER/ moves to Golgi body ;
ref. to forming, secondary / tertiary structure ;
antibody /protein/ polypeptide(s), modified/processed/glycosylated/ formation
of quaternary structure/ formation of disulphide bond(s) in Golgi (body / apparatus / complex) ; I ref. to packaging
(ii) vesicles move to cell/ surface/plasma, membrane (via cytoskeleton) ;
R secreting vesicles unqualified
vesicles fuse with cell (surface) membrane/exocytosis ; R active transport
movement of vesicle/ exocytosis requires energy or ATP/ is active ;
(c) memory cells ; A form immunological memory I ‘gives immunity’
remain/ stay in circulation/ blood/lymphatic system ;
R ‘last a long time/ long lived’ unqualified
for secondary response ;
fast(er) response when exposed again to same pathogen/ same antigen ;
A fast(er) clonal selection/ fast(er) clonal expansion
A divide quickly /rapidly
A long(er) lasting response
to form plasma cells (and more memory cells) ;
more antibodies produced/higher concentration of antibodies ;
R if in context of memory cells
to prevent person feeling ill/ to prevent symptoms ;
(d) W – cytokinesis / cytoplasmic division/ cell divides into two ;
I cell division
R mitosis / telophase
Z – (semi-conservative) replication (of DNA) ;
I S phase/ interphase of cell cycle
R copying of DNA
R protein synthesis
R if replication is given in any other phase of the cell cycle
(e) 1 breathing in/ inhale smoke/ ‘second hand’ smoke/ sidestream smoke ;
A passive smoking
I exposed to smoke
2 (tobacco smoke contains) carcinogen(s) ;
3 causes mutation/ described ;
e.g. change to/alters / damages, DNA R if in wrong type of cell
4 leads to uncontrolled cell division/ mitosis / growth ;
5 forming a tumour/ mass of cells ;
6 correct ref. to (proto-)oncogenes /tumour suppressor genes ;
e.g. formation of oncogenes / mutation of tumour suppressor genes / ‘switching off’ tumour suppressing genes
mutation of correct named gene = 2 marks
e.g. mutation of tumour suppressor gene
P53 (gene) mutates = 2 marks
Question
Bone marrow contains stem cells that divide by mitosis to form blood cells. Each time a stem
cell divides it forms a replacement stem cell and a cell that develops into a blood cell.
Fig. 3.1 shows changes in the mass of DNA in a human stem cell from the bone marrow
during three cell cycles.
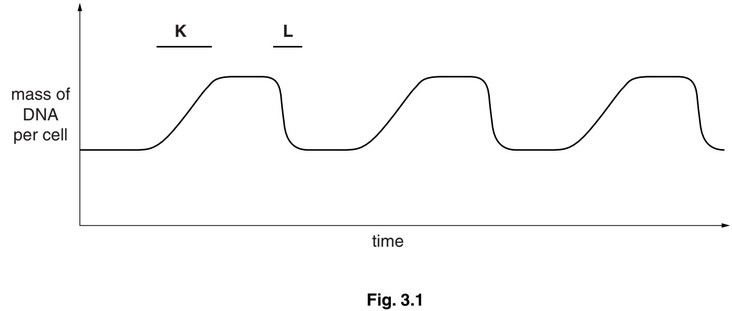
(a) With reference to Fig. 3.1, state:
(i) what happens to bring about the changes in the mass of DNA per cell at K and at L
K ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
L ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) how many blood cells are formed from the stem cell in the time shown
(iii) what happens to the number of chromosomes in the stem cell.
Stem cells in bone marrow give rise to phagocytes, B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes.
(b) Describe how a red blood cell develops from a stem cell.
(c) During an immune response, cells divide by mitosis.
Describe how mitosis is involved in an immune response.
(d) Describe the modes of action of T-lymphocytes during an immune response.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) K – (DNA) replication / synthesis / described ;
L – cytokinesis / cytoplasmic division / cell division ;
(ii) 3 ;
(iii) remain the same / stays constant / stay at 46 / AW ; ignore description of events
occurring before and during mitosis
(b) transcription (of specific genes) ; A reference to gene switching
protein / polypeptide, synthesis ; A translation
production of haemoglobin ;
further detail ; e.g. assembly of quaternary structure
(production of) carbonic anhydrase ;
loss of, mitochondria / named organelles ;
loss of nucleus ;
adopts biconcave disc shape ;
(c) occurs in both primary and secondary (immune) responses ;
selected / specific / AW ;
lymphocytes / B -cells / T-cells / divide (by mitosis) ;
clonal expansion / described in terms of producing, clone / many cells ;
A idea that different types of immune cell can result
reference mitosis in memory cells (for rapid) secondary response ;
(d) T helper / Th,
secrete, cytokines / interleukins ;
activate B-lymphocytes to, divide / form plasma cells ; A idea that leads to enhanced
antibody levels
enhances / AW, phagocyte / macrophage, response ; A angry macrophages ;
T cytotoxic / Tc / T killer / Tk
attach to / kill / AW, infected cells / damaged cells / tumour cells / cells with non-self
antigens / AW;
mechanism of killing ; e.g. perforin
T memory / Tm
already exposed to antigen ;
reference to role in secondary response ;
AVP ; ; e.g. T suppressor cells
function of suppressor cells
