Question
(a) Explain the significance of cereal crops in the human diet. [8]
(b) Describe and explain how gibberellins are involved in the germination of wheat or barley seeds. [7] [Total: 15]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
9 (a) 1 high, carbohydrate/ starch, content ; A 70–80%
2 source of, energy /ATP ;
3 protein provides amino acids ;
4 for growth ;
5 low in fat ; A 2–4%
6 contains essential fatty acids ;
7 source of, vitamin B/ vitamin E ;
8 deficient in, vitamin A/ vitamin D/ vitamin C ;
9 ref. to Golden Rice and vitamin A ; A ref. to other valid examples
10 wide range/AW, of minerals ;
11 named mineral plus use in human body ; e.g. calcium for bone development
12 high in fibre ;
13 for peristalsis/prevents constipation ;
14 easily, dried/ stored ;
15 AVP ; e.g. staple diet for much of the world/named staple crop and location
16 AVP ; e.g. different parts of grain have different nutrients/ref. to processing grain
(b) 1 seed is, dormant/metabolically inactive ;
2 water enters seed ;
3 embryo, produces/releases, gibberellin ;
4 gibberellin stimulates aleurone layer ;
5 (by) affecting, gene coding/transcription of mRNA, for amylase ;
6 to produce amylase ;
7 amylase hydrolyses starch ;
8 in endosperm ;
9 to, maltose/glucose ;
10 embryo uses sugars for respiration ;
11 energy /ATP, used for growth ;
Question
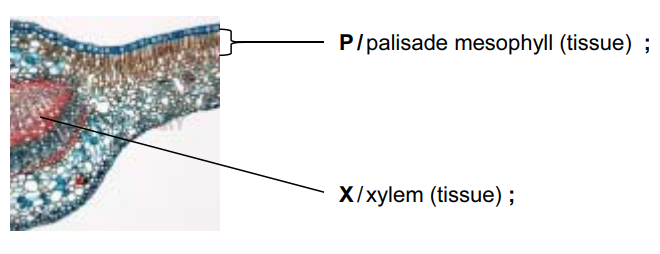
(a) Fig. 1.1 shows a section through part of a dicotyledonous leaf of the tea plant Camellia sinensis.
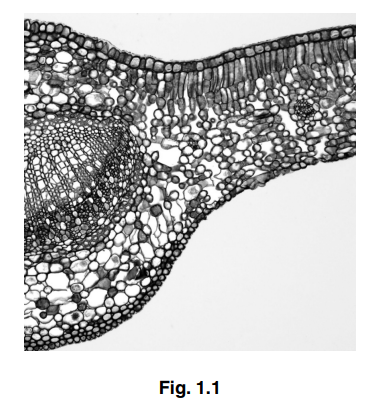
On Fig. 1.1, use label lines and letters to label each of the following parts:[2]
X – xylem tissue
P – palisade mesophyll tissue.
(b) The leaves of C. sinensis have a large surface area and are thin.
Explain how each of these two features help the leaf to carry out photosynthesis.[2]
(c) The lower epidermis contains stomata.
(i) State one structural difference between a guard cell and other lower epidermal cells.[1]
(ii) Abscisic acid has an important role in the closure of a stoma. It promotes the loss of potassium ions from guard cells.
Outline how the loss of potassium ions from guard cells will lead to the closure of a stoma.[3] [Total: 8]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1 (a)
(b) large surface area
(to get) more, light/ carbon dioxide ; A gas exchange I oxygen
thinness
small(er)/ short(er)/reduced, diffusion distance for gases OR
fast(er) diffusion of gases ; A named gas, either CO2 or O2
1 mark only if both points made but not related to features in italics
(c) (i) have chloroplasts / varying thickness of (cell) walls / no plasmodesmata ;
(ii) water potential/Ψ, of (guard) cell(s), increases /becomes less negative ; water leaves cell(s) ;
(by) osmosis / down a water potential gradient ; I diffuses
(guard cell) becomes, flaccid/ less turgid/AW ;
Question
(a) Explain the role of auxin in cell elongation in plants. [7]
(b) Describe the role of abscisic acid in the closure of stomata. [8] [Total: 15]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
10(a) seven from
1 acid-growth (hypothesis) ;
2 auxin stimulates proton pumps ;
3 (in) cell surface membrane ;
4 H+ pumped into cell wall ;
5 using energy / by active transport ;
6 pH of cell wall decreases / cell wall becomes (more) acidic ;
7 pH-dependent enzymes activated ;
8 ref. to expansins ;
9 bonds between cellulose microfibrils broken ;
10 idea that cell wall, ‘loosens’ /becomes more elastic /able to stretch ;
11 (more) water enters cell/ turgor pressure increases ;
12 (so) cell (wall) expands ;
10(b) eight from
1 plant secretes abscisic acid, in very dry conditions /at times of water stress ;
A abscisic acid is a stress hormone
2 abscisic acid binds to receptors ;
3 on cell surface membranes of guard cells ;
4 inhibits proton pump /H+ not pumped out of cell ;
5 high H+ conc inside cell ; A ref. to change in charge
6 (abscisic acid) stimulates Ca2+ influx ;
7 Ca2+ acts as second messenger ;
8 encourages K+ efflux / inhibits K+ influx ; A K+ channels open
9 water potential of cell increases ; A increase in solute potential
10 water moves out of cell by osmosis ;
11 volume of guard cells decreases ;
12 guard cells become flaccid ;
13 response very fast ;
