A student drew a plan diagram of some plant tissue.
The diagram is shown. It contains a mistake in the way that it is drawn.
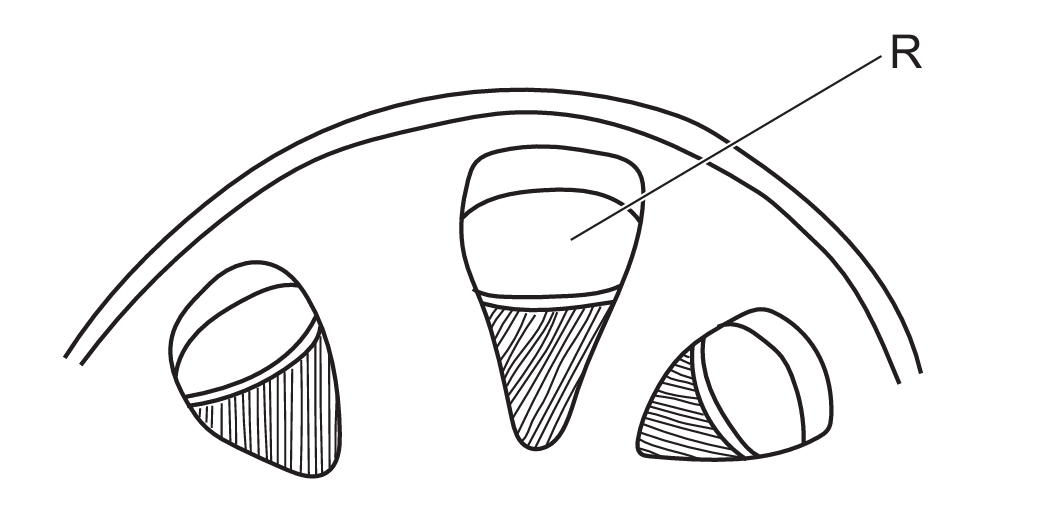
The maximum width of R is 15 mm on the diagram and its actual width is 250 μm.
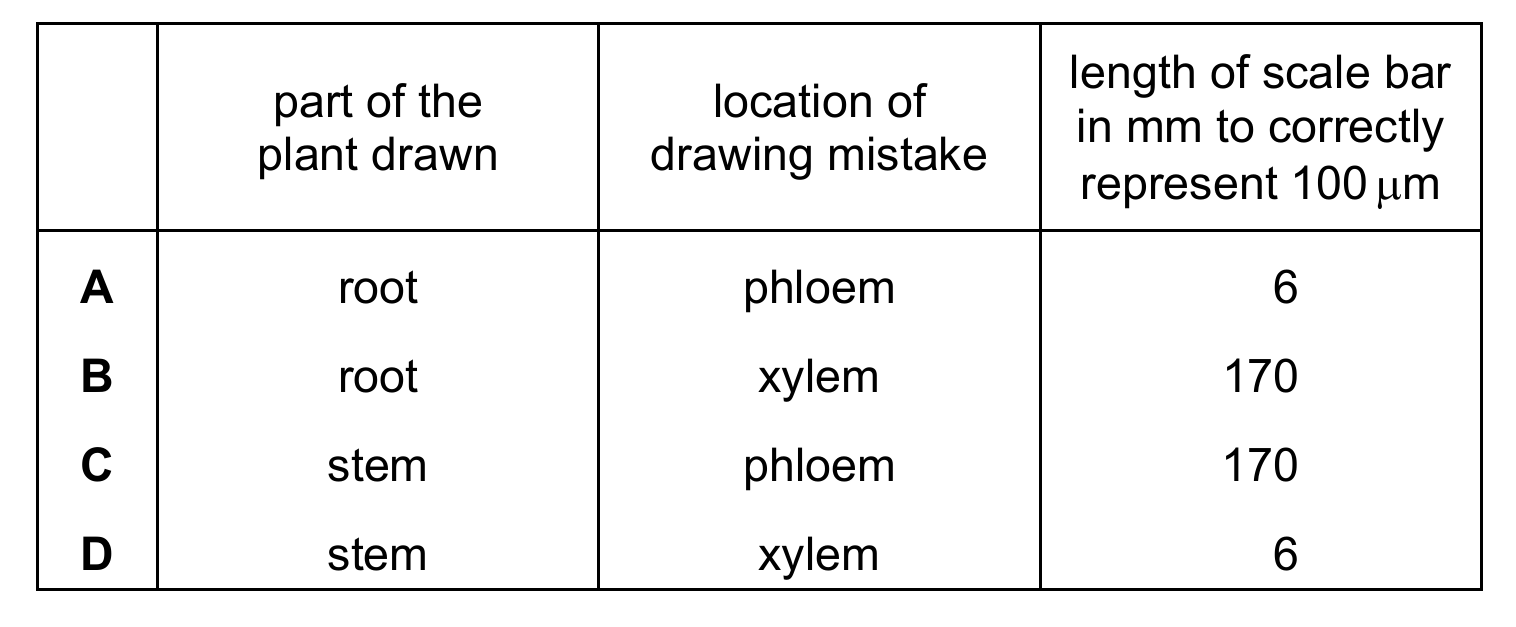
The student was asked to draw a scale bar on their diagram.
Which row is correct?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
First calculate the magnification: 15mm/250μm = 15,000μm/250μm = ×60. For a 100μm scale bar at ×60 magnification: 100μm × 60 = 6,000μm = 6mm. The xylem is typically drawn incorrectly in stem sections, making D the correct choice.
Which steps are needed to find the actual width of a xylem vessel viewed in transverse section using a ×10 objective lens?
- Convert from mm to µm by multiplying by \( 10^{-3} \).
- Calibrate the eyepiece graticule using a stage micrometer on a ×4 objective lens.
- Measure the width of the xylem vessel using an eyepiece graticule.
- Multiply the number of eyepiece graticule units by the calibration of the eyepiece graticule.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
To measure the actual width, you only need to measure using the graticule (step 3) and multiply by the calibration (step 4). Conversion from mm to µm (step 1) isn’t needed as measurements are typically in µm, and calibration should be done with the same objective lens (×10, not ×4).
The diagram shows some cell structures of one type of cell.
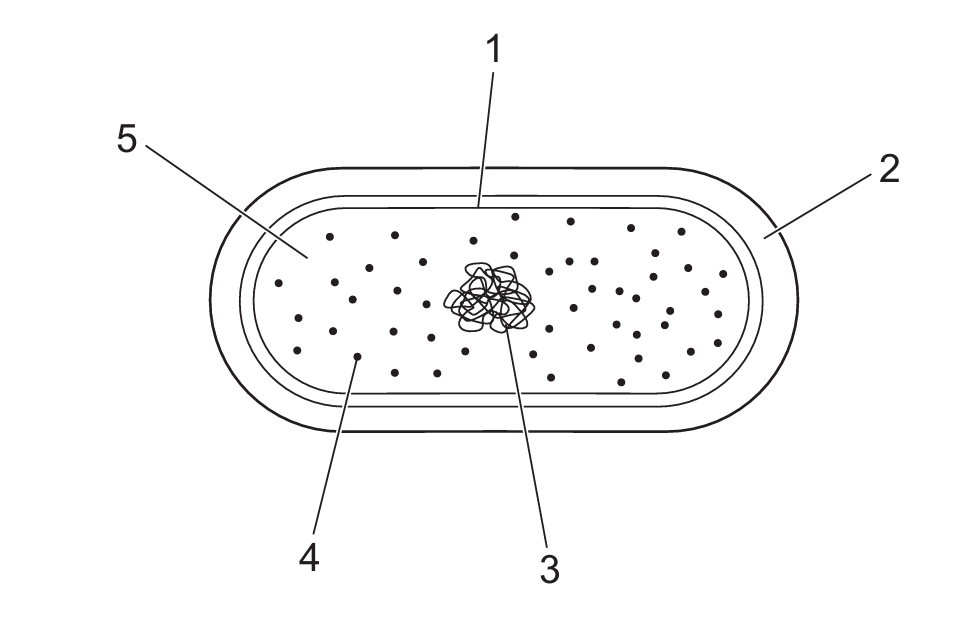
Which labelled cell structures are present in typical eukaryotic cells and typical bacterial cells?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Both eukaryotic and bacterial cells contain ribosomes (1), cytoplasm (3), cell membranes (4), and DNA (5). Structures like the nucleus (2) are unique to eukaryotes. Therefore, the correct answer is B (1, 3, 4, and 5).
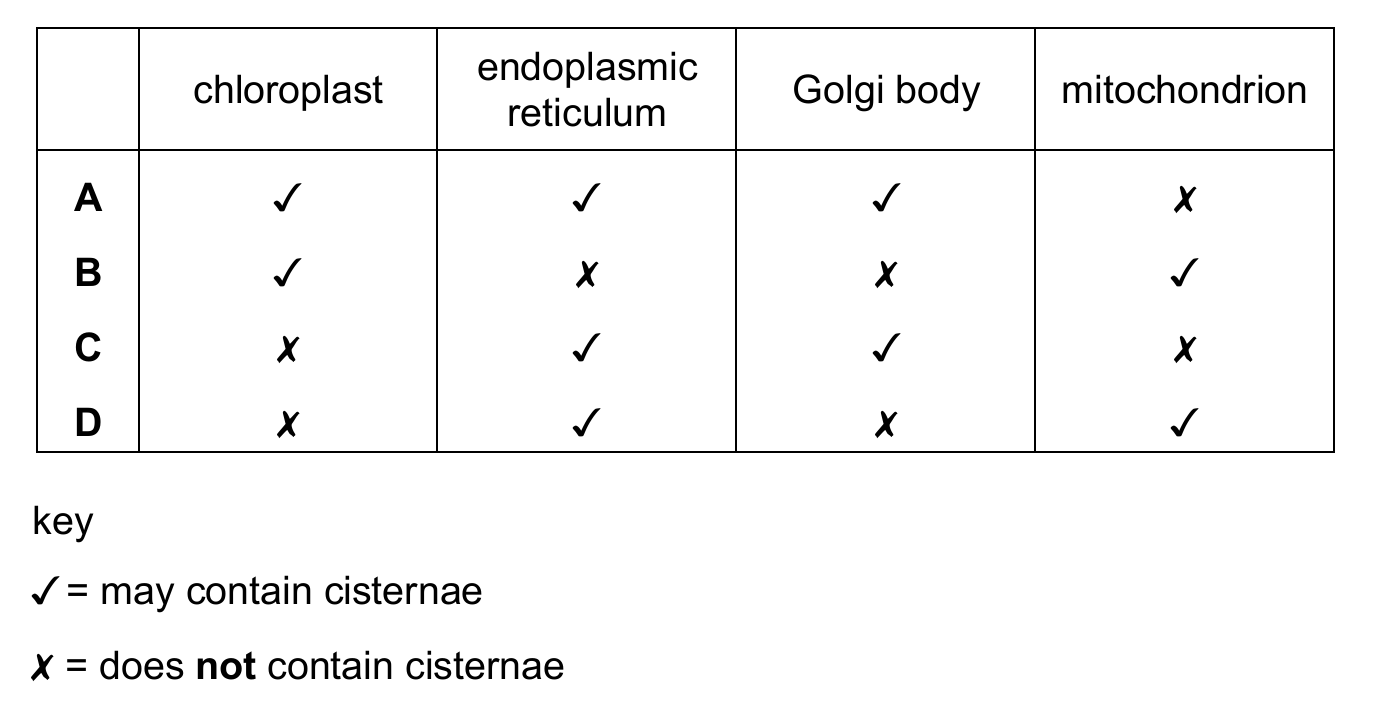
Which cell structures may contain cisternae?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Cisternae are flattened membrane sacs found in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Chloroplasts have thylakoids (not cisternae), and mitochondria have cristae. Thus, only ER and Golgi contain cisternae.
