Question
The diagrams show different types of bond found in biological molecules.
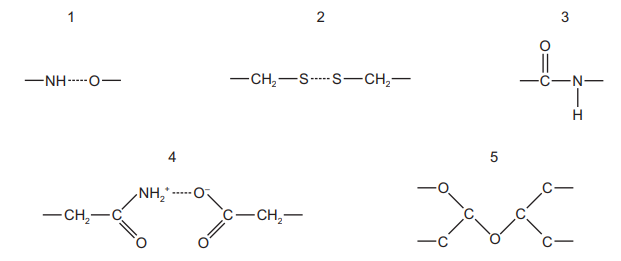
Which combination of bonds could not be found in a protein with a tertiary structure?
A 1, 2, 3 and 4 B 1, 2 and 4 only C 3 and 5 D 5 only
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
– Primary structure of proteins is the result of peptide bonds between amino acids.
– The secondary structure is the result of hydrogen bonding between nearby amino acids but R groups do not affect it.
– Ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and disulfide bridges are a result of interactions between the R groups and create the tertiary structure.
– The quaternary structure describes the way these separate polypeptide chains fit together in three dimensions.
Tertiary structure-
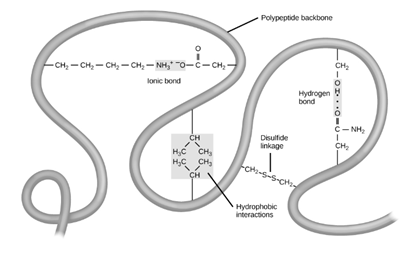
Thus, amongst the given structures, structure 5 could not be found in a protein with a tertiary structure
Question
The diagram shows the structure of four amino acids in solution.
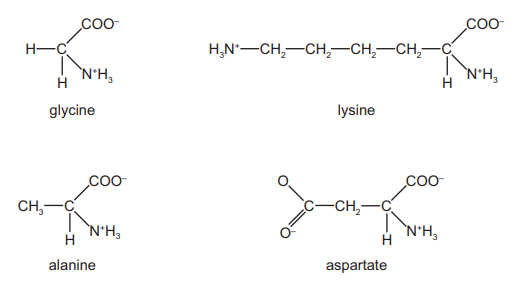
Which of these four amino acids have an overall charge?
- alanine and aspartate
- alanine and glycine
- aspartate and lysine
- glycine and lysine
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
From the given structures we can see that aspartate (or Aspartic acid) is a negatively charged, polar amino acid and lysine has net positive charge. Glycine and alanine on the other hand are non-polar and neutral.
Question
The diagram shows the relationship between the levels of protein structure and bonds.
Which row is correct?
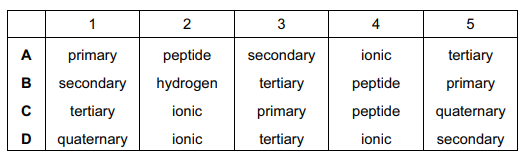
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
How many molecules of oxygen are bound to one molecule of haemoglobin, when it is fully saturated with oxygen?
A 1 B 2 C 4 D 8
▶️Answer/Explanation
When hemoglobin is fully saturated with oxygen, four molecules of oxygen are bound to one molecule of hemoglobin.
Therefore, the answer is C. 4.
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that binds to oxygen and transports it to tissues throughout the body. It has four subunits, each of which contains a heme group that can bind to one molecule of oxygen. When all four heme groups are bound to oxygen, the hemoglobin molecule is fully saturated with oxygen.
Question
Collagen is a macromolecule with three polypeptides lying closely side by side in the form of a triple helix.
Every third amino acid in each polypeptide has the shortest possible R-group or side chain (– H) to allow close packing of the polypeptides.
Which is the amino acid?
A)glucose
B)glycerol
C)glycine
D)guanine
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
The amino acid that has the shortest possible R-group or side chain (-H) and is found every third amino acid in collagen is glycine.
Therefore, the answer is C) glycine.
Collagen is a fibrous protein that provides structural support to tissues such as skin, bone, and cartilage. It is composed of three polypeptide chains that are arranged in a triple helix. The presence of glycine as every third amino acid in the polypeptide chain allows for tight packing of the chains, which is essential for the stability of the collagen triple helix. The small size of the glycine R-group allows for close contact between the polypeptide chains, and the flexibility of the glycine residue allows for the tight turns required for the triple helix structure.
