Question
There are many types of amino acids, but only twenty that are polymerised to make polypeptides and proteins in animals.
(a) Name the type of chemical reaction that occurs when two amino acids form a dipeptide.[1]
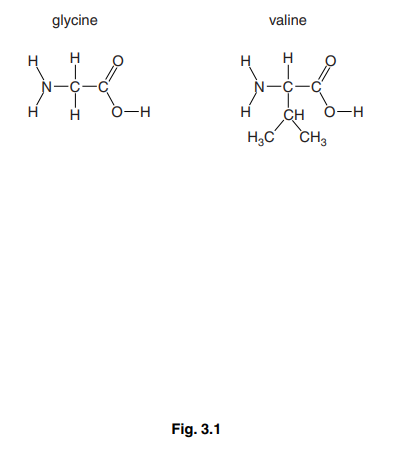
(b) Fig. 3.1 shows two amino acids, glycine and valine. Use the space below to make a drawing to show what happens when these two molecules join together to form a dipeptide.[4]
(c) Angiotensinogen is an inactive protein molecule. When blood pressure decreases, part of angiotensinogen is removed to form a short polypeptide, angiotensin that stimulates an increase in blood pressure.
Fig. 3.2 shows the base sequence within the gene for angiotensinogen that codes for this short polypeptide, the RNA codons and the primary structure of angiotensin.
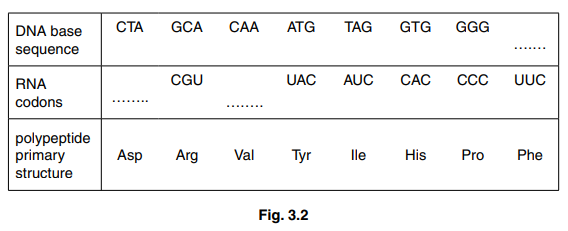
(i) Complete Fig. 3.2 to show the missing DNA triplet and the RNA codons. [1]
(ii) State the full name of the type of RNA shown in Fig. 3.2.[1]
Table 3.1 shows the blood pressure in the right ventricle and in the pulmonary artery of a person who is in good health.
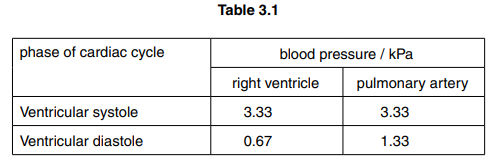
(d) Use the information in Table 3.1 to explain why the blood pressure in the pulmonary artery is the same as the pressure in the right ventricle during systole, but higher during diastole.[3]
(e) People with long-term chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) usually have blood which is poorly oxygenated during its passage through the lungs. This leads to a constriction of blood vessels in the lungs.
Suggest the likely effect of this on the heart.[2]
(f) Describe the signs and symptoms of COPD that help doctors make an early diagnosis of this condition.[2] [Total: 14]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
3 (a) condensation ; A dehydration
(b) accept glycine-valine or valine-glycine
peptide bond drawn correctly ;
amino and carboxylic acid ends shown ;
correct R-groups ;
water eliminated ;
(c)
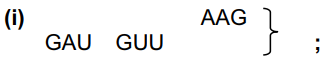
(ii) messenger ;
(d) during systole semi-lunar valve is open ;
during diastole semi-lunar valve is closed ;
proximity/AW pulmonary artery to (right) ventricle (so no pressure lost) ;
elastic recoil of pulmonary artery maintains blood pressure/AW ;
no/little blood in (right) ventricle, after contraction/during diastole ;
fills with blood at low pressure ;
(e) increase in power of contraction ; AW
increase in (systolic) blood pressure ;
strain on right ventricle/right ventricle does not function efficiently ;
growth of muscle in/right ventricle increases in thickness ;
insufficient oxygen to, heart/cardiac, muscle ;
heart failure/heart attack ;
(f) persistent/AW, cough ;
cough produces much mucus ;
wheezing ;
rapid breathing/difficulty breathing/breathlessness ;
bluish colour to the skin ;
recurrent chest infections/frequent colds or ‘flu/AW ;
barrel-shaped chest ;
chest pains ; R heart pains
fatigue/weakness, (with exercise) ;
Question
Statements A to E relate to biological molecules.
For each statement, identify the most appropriate term that matches the description.
A The molecule formed from a condensation reaction between fructose and glucose.
B The name of the bond broken when two amino acids are separated by hydrolysis
C The unbranched polymer consisting only of β-glucose molecules.
D The reagent used to test for the presence of proteins.
E The molecule produced, in addition to fatty acids, when a triglyceride is hydrolysed.[5] [Total: 5]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1
A sucrose ;
B peptide ; A amide
C cellulose ;
D biuret ; A (dilute) potassium/ sodium, hydroxide (solution) and (dilute) copper sulfate (solution)
R Millon’s solution
E glycerol ;
Question
Fig. 2.1 is a diagram of the structure of a protein channel for ions in a cell surface membrane.
Fig. 2.1a shows the channel when open and Fig. 2.1b shows the same channel when closed.
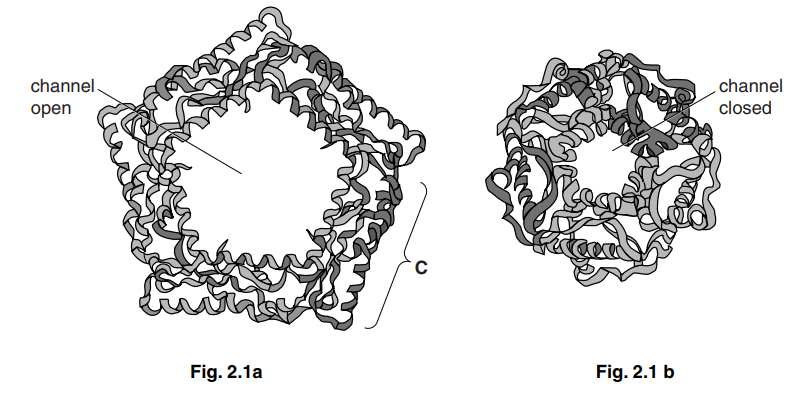
(a) (i) Name the process by which ions pass across the membrane using channel proteins.[1]
(ii) Explain why a channel protein is needed for ions to pass across a cell membrane.[2]
(b) The channel protein in Fig. 2.1 is made from five identical polypeptide chains.
(i) Name the level of protein structure which is present when five polypeptide chains form the protein.[1]
(ii) The part labelled C in Fig. 2.1 is another level of protein structure.
Name this level.[1]
(c) Channel proteins are examples of transmembrane proteins. The polypeptides are held together and also interact with phospholipids in the membrane.
Suggest how the polypeptides are held together and suggest how they interact with phospholipids.[3] [Total: 8]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
2 (a) (i) facilitated diffusion ;
(ii) ions are, charged/water-soluble ; A hydrophilic
unable to pass, through hydrophobic core/ hydrophobic (fatty acid) tails of,
phospholipid bilayer/ phospholipids(s) ;
(channel of) protein lined with amino acids with, hydrophilic/ polar, R groups /
side chains ; A hydrophilic channels
(b) (i) quaternary / 4°, (structure) ;
(ii) secondary structure ; A alpha/α, helix
(c) bonds must be named in the correct context of maintaining 4° structure and interactions with phospholipids
polypeptides held together
bonds between, R groups / side chains ;
two named bond types ; from
ionic
hydrogen
hydrophobic interactions
disulfide
van der Waal’s forces
I peptide bond
polypeptides interact with phospholipids
(regions with) hydrophilic / charged/ polar (R groups / side chains, of) amino acids
interact with, phosphate/ hydrophilic head , of phosholipid ;
(regions with) hydrophobic /non-polar (R groups / side chains, of) amino acids
interact with, fatty acid/ hydrocarbon/ hydrophobic, tails / chains ;
further detail of named bond ;
