In an experiment, pieces of onion epidermis are put into three different concentrations of sucrose solutions, P, Q and R. The pieces of onion are left for an hour and then examined using the low power of a light microscope.
Each diagram shows one cell from the epidermis that was placed in each of the sucrose concentrations.
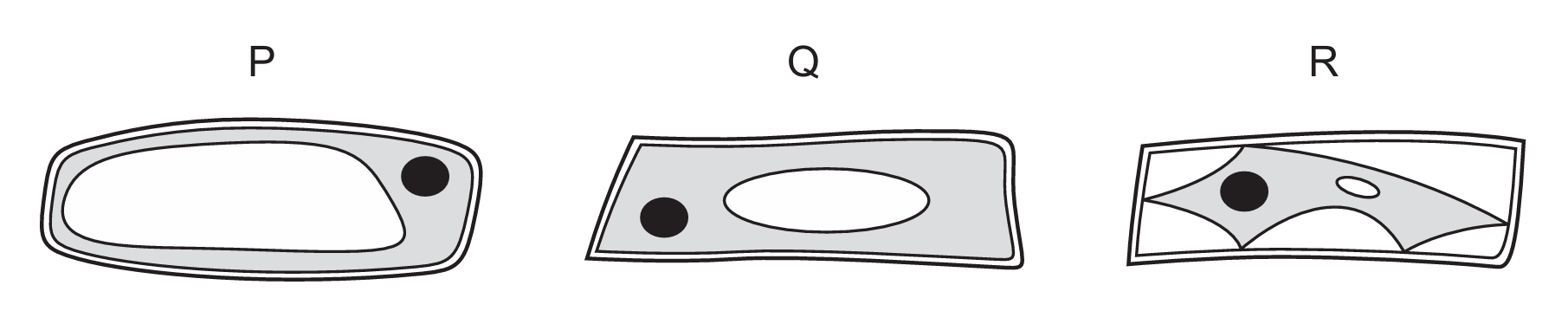
What explains the appearance of cells in solution Q?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The appearance of cells in solution Q indicates no net movement of water, meaning the water potential inside the cell (cell sap) equals that outside (solution Q). While A mentions solute concentration, water potential (D) is the correct measure as it accounts for both solute concentration and pressure potential.
Which statements about phospholipids in cell membranes are correct?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Only 2 and 4 are correct: tails are hydrophobic (inward-facing) and phospholipids allow flexibility. Statement 1 is wrong (tails block ions), and 3 is incorrect (heads face both cytoplasm and extracellular fluid).
A mixture of glucose and starch solutions was placed in a length of dialysis (Visking) tubing and the tubing sealed. The tubing was then placed in a boiling tube containing distilled water. Two samples were immediately removed from this water (time 0 minutes) and tested with either iodine solution or Benedict’s solution. This was repeated at 10 minute intervals for 30 minutes.
The iodine solution gave an orange-brown colour each time.
The table shows the results of the Benedict’s test.
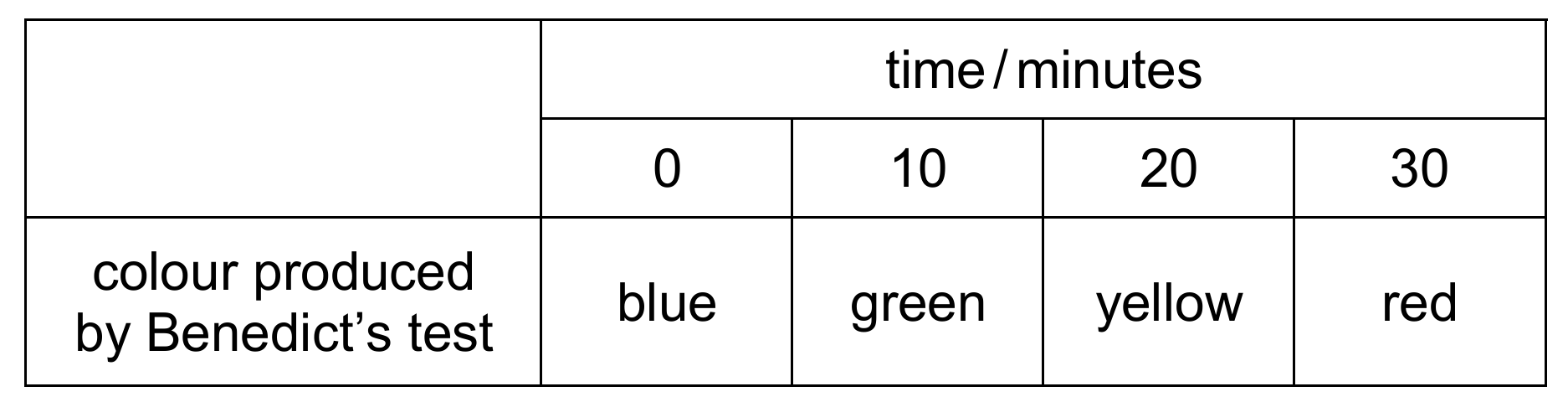
What may be concluded from these results?
- The pores in the Visking tubing are too small for a starch molecule to pass through.
- Glucose diffuses through the Visking tubing down a diffusion gradient
- Water diffuses into the Visking tubing.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
1 is correct (iodine stays orange-brown, showing starch didn’t leave tubing). 2 is correct (Benedict’s color change shows glucose diffused out). 3 cannot be confirmed as no volume measurements were taken. Thus, B (1 and 2 only) is correct.
Which property of water, related to its role in blood and tissue fluid, is correctly described?
A. Water is a solvent for all biological molecules.
B. Water is a solvent for most non-polar molecules.
C. Water requires little energy to increase its temperature because it has a high specific heat capacity.
D. Water cools down slowly because it has a high specific heat capacity.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Option D is correct: Water’s high specific heat capacity (4.18 J/g°C) means it absorbs/releases large amounts of heat with minimal temperature change, enabling stable body temperatures and slow cooling in blood/tissue fluid.
Option A is incorrect: Water dissolves polar/ionic molecules (e.g., glucose, salts) but not all (e.g., lipids).
Option B is incorrect: Non-polar molecules (e.g., oils) are insoluble in water.
Option C is incorrect: High specific heat capacity implies water resists temperature changes, requiring more energy to heat.
