A student filled dialysis tubing with a sucrose solution and knotted both ends. This formed a cylinder with a length of 5.0 cm and a radius of 2.0 cm.
What is the surface area to volume ratio for this cylinder of dialysis tubing?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Surface area of cylinder = \(2πrh + 2πr^2 = 2π(2)(5) + 2π(4) = 20π + 8π = 28π\). Volume = \(πr^2h = π(4)(5) = 20π\). Ratio = \(28π:20π = 1.4:1.0\). Thus, the correct answer is C (1.4:1.0).
The photomicrograph shows a type of blood cell.
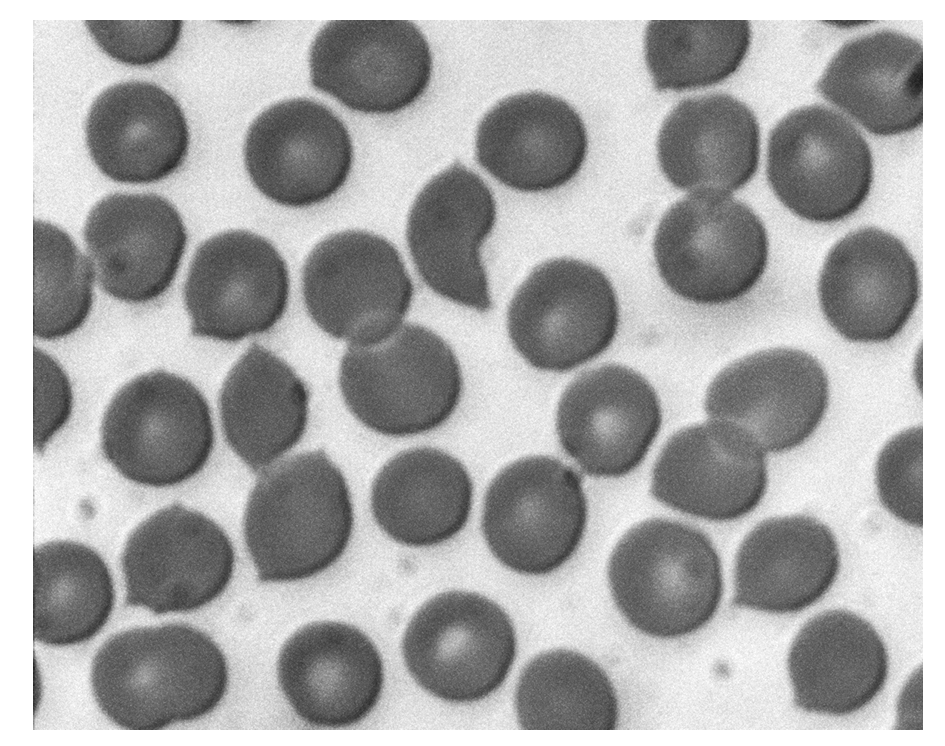
Which statements about these cells are correct?
- Oxygen diffuses through the phospholipid bilayer.
- Sodium ions diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer.
- Water passes in and out of these cells by osmosis.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Statement 1 is correct – small non-polar oxygen can diffuse through the bilayer. Statement 3 is correct – water moves via osmosis through aquaporins. Statement 2 is incorrect – charged sodium ions require channel proteins. Therefore, the correct combination is 1 and 3 only.
Gout is a type of arthritis in which small uric acid crystals form inside and around the joints. It causes sudden attacks of severe pain and swelling.
The diagram shows how uric acid is formed from hypoxanthine catalysed by the enzyme xanthine oxidase.
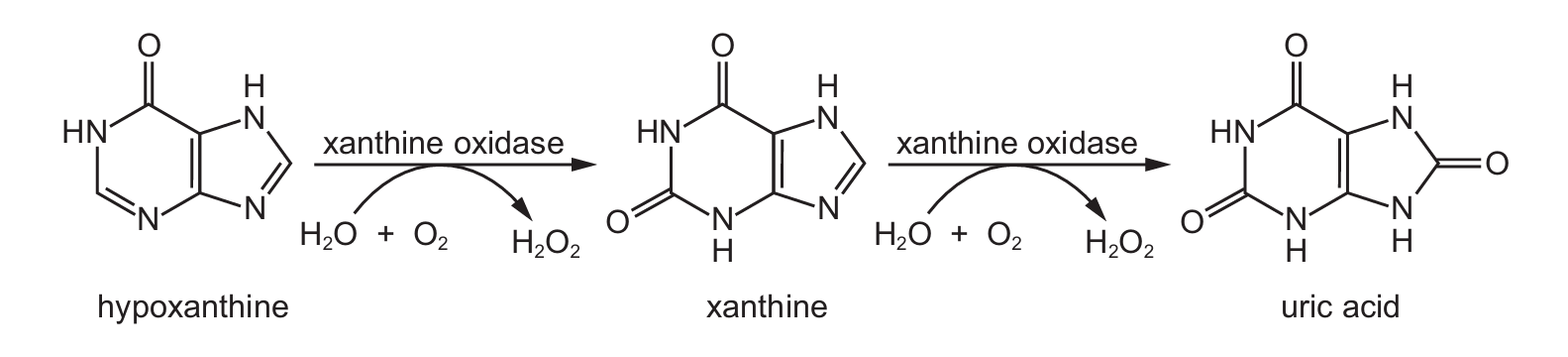
Gout can be treated using a drug called allopurinol which has a similar shape to hypoxanthine.
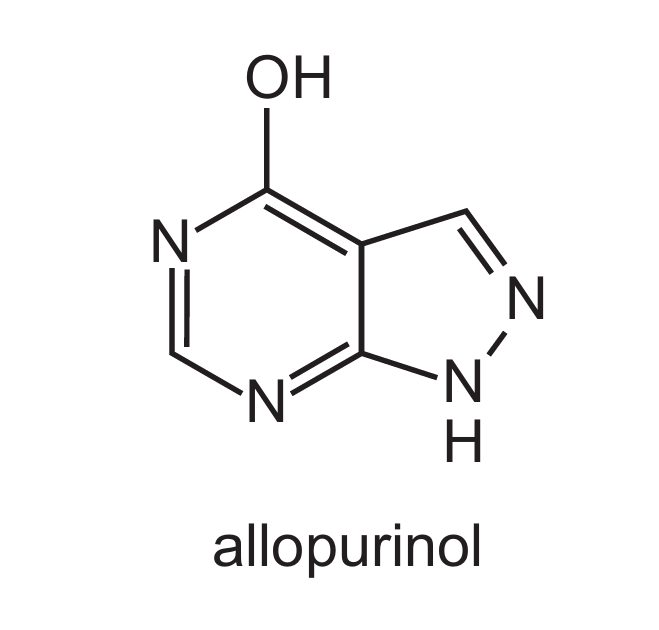
What can be concluded from this information about how allopurinol prevents the formation of uric acid?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Allopurinol is a competitive inhibitor that mimics hypoxanthine’s shape, binding to xanthine oxidase’s active site. This blocks hypoxanthine from binding, reducing uric acid production without denaturing the enzyme (C/D are incorrect).
The initial rate of a reaction catalysed by an enzyme was measured at various substrate concentrations.
Which graph shows the effect of a low concentration of non-competitive inhibitor on the reaction?
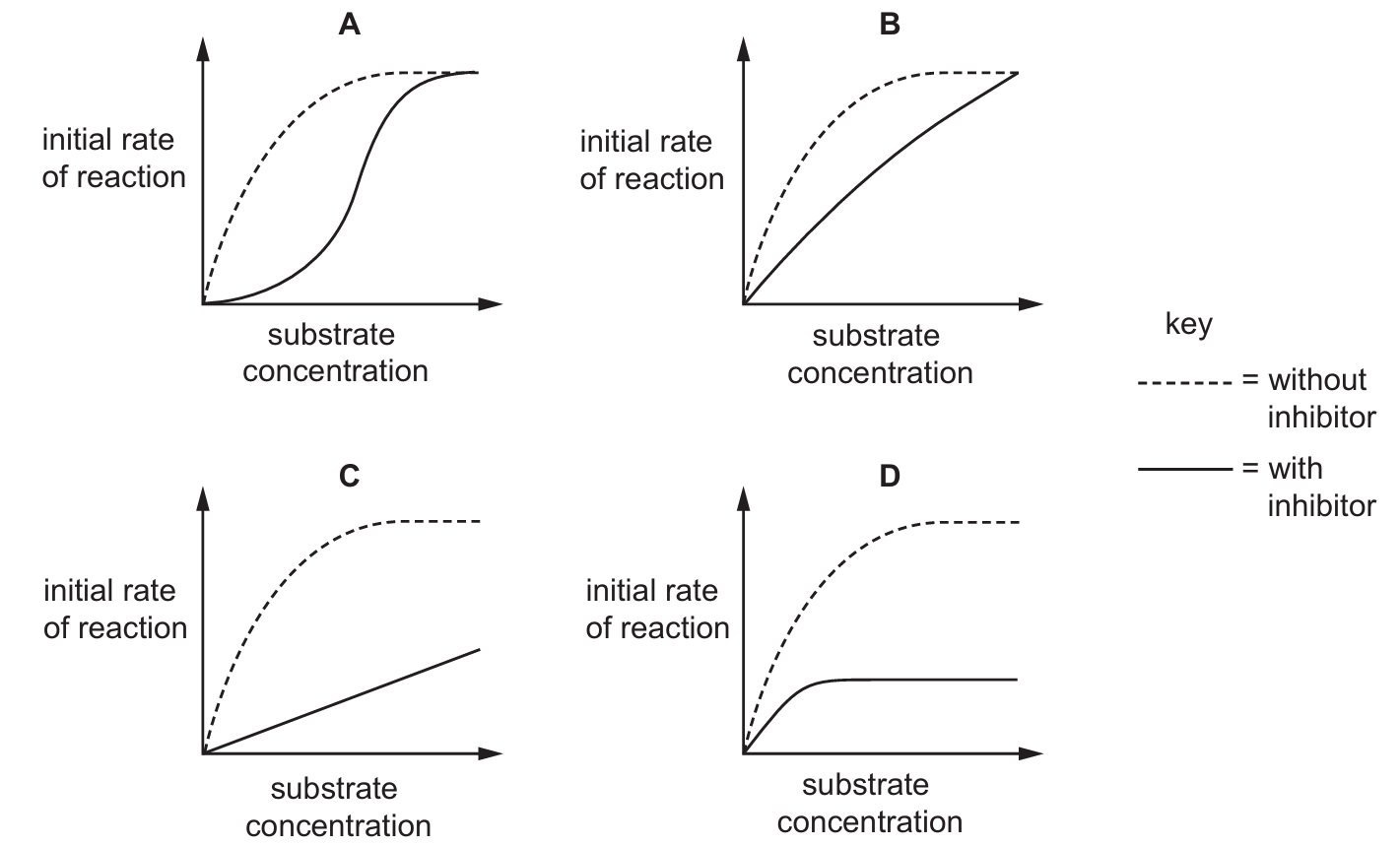
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
A non-competitive inhibitor reduces Vmax but doesn’t affect Km, shown by parallel curves. The inhibitor binds away from the active site, altering enzyme shape and reducing maximum reaction rate regardless of substrate concentration.
