The number of substrate molecules one enzyme molecule can convert to product in a second is called the turnover number. This number is obtained when all conditions are optimum for the specific enzyme-catalysed reaction.

How many times faster at converting substrate to product is catalase compared to phosphatase?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
From the data provided (assuming the image shows turnover numbers), catalase has a turnover number of 40,000,000 per second, while phosphatase has a turnover number of 13,860 per second. To find how many times faster catalase is compared to phosphatase, we divide the turnover number of catalase by that of phosphatase:
\[ \text{Ratio} = \frac{40,000,000}{13,860} \approx 2884 \]
Thus, catalase is approximately 2884 times faster than phosphatase, making option (C) correct.
Which aspect of enzyme activity can be compared by the Michaelis-Menten constant?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The Michaelis-Menten constant (\(K_m\)) represents the substrate concentration at which an enzyme achieves half of its maximum reaction rate. A lower \(K_m\) indicates higher affinity between the enzyme and its substrate, as less substrate is needed to reach half of \(V_{max}\). Thus, \(K_m\) allows comparison of affinities of different enzymes for their substrates (Option B). It does not measure activation energy (A), changing affinities at different concentrations (C), or temperature effects on \(V_{max}\) (D).
The graph shows the effect of substrate concentration on the rates of reaction of three enzymes, X, Y, and Z.
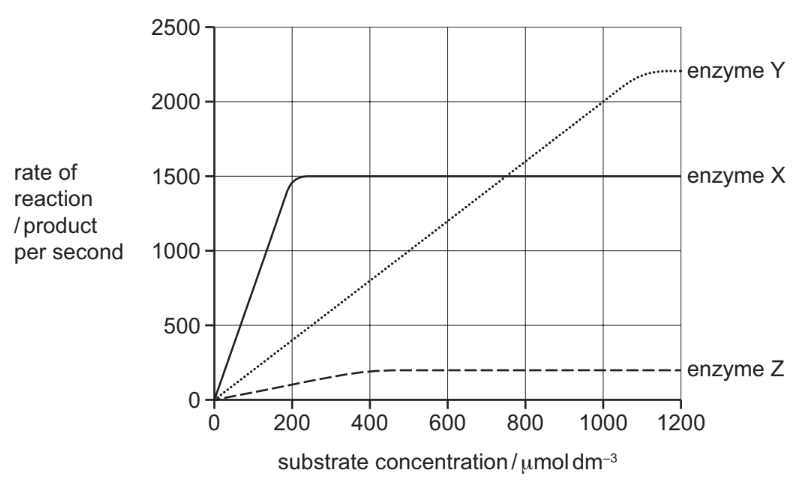
What is the correct order of affinity of these enzymes for their substrates, starting with the enzyme with the highest affinity?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The enzyme with the highest affinity for its substrate reaches maximum reaction rate (Vmax) at the lowest substrate concentration. From the graph, enzyme X saturates first, followed by Z, and then Y. Thus, the order of affinity is X → Z → Y, making option B correct.
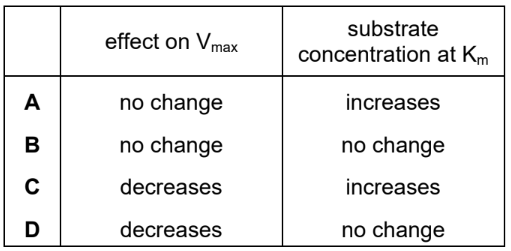
Which row describes the expected effect on Vmax and Km when a competitive reversible inhibitor is added to an enzyme-catalysed reaction?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
A competitive inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active site of the enzyme, increasing the apparent \( K_m \) (substrate concentration needed for half-maximal activity) because more substrate is required to outcompete the inhibitor. However, \( V_{max} \) remains unchanged since, at high substrate concentrations, the inhibitor can be fully outcompeted, allowing the enzyme to reach its maximum reaction rate.
