Question [Maximum marks: 11]
Penicillin is an antibiotic that interferes with the synthesis of cell walls in bacteria. Even before
penicillin became widely available in the 1940s, the enzyme penicillinase which breaks down
penicillin had been isolated. This enzyme is now found in many bacteria and gives them
resistance to penicillin.
Fig. 4.1 is a ribbon model of the structure of the enzyme penicillinase. The arrow indicates
the active site of the enzyme.
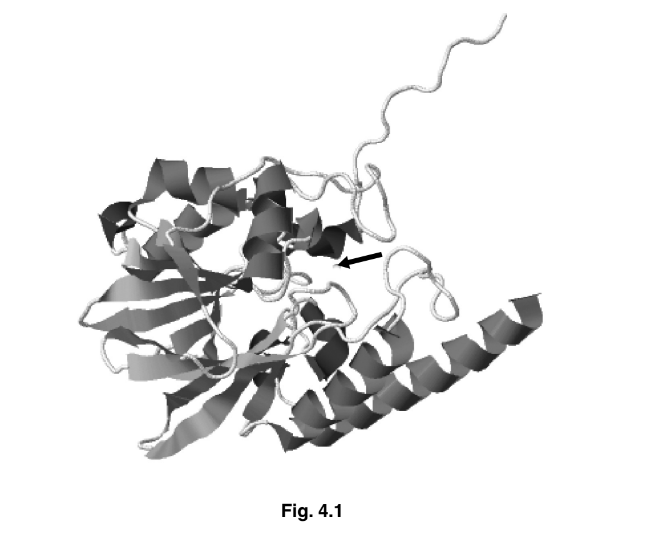
(a) Explain why the shape of the active site of an enzyme, such as penicillinase, is important.
(b) With reference to Fig. 4.1, identify the aspects of protein structure that are shown and
those that are not shown.
Fig. 4.2 shows the changes in energy during the progress of an uncatalysed reaction.
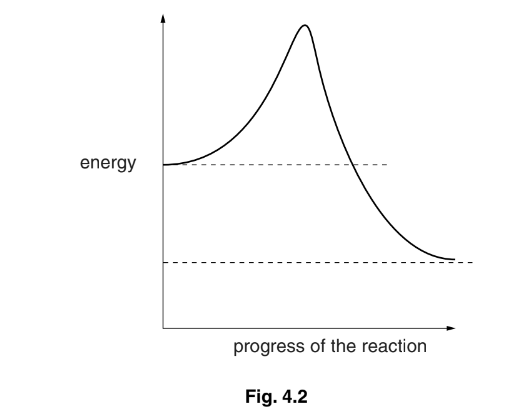
(c) (i) Draw on Fig. 4.2 a curve to show changes in energy during the progress of the
same reaction when catalysed by an enzyme.
(ii) State the term given to the energy level that must be overcome before a reaction can progress.
(d) Antibiotic resistance is a serious worldwide problem.
Suggest how antibiotics can be used effectively to avoid the development of widespread
resistance in bacteria.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: 4(a) this can be answered in the context of penicillinase
1 complementary shape ;
2 substrate, fits into / enters / binds to / with, active site ;
A enzyme-substrate complex / ESC
3 ref. to specificity ;
4 lock and key / induced fit ; A description of induced fit
5 ref. to temporary bonds form with, active site / R groups (of amino acid residues) ; [max 3]
4(b) shown to max 2
secondary structure ;
α / alpha, helix ; R ‘helix’ / helical structure unqualified by alpha
β pleated sheet ;
tertiary structure / folding ; ignore 3D shape or structure
globular ;
not shown to max 2
amino acids / primary structure / sequence of amino acids ;
(types of) R groups ;
bonds / named bonds ; A peptide
quaternary structure ;
prosthetic group ; [max 3]
4(c) (i) one lower peak inside line than uncatalysed ;
start and finish at, dotted lines / same energy levels as uncatalysed ;
(ii) activation (energy) / (energy of) activation ;
4(d) 1 do not prescribe for viral diseases ;
2 only use when necessary / do not overprescribe ;
3 only available on prescription / not available ‘over the counter’ ;
4 people must, complete the course / take as instructed ;
R take a long course
5 test to find out which is most appropriate antibiotic to use ;
A use most, appropriate / effective, antibiotics
A use narrow-spectrum antibiotics
6 details of sensitivity test ;
7 rotate / AW, antibiotics / use in combination ; R use many antibiotics
8 do not use same antibiotics for humans and animals ; [max 2]
