During transcription, base pairing occurs between nucleotides.
Fig. 3.1 is a diagram to show complementary base pairing between a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide.
Only the base pair is shown in molecular detail.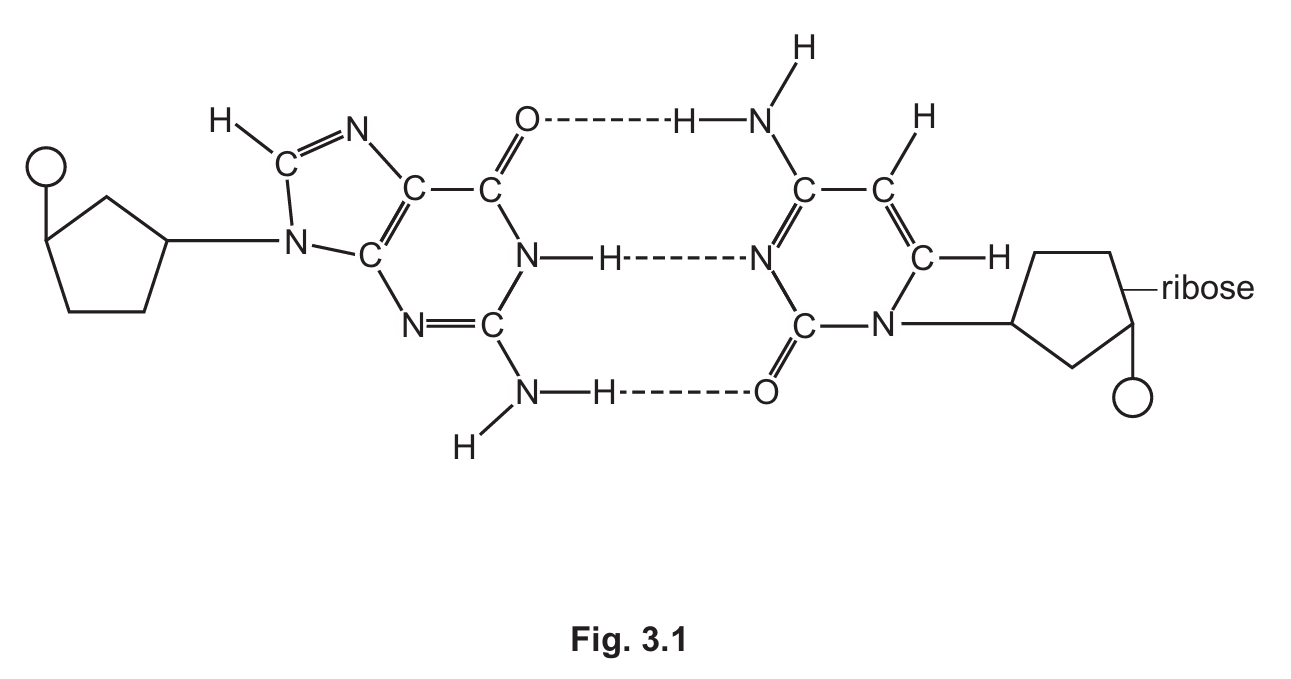
(a) Explain why Fig. 3.1 does not include any phosphodiester bonds.
(b) Identify and describe the DNA-RNA nucleotide pair shown in Fig. 3.1.
You may add labels and annotations to Fig. 3.1 if you wish.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Answer: Because phosphodiester bonds form between nucleotides on the same strand during polynucleotide formation.
Detailed Explanation: The diagram shows only a single base pair interaction between a DNA nucleotide and an RNA nucleotide. Phosphodiester bonds are the covalent bonds that connect adjacent nucleotides within the same nucleic acid strand, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone. Since this diagram focuses solely on the hydrogen bonding between complementary bases from different strands (DNA template and growing RNA strand), it doesn’t show the phosphodiester bonds that would be present in the polynucleotide chains themselves. These bonds would be visible if the diagram showed multiple nucleotides linked together in each strand.
(b)
Answer: The base pair shown is guanine (G) on the DNA strand pairing with cytosine (C) on the RNA strand.
Detailed Explanation: The DNA nucleotide (left side) contains guanine (G), which is a purine base with a double-ring structure. The RNA nucleotide (right side) contains cytosine (C), which is a pyrimidine with a single-ring structure. They form three hydrogen bonds between them, as indicated by the dotted lines in the diagram. The DNA nucleotide has deoxyribose sugar (missing the 2′-OH group), while the RNA nucleotide has ribose sugar. The circle represents the phosphate group that would connect to other nucleotides in the chain. This G-C pairing is crucial during transcription when RNA polymerase builds an RNA strand complementary to the DNA template strand.
Additional points that could be annotated on the diagram:
- Label the pentose sugars as deoxyribose (DNA) and ribose (RNA)
- Mark the hydrogen bonds between the bases
- Identify the phosphate groups
- Note the 5′ and 3′ ends (though not fully shown in this snippet)
- Label the nitrogenous bases as purine (G) and pyrimidine (C)
