Question
Which statement describes a process that occurs during protein synthesis?
A Transcription is the linking together of a tRNA molecule and a specific amino acid.
B Transcription is the linking together of free DNA nucleotides.
C Translation is the linking together of amino acids coded for by mRNA.
D Translation is the synthesis of an mRNA molecule by base pairing of nucleotides with DNA.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Option C: Translation is the linking together of amino acids coded for by mRNA is the statement that describes a process that occurs during protein synthesis.
During translation, the mRNA molecule is read by ribosomes, which use the genetic code to synthesize a specific sequence of amino acids, which are assembled into a polypeptide chain.
Transcription, on the other hand, is the process by which an RNA molecule is synthesized from a DNA template. During transcription, RNA polymerase reads the DNA template and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule by base-pairing free RNA nucleotides with the DNA template.
Option A is incorrect because it describes the process of aminoacylation, which is the linking together of a tRNA molecule and a specific amino acid.
Option B is incorrect because it describes the process of DNA replication, which is the synthesis of a new DNA molecule from an existing DNA template.
Option D is incorrect because it describes the process of transcription, not translation.
Question
The table gives tRNA anticodons for four amino acids.
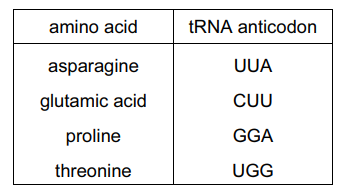
A cell makes a polypeptide with the amino acid sequence:
glutamic acid – asparagine – threonine – proline
What was the sequence of bases on the strand of the DNA which was complementary to the mRNA from which this polypeptide was formed?
- CTTTTATGGGGA
- CUUUUAUGGGGA
- GAAAATACCCCT
- GAAAAUACCCCU
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
Part of the amino acid sequences in normal and sickle cell haemoglobin are shown.
normal haemoglobin sickle cell haemoglobin
thr-pro-glu-glu thr-pro-val-glu
Possible mRNA codons for these amino acids are shown below.
glutamine (glu) GAA GAG proline (pro) CCU CCC
threonine (thr) ACU ACC valine (val) GUA GUG
Which tRNA molecule is not involved in the formation of this part of the sickle cell haemoglobin?
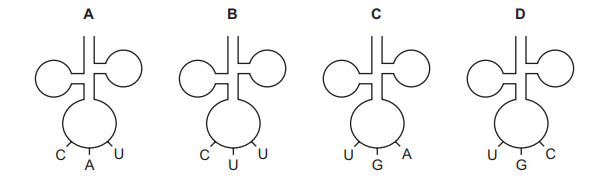
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
The mRNA codon for valine is GUA in sickle cell haemoglobin, whereas it is GAA in normal haemoglobin. This means that the tRNA-Val molecule with the anticodon GUA is required to deliver valine to the ribosome during translation of the sickle cell haemoglobin mRNA. In contrast, the tRNA-Val molecule with the anticodon GAA is required to deliver valine to the ribosome during translation of the normal haemoglobin mRNA. Therefore, tRNA-Val (GUA, GUG) is not involved in the formation of the sickle cell haemoglobin sequence, and option D is the correct answer.
Question
Some antibiotics work by binding to ribosomes and preventing protein synthesis.
Which statement explains why these antibiotics kill bacterial cells but not human cells?
1. In bacterial cells mRNA is formed in the cytoplasm from naked DNA.
2. Ribosomes in human cells have a different structure from those in bacterial cells.
3. The antibiotics cannot pass through human cell surface membranes.
4. The tRNA molecules in bacterial cells are different from those in human cells.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
The correct answer is B. Ribosomes in human cells have a different structure from those in bacterial cells.
Antibiotics that work by binding to ribosomes and preventing protein synthesis are called bacteriostatic antibiotics. These antibiotics target the bacterial ribosome and interfere with the translation of bacterial mRNA into proteins. Since bacterial ribosomes have a different structure from eukaryotic ribosomes, bacteriostatic antibiotics do not affect protein synthesis in human cells.
Option A is incorrect because mRNA is formed in the cytoplasm in both bacterial and human cells. In bacterial cells, mRNA is transcribed from DNA in the cytoplasm by RNA polymerase, while in human cells, mRNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and then transported to the cytoplasm.
Option C is incorrect because many bacteriostatic antibiotics can pass through human cell membranes, but they do not affect human cells because they do not bind to human ribosomes.
Option D is incorrect because tRNA molecules in bacterial cells and human cells have the same function and structure, and they are both involved in protein synthesis. The difference in ribosome structure is what makes bacteriostatic antibiotics selective for bacterial cells.
Question
Which statements about tRNA are correct?
- contains base pairing
- contains hydrogen bonds
- is single stranded
A 1, 2 and 3 B 1 and 2 only C 1 and 3 only D 2 and 3 only
▶️Answer/Explanation
>Ans:
A
The correct answer is A. 1, 2 and 3.
tRNA (transfer RNA) is a type of RNA molecule that carries specific amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. The following statements about tRNA are correct:
1. Contains base pairing: tRNA is a single-stranded RNA molecule that folds into a cloverleaf shape due to complementary base pairing between different regions of the molecule. These base pairing interactions help to stabilize the tRNA structure.
2. Contains hydrogen bonds: tRNA contains hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs, which help to stabilize the tRNA structure.
3. Is single-stranded: tRNA is a single-stranded RNA molecule that folds into a specific three-dimensional structure due to the complementary base pairing between different regions of the molecule.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer.
