The diagram shows a section through a root of a dicotyledonous plant.
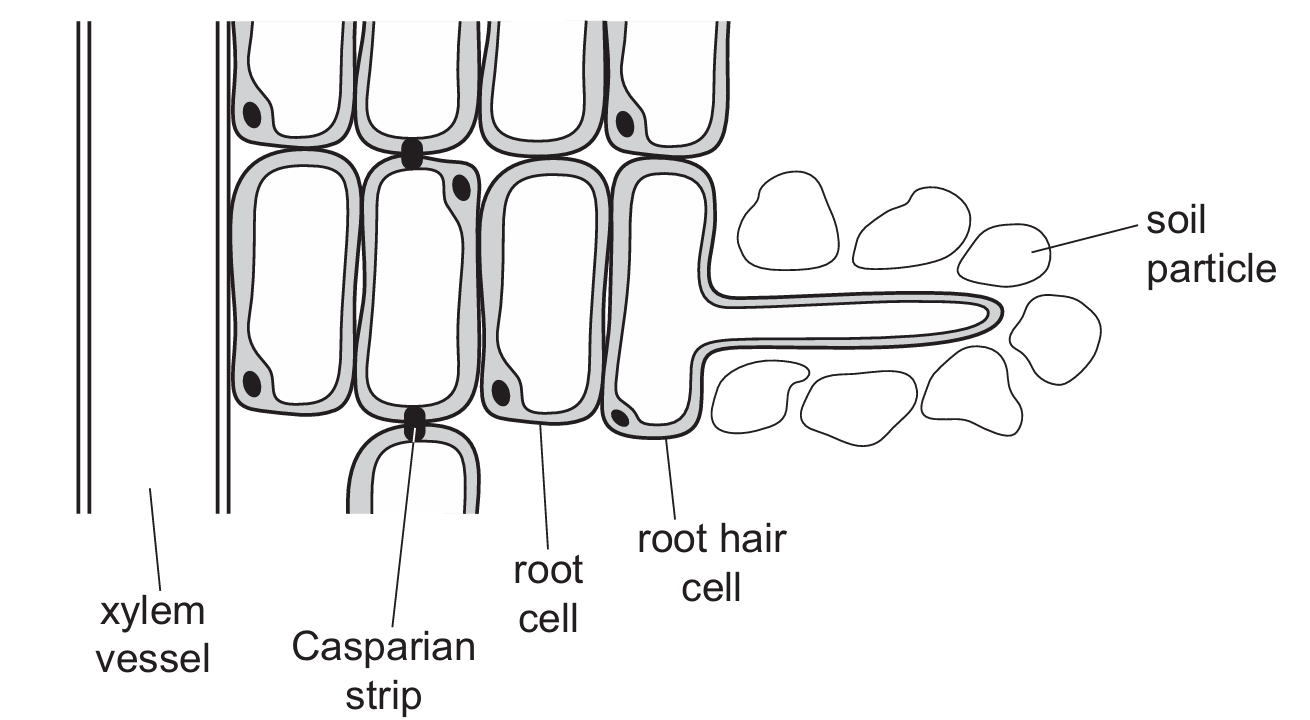
Which statement correctly describes the movement of water and solutes through this root?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The Casparian strip, made of suberin, blocks the apoplast pathway in the endodermis, forcing water and solutes into the symplast pathway for selective uptake. This control point prevents unwanted substances from entering the xylem directly.
Four students have drawn and labelled part of a structure seen on an electron micrograph.
Which student has labelled their drawing correctly?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The structure described is a phloem sieve tube element, which contains mitochondria (for energy), sieve plates (for connection between cells), and thin cytoplasm (as most organelles degenerate). Nucleus (C) and chloroplasts (D) are absent in mature sieve tube elements.
Which types of molecules are cotransported into companion cells?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Companion cells cotransport monomers (e.g., amino acids) and disaccharides (e.g., sucrose) using proton gradients. Polymers (B/C/D) are too large for cotransport and must be broken down first. Sucrose (a disaccharide) is the main transported sugar in phloem.
The diagram shows a phloem sieve tube element and a companion cell that are involved in translocation of sucrose.
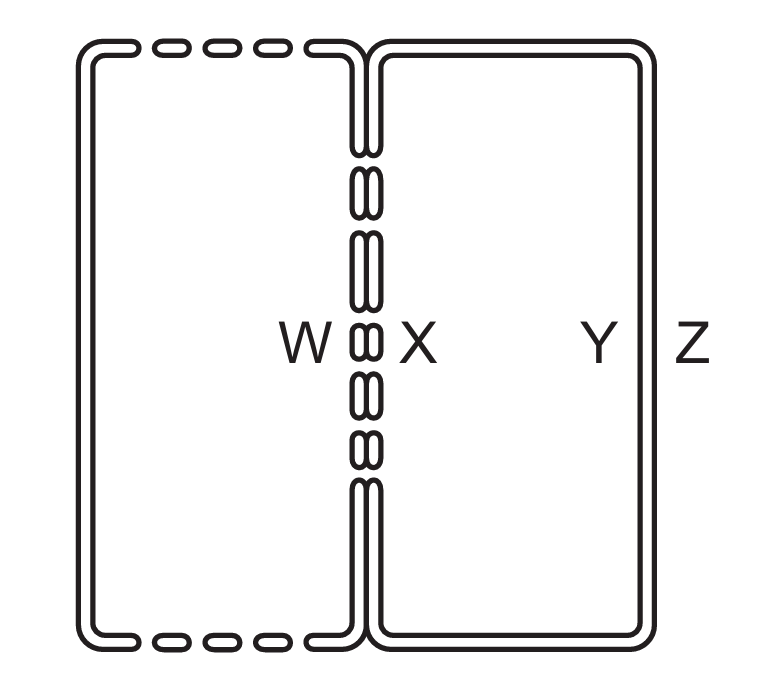
Which process correctly describes the translocation of sucrose through these cells?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Protons (H⁺) are actively pumped from the companion cell (Y) into the sieve tube (Z) using ATP. This creates a proton gradient that drives sucrose uptake via cotransport. Thus, B is correct as it describes the initial step in the mass flow hypothesis.
