Question
Lignin and suberin are polymers that are present in plant tissues.
(a) Describe and explain the roles of lignin and suberin in the transport of water through the roots and stem of a plant.
(b) The enzyme laccase catalyses the formation of lignin in plants. Fig. 4.1 is a diagram of the mode of action of laccase.
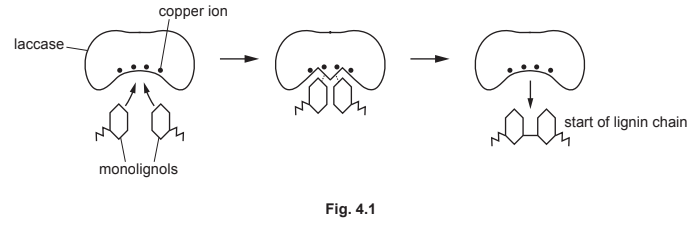
Describe and explain the mode of action of laccase when catalysing the formation of lignin.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution
(a)
Suberin:
- Forms a hydrophobic barrier in the Casparian strip of endodermal cells
- Forces water to switch from apoplast to symplast pathway, enabling selective mineral absorption
- Prevents backflow of water and toxins into root cortex
Lignin:
- Reinforces xylem vessel walls through secondary thickening
- Prevents collapse under tension during transpiration
- Creates waterproof conduits for efficient water transport
Explanation: Suberin regulates water entry into the vascular cylinder, while lignin maintains xylem structural integrity under negative pressure.
(b)
- Laccase uses induced fit – its active site conformationally changes to bind monolignol substrates
- Forms enzyme-substrate complexes with phenolic compounds (monolignols)
- Oxidizes monolignols via copper ion cofactors, enabling radical coupling
- Lowers activation energy for polymerization into lignin’s complex 3D structure
- Regenerates after releasing the lignin polymer
Explanation: The diagram shows laccase’s catalytic cycle where it facilitates oxidative coupling of monolignol precursors into the heterogeneous lignin polymer.
