Question
How does smoking increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis?
- by damaging artery walls
- by decreasing blood pressure
- by increasing the risk of blood clotting
- by reducing the oxygen supply to cardiac muscle
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Option A is the correct answer.
Smoking increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis by damaging artery walls. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the inner lining of arteries, called the endothelium. This damage can cause the endothelium to become inflamed and to release chemicals that attract white blood cells to the site of the damage. These white blood cells can then stick to the endothelium and begin to accumulate, forming a fatty deposit called a plaque. Plaques can narrow the arteries and reduce blood flow, leading to atherosclerosis. Smoking can also increase the risk of blood clotting, which can further narrow the arteries and increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Question
Which statements about arteries are correct?
- Artery walls can resist high pressure.
- Arteries pump blood out of the heart.
- Blood in arteries has the same flow rate as in veins.
- The pulse in arteries is the result of a surge in blood that causes expansion of the artery wall.
- There are semilunar valves at the junction of arteries with the heart.
A 1, 2, and 4 B 1, 3 and 5 C 1, 4 and 5 D 2, 3 and 4
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Option C is the correct answer because the following statements about arteries are correct:
1) Artery walls can resist high pressure. Arteries have thick, muscular walls that can resist high pressure and maintain the blood flow.
4) The pulse in arteries is the result of a surge in blood that causes expansion of the artery wall. Arteries have a pulse that is the result of a surge in blood that causes expansion of the artery wall.
5) There are semilunar valves at the junction of arteries with the heart. This statement is incorrect, so option C cannot be the correct answer.
Question
The photomicrograph shows a section through two structures found in mammals viewed using a light microscope.
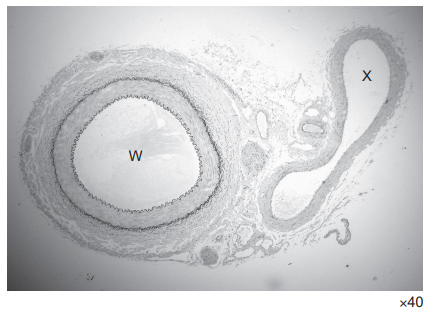
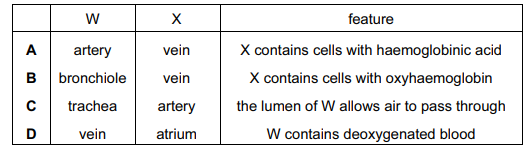
Which row is correct?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
W in the given photomicrograph shows a section through mammalian artery viewed using a light microscope and X represents veins.
Arteries have thick walls because they need to withstand high pressure generated by the heart.
Veins are blood vessels that carry blood low in oxygen from the body back to the heart for reoxygenation. They are thin-walled as the blood that flows through veins is under low pressure. Veins carry cells with haemoglobinic acid.
Question
Which row is correct for the pulmonary vein?
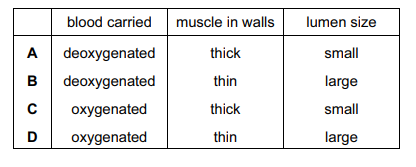
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Pulmonary veins are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from your lungs to your heart. Your pulmonary veins are part of your body’s pulmonary circuit. This is a system of blood vessels that moves blood between your heart and your lungs.
Question
Which features enable the aorta to withstand ventricular systole?
- collagen fibres and elastin fibres
- collagen fibres and smooth muscle
- elastin fibres and endothelium
- endothelium and smooth muscle
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
The atrioventricular (AV) valves prevent backflow of blood into the atria during ventricular contraction (systole), and the aortic/pulmonary (semilunar) valves prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles during ventricular relaxation (diastole).
Elastic arteries are those nearest the heart (aorta and pulmonary arteries) that contain much more elastic tissue in the tunica media than muscular arteries. This feature of the elastic arteries allows them to maintain a relatively constant pressure gradient despite the constant pumping action of the heart.
collagen fibres and elastin fibres enable the aorta to withstand ventricular systole.
Thus, the correct option is A.
