Question
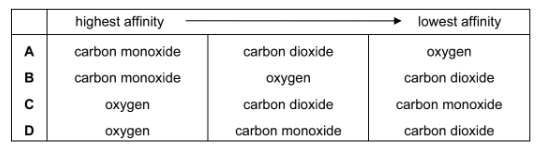
Which is correct about the affinity between haemoglobin and the gases carbon dioxide, carbon
monoxide and oxygen?
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Haemoglobin has a higher affinity for carbon monoxide than it does for oxygen. This is because carbon monoxide binds to haemoglobin with a higher affinity than oxygen, forming a stable complex that is difficult to break. This can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, as the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is reduced. Haemoglobin has a lower affinity for carbon dioxide than it does for oxygen, which allows for the efficient unloading of carbon dioxide from the blood in the lungs.
Question
What would be seen in an electron micrograph of a bronchus wall?
1 cartilage cells
2 ciliated cells
3 exocytotic vesicles
A 1 and 2 only
B 1 and 3 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 1, 2 and 3
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
The correct, option D is the correct answer. An electron micrograph of a bronchus wall would show cartilage cells, ciliated cells, and exocytotic vesicles. The cartilage cells provide structural support to the bronchus, while the ciliated cells have hair-like projections that help to move mucus and trapped particles out of the airway. Exocytotic vesicles are involved in the secretion of mucus by the goblet cells in the bronchus wall. Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Question
Which statement about chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is not correct?
- The disease can often be reversed by treatment.
- The patient coughs a lot, bringing up mucus.
- The patients are normally over 30 years old.
- The patient’s symptoms normally do not change.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
The correct, option D is the correct answer. The statement that is not correct is “The patient’s symptoms normally do not change.” The symptoms of COPD can worsen over time, and the disease can lead to significant disability and reduced life expectancy. While treatment can help to manage symptoms and improve quality of life, the disease itself cannot be fully reversed. Patients with COPD often cough frequently and produce excessive amounts of mucus, which can lead to shortness of breath and other respiratory symptoms. COPD is most commonly seen in patients over the age of 40, although it can occur in younger patients as well. Therefore, option D is the correct answer. I apologize for any confusion my previous response may have caused.
Question
What correctly describes the effect of carcinogens on lung tissue?
- Cells of the alveoli walls divide more rapidly than normal by reduction division causing a tumour to develop.
- Cilia are paralysed and mucus accumulates in the lungs, causing DNA to change and a tumour to develop.
- DNA changes, causing bronchial epithelial cells to divide by mitosis in an uncontrolled way, causing a tumour to develop.
- Haemoglobin carries less oxygen, causing bronchial cells to divide by mitosis in an uncontrolled way, causing a tumour to develop.
▶️Answer/Explanation
The correct answer is C, “DNA changes, causing bronchial epithelial cells to divide by mitosis in an uncontrolled way, causing a tumor to develop.”
Carcinogens are substances that can cause cancer by damaging DNA in cells. When carcinogens come in contact with lung tissue, they can cause damage to the DNA of the bronchial epithelial cells. This damage can cause the cells to divide uncontrollably, leading to the development of a tumor. The uncontrollable cell division can lead to the formation of a mass of cells that can invade and destroy nearby tissue. Cilia are not typically affected by carcinogens, so option B is incorrect. Option A is incorrect because the alveoli walls do not normally divide by reduction division. Option D is incorrect because haemoglobin is not involved in the development of lung cancer.
Question
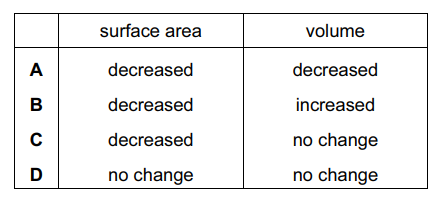
A disease damages alveoli walls.
What effect does this have on the gas exchange surface area and on the volume of the lungs?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
If a disease damages the alveoli walls, it can significantly reduce the gas exchange surface area of the lungs, which can lead to a decrease in the amount of oxygen that is absorbed into the bloodstream and an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide that is retained in the body. This can lead to shortness of breath, fatigue, and other respiratory symptoms. The volume of the lungs may not necessarily change, but the ability of the lungs to function properly can be severely impaired.
