CIE AS/A Level Biology -19.3 Genetically modified organisms in agriculture- Study Notes- New Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Biology -19.3 Genetically modified organisms in agriculture- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Ace A level Biology Exam with CIE AS/A Level Biology -19.3 Genetically modified organisms in agriculture- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Key Concepts:
- explain that genetic engineering may help to solve the global demand for food by improving the quality and productivity of farmed animals and crop plants, using the examples of GM salmon, herbicide resistance in soybean and insect resistance in cotton
- discuss the ethical and social implications of using genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in food production
Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
🌱 Introduction
- Genetic engineering can enhance food production and quality to meet global demand.
- It allows scientists to modify animals and plants for desirable traits, improving yield, efficiency, and resilience.
🔬 Examples and Benefits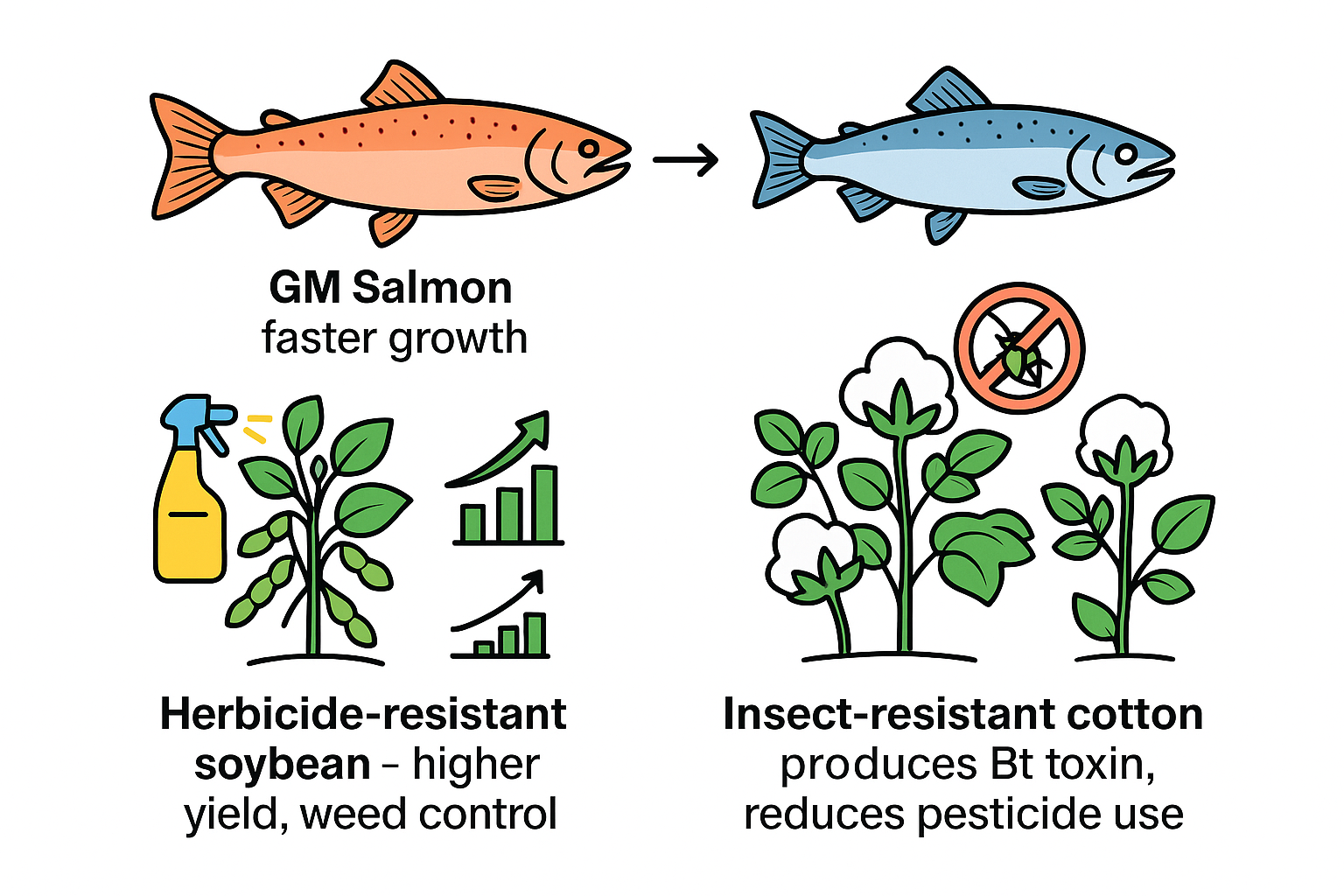
- GM Salmon
- Engineered to grow faster than wild-type salmon.
- Benefit: Shortens production time, increases fish supply, and reduces pressure on wild fish stocks.
- Herbicide-Resistant Soybean
- Modified to tolerate specific herbicides.
- Benefit: Farmers can control weeds without harming the crop, leading to higher yields and reduced labor costs.
- Insect-Resistant Cotton
- Engineered to produce Bt toxin, which kills specific insect pests.
- Benefit: Reduces the need for chemical insecticides, lowers crop loss, and protects the environment.
🧠 Key Takeaways
Genetic engineering improves productivity, quality, and sustainability in agriculture.
GM crops and animals help meet global food demands while reducing environmental impact.
Careful management is needed to address ecological, ethical, and market concerns.
Genetic engineering improves productivity, quality, and sustainability in agriculture.
GM crops and animals help meet global food demands while reducing environmental impact.
Careful management is needed to address ecological, ethical, and market concerns.
Ethical and Social Implications of GMOs in Food Production
🌱 Introduction
- Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are widely used in agriculture to improve crop yield, quality, and resistance to pests or herbicides.
- However, their use raises important ethical and social considerations that must be addressed.
🔬 Ethical Considerations
- Human Health
- Concerns exist about potential long-term health effects of consuming GM foods.
- Ethical responsibility requires thorough testing and regulation to ensure safety.
- Environmental Impact
- GM crops may affect non-target species or lead to loss of biodiversity.
- Ethical questions arise about human intervention in natural ecosystems.
- Animal Welfare
- GM animals (e.g., fast-growing salmon) may experience health or welfare issues due to genetic modifications.
- Ownership and Patents
- Many GM seeds are patented by corporations, raising ethical concerns about control over food supply and farmers’ rights.
🔬 Social Considerations
- Public Acceptance and Perception
- Consumers may be hesitant to eat GM foods due to perceived risks or ethical concerns.
- Transparency and labeling are important for consumer choice.
- Economic Impact
- GMOs can increase crop productivity, but small farmers may struggle with seed costs or dependency on corporations.
- Global Food Security vs Equity
- GMOs can help meet global food demand, but unequal access may increase disparities between wealthy and poorer regions.
🧠 Key Takeaways
GMOs offer significant benefits for food production, but must be managed responsibly.
Ethical and social issues include health, environment, animal welfare, ownership, and equity.
Transparency, regulation, and fair access are critical for balancing benefits with societal concerns.
GMOs offer significant benefits for food production, but must be managed responsibly.
Ethical and social issues include health, environment, animal welfare, ownership, and equity.
Transparency, regulation, and fair access are critical for balancing benefits with societal concerns.
