CIE AS & A Level Biology Papers 1 prediction - 2025
CIE AS & A Level Biology Papers 1 prediction- 2025
To excel in A level Biology Exam, consistent practice with CIE AS & A Level Revision resources is key. CIE AS & A Level Biology Papers 1 predictions will guide you for exam pattern.
IITian Academy offers a vast collection of questions that can aid your understanding of specific topics and solidify your concepts. By practicing regularly and focusing on these key areas, you’ll be well-prepared for the A level Biology exam
Question 1
The magnification of the photomicrograph is ×4000.
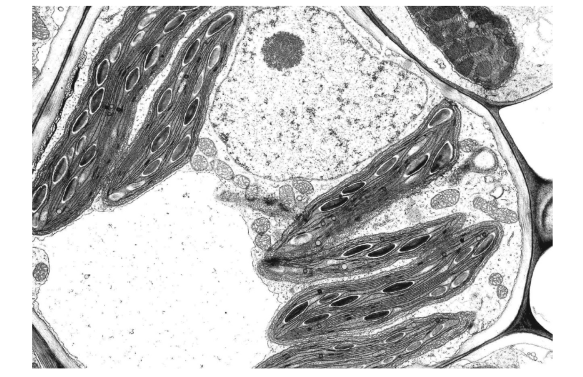
What is the actual size of the nucleolus?
A 1μm B 2μm C 5μm D 20μm
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question 2
Pancreatic cells have a diameter of 35µm.
Red blood cells have a diameter of 7000nm.
Which statement is correct?
- Pancreatic cells are 5 times larger than red blood cells.
- Pancreatic cells are 50 times larger than red blood cells.
- Pancreatic cells are 5 times smaller than red blood cells.
- Pancreatic cells are 50 times smaller than red blood cells.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question 3
What are always present in prokaryote cells?
A capsules
B flagella
C pili
D ribosomes
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question 4
Which is correct about the affinity between haemoglobin and the gases carbon dioxide, carbon
monoxide and oxygen?
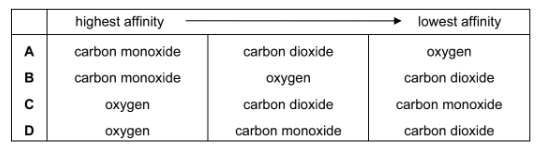
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question 5
Which statements about arteries are correct?
- Artery walls can resist high pressure.
- Arteries pump blood out of the heart.
- Blood in arteries has the same flow rate as in veins.
- The pulse in arteries is the result of a surge in blood that causes expansion of the artery wall.
- There are semilunar valves at the junction of arteries with the heart.
A 1, 2, and 4 B 1, 3 and 5 C 1, 4 and 5 D 2, 3 and 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 6
During transpiration, from where does the evaporation of water occur?
A intercellular spaces
B leaf surface
C mesophyll cell walls
D stomatal pores
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question 7
Tests were performed on samples from a mixture of biological molecules.
When iodine in potassium iodide solution was added to a sample, the mixture turned black.
When the biuret test was carried out on another sample, the mixture turned purple.
Which biological molecules were in the mixture?
A amylase and starch
B cellulose and starch
C phospholipid and cellulose
D starch and phospholipid
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question 8
Each list, 1, 2 and 3, shows some substances found in animal tissues.
- glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, water.
- glycogen, antibodies, adenine, phospholipids.
- haemoglobin, carbon dioxide, mRNA, monosaccharides.
Which shows one or more substances that contain nitrogen atoms?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question 9
Which molecules have properties that are dependent on hydrogen bonds?
- cellulose
- glycogen
- haemoglobin
- water
A 1, 2 and 3 only B 1, 2 and 4 only C 1, 3 and 4 only D 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 10
What cannot occur as a result of a condensation reaction?
- breaking of a glycosidic bond
- formation of a disaccharide
- joining together two amino acids
- production of a molecule of water
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question 11
In order to estimate the quantity of glucose in a solution, equal volumes of a range of known concentrations were mixed with equal excess volumes of Benedict’s solution and placed in a thermostatically controlled water-bath at 90°C for the same length of time.
The unknown solution was then treated in the same way and the colours of the known and unknown solutions compared.
What is the independent variable in this procedure?
- concentration of glucose
- final colour of solutions
- temperature of water-bath
- volumes of glucose solutions
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question 12
What are always present in prokaryote cells?
A capsules
B flagella
C pili
D ribosomes
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question 13
Which statements about competitive inhibitors of enzyme action are correct?
- Increasing the concentration of the enzyme’s substrate will reduce their effect.
- They bind to an enzyme at its active site.
- They reduce the activation energy required for a reaction to take place.
- They reduce the maximum rate of reaction.
A 1 and 2 only B 1 and 3 only C 2 and 3 only D 2, 3 and 4 only
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question 14
A student carried out four tests for biological molecules on a solution. The observations are shown in the table.
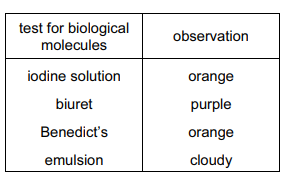
Which molecules may be present in this solution?
- glucose, starch, protein
- lipid, protein, glucose
- protein, starch, sucrose
- starch, protein, lipid
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question 15
Which type of cell has a large number of glycoproteins on the cell surface membrane?
- ciliated cell
- goblet cell
- lymphocyte
- red blood cell
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 16
The fluidity of the cell surface membrane can be changed by a number of factors.
As the fluidity of cell surface membranes decreases, which process would be least changed?
- active transport
- diffusion
- endocytosis
- osmosis
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question 17
Which process allows the movement of molecules that are too large to enter through a cell surface membrane?
- active transport
- endocytosis
- exocytosis
- facilitated diffusion
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question 18
Which descriptions are correct about transport across cell surface membranes?
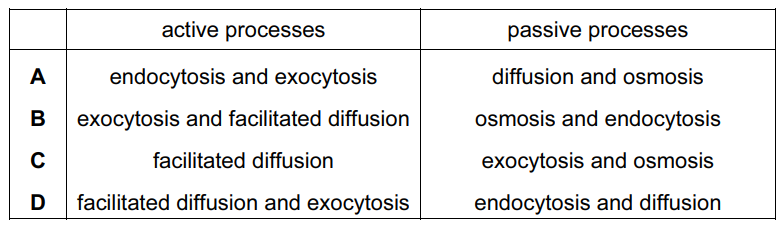
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question 19
The diagram represents a cell surface membrane of a metabolically active cell and the direction of movement of some molecules through the membrane.
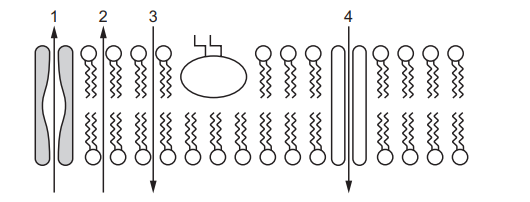
Which row shows a process by which the molecules may be moving through the membrane at each of the points 1, 2, 3 and 4?
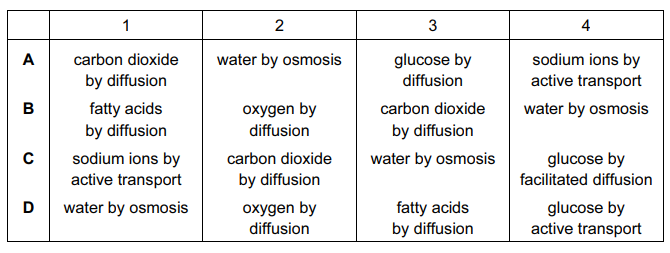
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 20
Which event is part of the mitotic cell cycle?
- anaphase
- cytokinesis
- DNA replication
- interphase
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question 21
Which feature of stem cells enables them to replace cells in tissues such as the skin?
- They are undifferentiated cells that are present at birth.
- They differentiate to form skin cells.
- They divide by mitosis to supply some cells that can differentiate.
- They have the full number of chromosomes.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 22
For organisms undergoing sexual reproduction, a reduction division occurs before fertilisation.
Which reasons explain why this is necessary?
1 increase genetic variation
2 prevent doubling of the chromosome number
3 reduce the chances of mutation
A 1 only
B 2 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 1, 2 and 3
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question 23
What does the enzyme DNA polymerase synthesise in a cell?
- a polypeptide using DNA as a template
- a strand of DNA using a polypeptide as a template
- a strand of DNA using DNA as a template
- a strand of mRNA using DNA as a template
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 24
Two sets of bacteria were grown using different types of nitrogen-containing growth media.
One set was grown in a medium containing the ‘heavy’ isotope of nitrogen, 15N, until all the DNA was labelled. The other set were grown in a medium containing the ‘light’ isotope of nitrogen, 14N, until all the DNA was labelled.
The DNA from each set of bacteria was extracted and centrifuged. The diagram shows the position in the centrifuge tubes of this DNA.
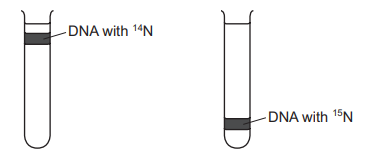
Bacteria with 15N labelled DNA were transferred to a medium containing 14N and allowed to reproduce once. The DNA of the new generation of bacteria was extracted and centrifuged.
Which tube shows the position of DNA from this new generation of bacteria?
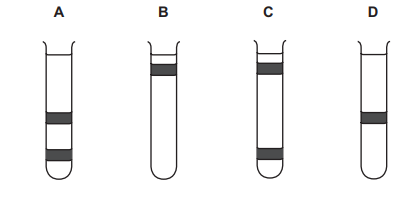
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question 25
DNA contains the ……X…… base ……Y…… which is joined to adenine with ……Z…… hydrogen bonds.
Which row correctly completes the statement about DNA?
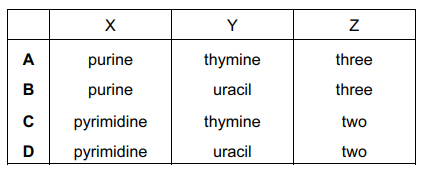
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 26
Two polynucleotide strands make up a DNA molecule.
What is a correct description?
- The percentage of cytosine is 50% of that of guanine in the whole molecule.
- The percentage of cytosine is the same as that of guanine in each strand.
- The percentage of cytosine is the same as that of guanine in the whole molecule.
- The percentage of cytosine is the same in each strand of the molecule.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 27
The graph shows the progress of a reaction in the presence and absence of an enzyme.
What is the activation energy of the reaction in the presence of the enzyme?

Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question 28
Halophytes are plants that can survive in regions where they are regularly exposed to sea water. Sea water has a water potential of approximately –2500kPa.
What adaptations would you expect halophytes to show?
- root hair cells that maintain a more negative water potential than sea water
- root hair cells that accumulate salts and other solutes
- stomata that are open most of the time
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question 29
Which description is correct for xylem vessel elements?
- cells joined to form a tube, pits at intervals, sieve plates between cells, surrounded by the endodermis in roots
- contains cells joined end to end, containing cytoplasm, cell walls with lignin, located to the outside of phloem in vascular bundles
- contains elongated cells with end walls broken down, located in vascular bundles in the stem and centrally in the roots
- dead elongated cells, lignified cell walls with pits at intervals, associated with companion cells in the roots only
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 30
Halophytes are plants that can survive in regions where they are regularly exposed to sea water. Sea water has a water potential of approximately –2500kPa.
What adaptations would you expect halophytes to show?
- root hair cells that maintain a more negative water potential than sea water
- root hair cells that accumulate salts and other solutes
- stomata that are open most of the time
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question 31
The diagram shows transverse sections of two plant structures.
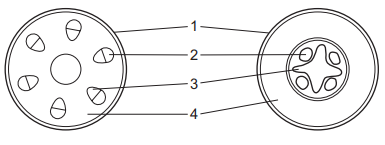
Which row shows the correct labels?
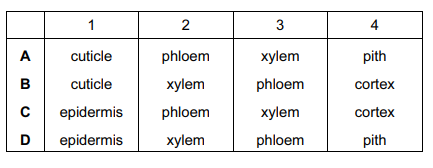
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 32
What correctly describes an event in the cardiac cycle that follows atrial systole?
- A wave of excitation passes through the sinoatrial node (SAN), before spreading down to the base of the septum.
- Electrical impulses pass from the muscles of the atria to the muscles of the ventricles to cause ventricular systole.
- Electrical impulses pass through conducting fibres, which cause a delay before spreading to Purkyne tissue.
- The opening and closing of the semilunar valves occurs later than the opening and closing of the atrioventricular valves.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 33
Which properties of water reduce temperature changes inside cells?
1 cohesion
2 latent heat of vaporisation
3 specific heat capacity
A 1 and 2 B 1 and 3 C 2 and 3 D 3 only
Answer/Explanation
Answer: D
Question 34
Which statements about arteries are correct?
- Artery walls can resist high pressure.
- Arteries pump blood out of the heart.
- Blood in arteries has the same flow rate as in veins.
- The pulse in arteries is the result of a surge in blood that causes expansion of the artery wall.
- There are semilunar valves at the junction of arteries with the heart.
A 1, 2, and 4 B 1, 3 and 5 C 1, 4 and 5 D 2, 3 and 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 35
Which statement helps to explain why there is no cartilage in the walls of the bronchioles?
A Cartilage would make the bronchioles too narrow.
B Gases must diffuse across the walls of the bronchioles.
C Smooth muscle is sufficient to support the walls of the bronchioles.
D The bronchiole walls do not need to change shape.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 36
Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). A person with emphysema has difficulties in breathing out.
Why does emphysema cause difficulties in breathing out?
A Smooth muscle fibres in the airways are destroyed.
B Too little mucus is produced in the bronchi.
C The elasticity of the alveoli decreases.
D The surface area of the alveoli becomes larger.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question 37
The heart rate of a person at rest was recorded at intervals over two 15-minute periods.
During the first five minutes of the second 15-minute period, the person smoked a cigarette.
The graph shows the results recorded during the two 15-minute periods.
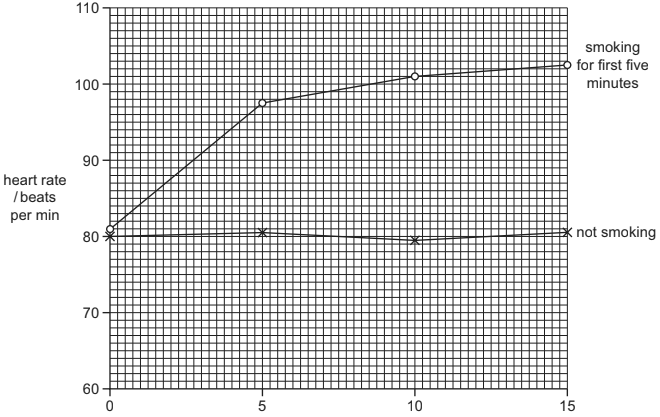
What can be concluded from the graph?
A Carbon monoxide affects the heart rate.
B Carbon monoxide binds to haemoglobin increasing the flow of blood.
C Nicotine increases the heart rate so is a stimulant.
D The heart rate increases as a result of smoking.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question 38
The diagram shows one way of testing the effect of an antibiotic on bacteria.
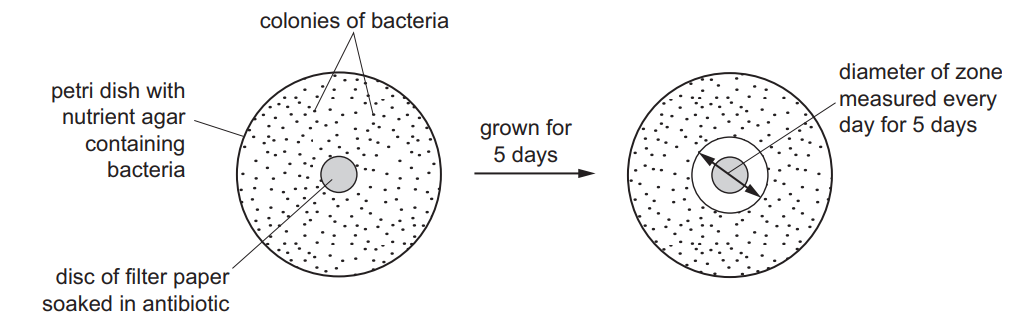
The table shows the results of testing five different types of bacteria. Zones of less than 13 mm show the presence of resistant bacteria.
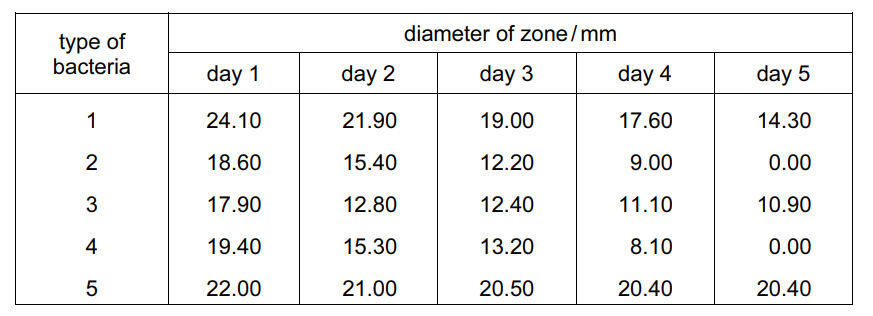
Which statement can be supported by this data?
- All the types of bacteria become resistant to antibiotics over time.
- Only types 2, 3 and 4 of the bacteria show resistance to the antibiotic.
- The antibiotic can be used to treat types 1 and 3 only.
- Type 5 of the bacteria can never become resistant to the antibiotic.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question 39
Which development in vaccine production would be most important in the fight to eradicate measles in developing countries?
- a combined vaccine to combat it and other diseases
- a single vaccine, without the need for boosters
- a vaccine containing only live measles viruses
- a vaccine produced by genetic engineering techniques
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question 40
A person’s blood group is determined by antigens present on the red blood cells.
The table shows the antigens and antibodies in the blood of people with different blood groups.

During a blood transfusion, it is essential that the recipient’s blood does not contain antibodies to the donor’s blood.
Which blood group can be given to a person with blood group AB?
- AB only
- O only
- B and A only
- A, B, AB and O
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
