CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 18.2 Esters Study Notes- 2025-2027 Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 18.2 Esters Study Notes – New Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 18.2 Esters Study Notes at IITian Academy focus on specific topic and type of questions asked in actual exam. Study Notes focus on AS/A Level Chemistry latest syllabus with Candidates should be able to:
recall the reaction (reagents and conditions) by which esters can be produced:
(a) the condensation reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid with concentrated H₂SO₄ as catalystdescribe the hydrolysis of esters by dilute acid and by dilute alkali and heat
Preparation of Esters
Esters are prepared at A level by a condensation reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
(a) Condensation Reaction between an Alcohol and a Carboxylic Acid
An ester is produced when an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, which acts as a catalyst.
Conditions: heat under reflux with concentrated \( \mathrm{H_2SO_4} \).
General equation: \( \mathrm{RCOOH + R’OH \rightleftharpoons RCOOR’ + H_2O} \)

This reaction is reversible and therefore does not go to completion.
Example
State the reagents and conditions needed to prepare ethyl ethanoate.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Ethyl ethanoate is prepared by reacting ethanol with ethanoic acid.
Concentrated sulfuric acid is used as a catalyst.
The mixture is heated under reflux.
Example
Explain the role of concentrated sulfuric acid in the preparation of an ester from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Concentrated sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst, increasing the rate of reaction.
It also acts as a dehydrating agent by removing water.
Removing water shifts the equilibrium towards ester formation.
Hydrolysis of Esters
Esters can be broken down by hydrolysis, in which water is used to break the ester linkage. At A level, ester hydrolysis is carried out under acidic or alkaline conditions with heating.
(a) Acidic Hydrolysis of Esters
When an ester is heated with dilute acid, such as dilute hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, it undergoes acidic hydrolysis to form a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
Conditions: heat under reflux with dilute acid.
General equation: \( \mathrm{RCOOR’ + H_2O \rightleftharpoons RCOOH + R’OH} \)
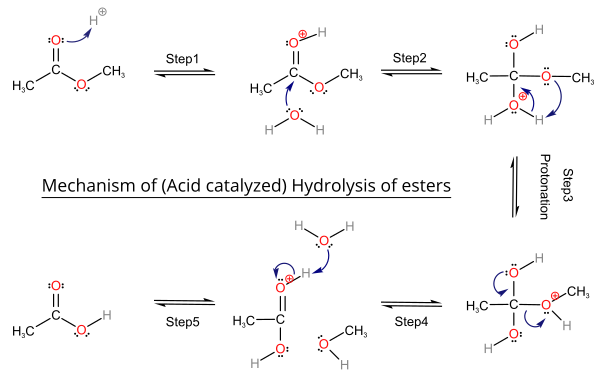
This reaction is reversible.
(b) Alkaline Hydrolysis of Esters
When an ester is heated with dilute alkali, such as sodium hydroxide, it undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to form a carboxylate salt and an alcohol.
Conditions: heat under reflux with dilute alkali.
General equation: \( \mathrm{RCOOR’ + NaOH \rightarrow RCOO^-Na^+ + R’OH} \)
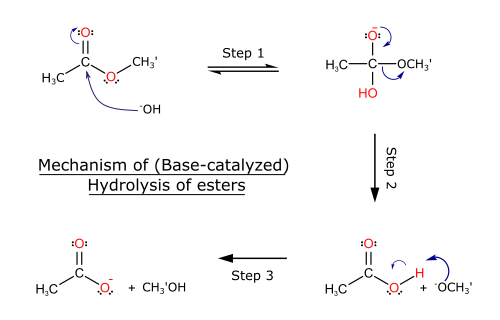
This reaction is irreversible. Acidification is required if a carboxylic acid is needed.
Example
Describe the products formed when ethyl ethanoate is heated under reflux with dilute hydrochloric acid.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Ethyl ethanoate undergoes acidic hydrolysis.
Ethanoic acid and ethanol are produced.
The reaction is reversible.
Example
Explain why alkaline hydrolysis of an ester must be followed by acidification to obtain a carboxylic acid.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Alkaline hydrolysis initially forms a carboxylate salt.
The carboxylate ion does not contain the –COOH functional group.
Acidification protonates the carboxylate ion to form the carboxylic acid.
