CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 19.2 Nitriles and hydroxynitriles Study Notes- 2025-2027 Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 19.2 Nitriles and hydroxynitriles Study Notes – New Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 19.2 Nitriles and hydroxynitriles Study Notes at IITian Academy focus on specific topic and type of questions asked in actual exam. Study Notes focus on AS/A Level Chemistry latest syllabus with Candidates should be able to:
recall the reactions by which nitriles can be produced:
(a) reaction of a halogenoalkane with KCN in ethanol and heatrecall the reactions by which hydroxynitriles can be produced:
(a) the reaction of aldehydes and ketones with HCN, KCN as catalyst, and heatdescribe the hydrolysis of nitriles with dilute acid or dilute alkali followed by acidification to produce
a carboxylic acid
Preparation of Nitriles
At AS Level, nitriles are prepared by a nucleophilic substitution reaction between a halogenoalkane and the cyanide ion.
(a) Reaction of a Halogenoalkane with Potassium Cyanide
A nitrile can be produced by reacting a halogenoalkane with potassium cyanide, \( \mathrm{KCN} \), dissolved in ethanol.
Conditions: heat under reflux with ethanolic potassium cyanide.
General equation: \( \mathrm{R\!-\!X + CN^- \rightarrow R\!-\!CN + X^-} \)

The reaction occurs by nucleophilic substitution, with the cyanide ion acting as the nucleophile.
This reaction increases the carbon chain length by one carbon atom.
Example
State the reagents and conditions needed to prepare propanenitrile from bromoethane.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Bromoethane is heated under reflux with potassium cyanide in ethanol.
The cyanide ion substitutes the bromine atom to form propanenitrile.
Example
Explain why ethanol is used as the solvent rather than water in the preparation of a nitrile from a halogenoalkane.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Ethanol dissolves both the halogenoalkane and potassium cyanide.
Using ethanol favours nucleophilic substitution rather than hydrolysis.
Water would promote the formation of alcohols instead of nitriles.
Preparation of Hydroxynitriles
Hydroxynitriles can be prepared at AS Level by the addition of hydrogen cyanide to aldehydes and ketones.
(a) Reaction of Aldehydes and Ketones with Hydrogen Cyanide
Aldehydes and ketones react with hydrogen cyanide, using potassium cyanide as a catalyst, to form hydroxynitriles.

Conditions: hydrogen cyanide, catalytic potassium cyanide, gentle heating.
General equation: \( \mathrm{RCHO + HCN \rightarrow RCH(OH)CN} \)
(for aldehydes)
General equation: \( \mathrm{RCOR’ + HCN \rightarrow RC(OH)(CN)R’} \)
(for ketones)
This reaction is a nucleophilic addition, with the cyanide ion acting as the nucleophile.
Example
State the reagents and conditions needed to prepare 2-hydroxypropanenitrile from propanone.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Propanone is reacted with hydrogen cyanide.
Potassium cyanide is used as a catalyst.
The mixture is gently heated.
Example
Explain the role of potassium cyanide in the reaction between an aldehyde and hydrogen cyanide.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Potassium cyanide provides cyanide ions.
The cyanide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon.
This initiates nucleophilic addition, allowing hydroxynitrile formation.
Hydrolysis of Nitriles
Nitriles can be converted into carboxylic acids by hydrolysis. This reaction can be carried out using either dilute acid or dilute alkali, followed by acidification if required.
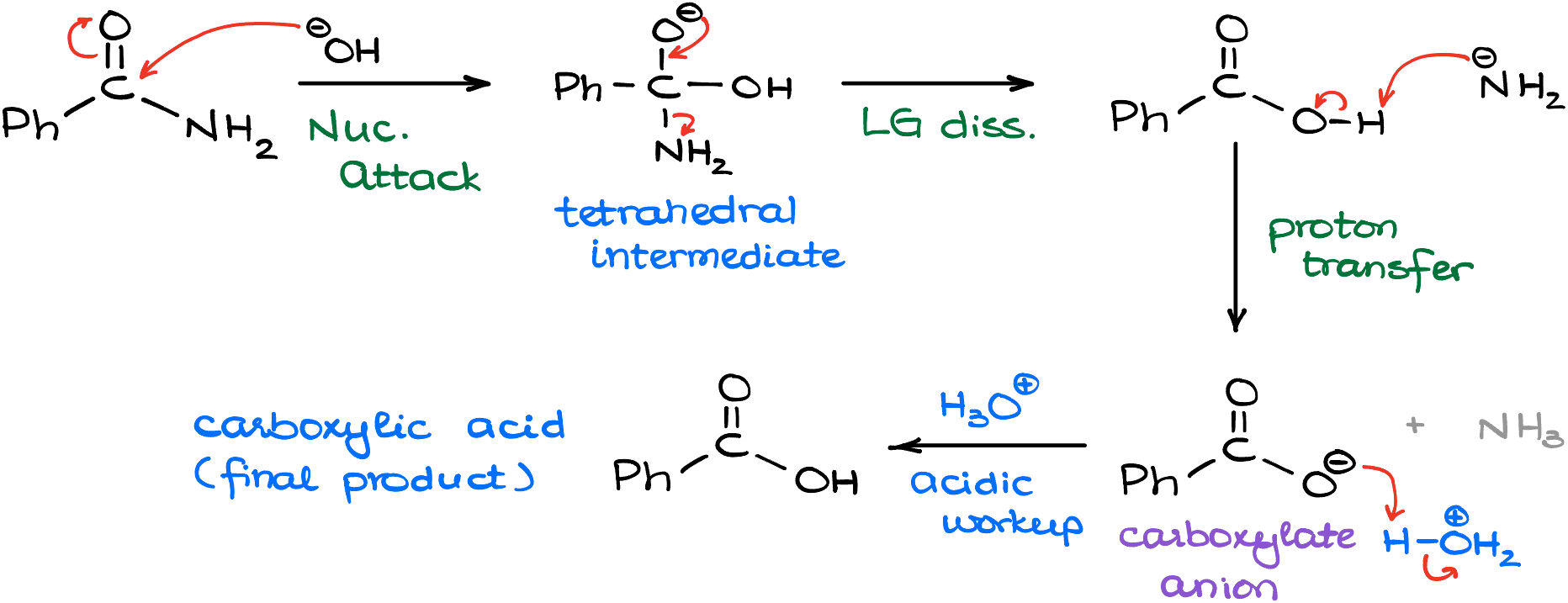
Hydrolysis with Dilute Acid
When a nitrile is heated with a dilute acid, such as dilute hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, it is hydrolysed to form a carboxylic acid.
Conditions: heat under reflux with dilute acid.
General equation: \( \mathrm{RCN + 2H_2O + H^+ \rightarrow RCOOH + NH_4^+} \)
Hydrolysis with Dilute Alkali
When a nitrile is heated with a dilute alkali, such as sodium hydroxide, it is hydrolysed to form a carboxylate salt and ammonia.
Conditions: heat under reflux with dilute alkali.
General equation: \( \mathrm{RCN + 2H_2O + OH^- \rightarrow RCOO^- + NH_3} \)
Acidification is required after alkaline hydrolysis to convert the carboxylate salt into the carboxylic acid.
Acidification: \( \mathrm{RCOO^- + H^+ \rightarrow RCOOH} \)
Example
Describe how propanoic acid can be prepared from propanenitrile.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Propanenitrile is heated under reflux with dilute acid or dilute alkali.
If dilute alkali is used, a carboxylate salt is formed.
The reaction mixture is then acidified to produce propanoic acid.
Example
Explain why acidification is not required after the hydrolysis of a nitrile with dilute acid.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Acidic hydrolysis produces the carboxylic acid directly.
The –COOH functional group is already present.
In alkaline hydrolysis, a carboxylate ion is formed instead, which is why acidification is only needed in that case.
