CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 2.1 Relative masses of atoms and molecules Study Notes- 2025-2027 Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 2.1 Relative masses of atoms and molecules Study Notes – New Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 2.1 Relative masses of atoms and molecules Study Notes at IITian Academy focus on specific topic and type of questions asked in actual exam. Study Notes focus on AS/A Level Chemistry latest syllabus with Candidates should be able to:
- define the unified atomic mass unit as one twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom
- define relative atomic mass, Ar , relative isotopic mass, relative molecular mass, Mr , and relative formula mass in terms of the unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u or amu)
The unified atomic mass unit is a standard unit used to express atomic and molecular masses. It is defined using the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
\( \text{1 unified atomic mass unit} = \dfrac{1}{12} \text{ of the mass of a } \mathrm{^{12}C} \text{ atom} \)
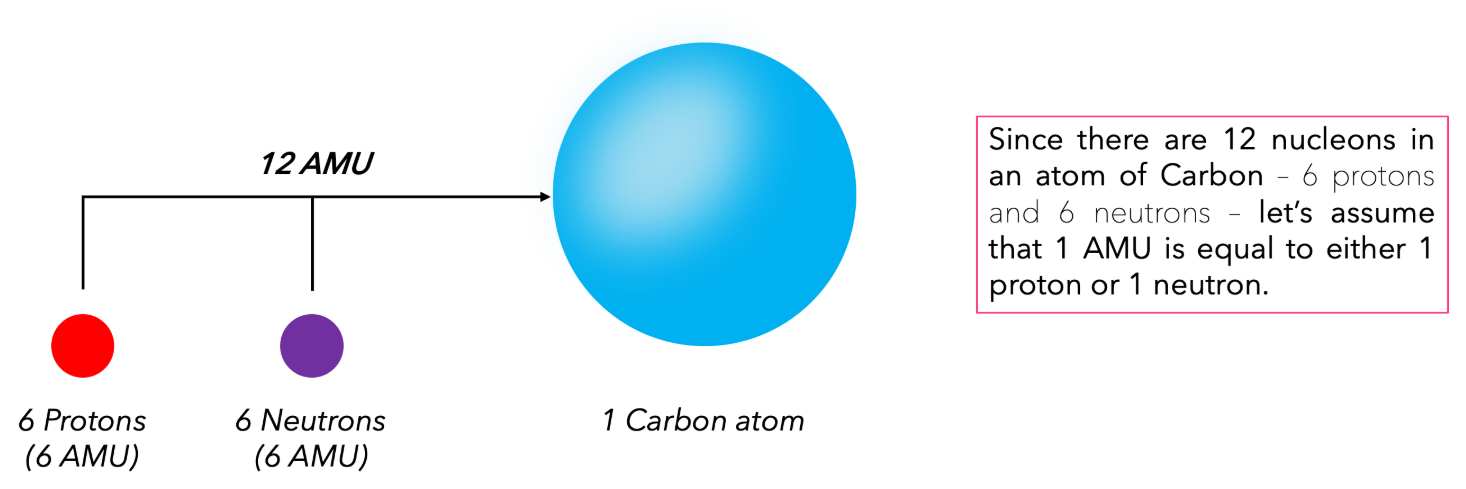
This definition ensures that carbon-12 has an exact atomic mass of 12 u.
Key Points
- Symbol: \( \mathrm{u} \) or \( \mathrm{amu} \).
- \( 1\,\mathrm{u} = \dfrac{1}{12} \) of the mass of one atom of \( \mathrm{^{12}C} \).
- Approximately \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \approx 1.66\times10^{-27}\,\mathrm{kg} \).
- Used to simplify atomic and molecular mass comparisons.
Example
State the definition of \( \mathrm{1\,u} \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( \mathrm{1\,u} \) is defined as \( \dfrac{1}{12} \) of the mass of one atom of \( \mathrm{^{12}C} \).
Example
If one carbon-12 atom has a mass of \( 1.9926\times10^{-26}\,\mathrm{kg} \), calculate the value of \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\[ 1\,\mathrm{u} = \dfrac{1}{12} \times 1.9926\times10^{-26}\,\mathrm{kg} \]
\[ 1\,\mathrm{u} = 1.6605\times10^{-27}\,\mathrm{kg} \]
This matches the accepted value.
Example
Nitrogen-14 has an atomic mass of \( 14.003\,\mathrm{u} \). Explain what this means in terms of the unified mass unit definition.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Since \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \) is defined as \( \dfrac{1}{12} \) of the mass of a \( \mathrm{^{12}C} \) atom, the mass of nitrogen-14 is:
\[ 14.003\,\mathrm{u} = 14.003 \times \left( \dfrac{1}{12}\,\mathrm{mass\ of\ one\ ^{12}C\ atom} \right) \]
This means a nitrogen-14 atom is 14.003 times heavier than \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \), where \( \mathrm{u} \) itself is defined by carbon-12.
Relative Mass Terms (Based on the Unified Atomic Mass Unit)
All relative masses in chemistry are defined by comparing the mass of a particle to the unified atomic mass unit, where:
\( 1\,\mathrm{u} = \dfrac{1}{12} \text{ of the mass of a } \mathrm{^{12}C} \text{ atom} \)
Relative masses are ratios, so they have no units.
Relative Atomic Mass, \( \mathrm{A_r} \)
Average mass of an atom of an element compared with \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \).

- Takes isotopes and their abundances into account.
- Definition: \( \mathrm{A_r} = \dfrac{\text{average mass of one atom}}{1\,\mathrm{u}} \)
Relative Isotopic Mass
Mass of a particular isotope compared with \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \).![]()
- Does not consider abundance.
- Definition: \( \text{Relative isotopic mass} = \dfrac{\text{mass of one isotope atom}}{1\,\mathrm{u}} \)
Relative Molecular Mass, \( \mathrm{M_r} \) (Molecules Only)
Sum of the relative atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule.
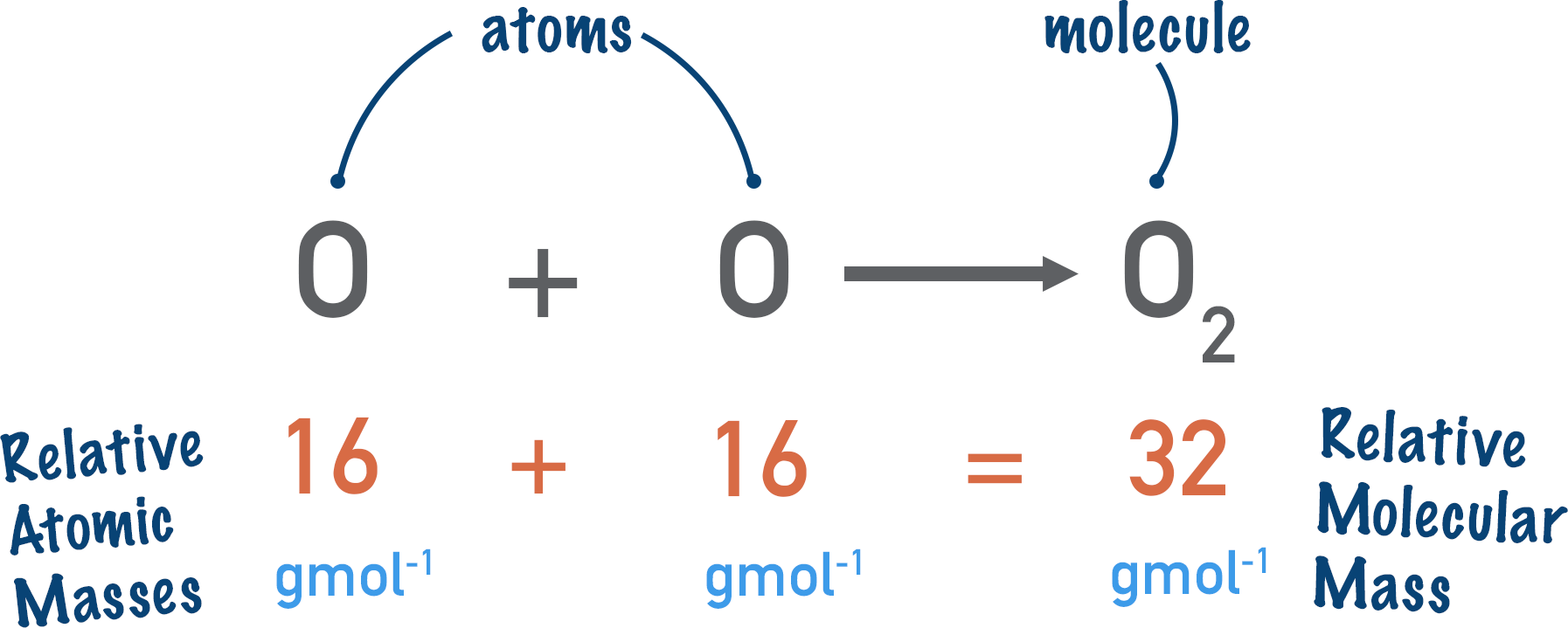
- Definition: \( \mathrm{M_r} = \dfrac{\text{mass of one molecule}}{1\,\mathrm{u}} \)
- Used for covalent substances (e.g., \( \mathrm{H_2O} \), \( \mathrm{CO_2} \)).
Relative Formula Mass
The sum of the relative atomic masses of all atoms in the empirical formula.

- Used for ionic compounds (e.g., \( \mathrm{NaCl} \), \( \mathrm{CaCO_3} \)).
- Definition: \( \text{Relative formula mass} = \dfrac{\text{mass of one formula unit}}{1\,\mathrm{u}} \)
Example
Define relative atomic mass in terms of the unified atomic mass unit.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Relative atomic mass is the average mass of an atom of an element compared with \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \), where \( 1\,\mathrm{u} = \dfrac{1}{12} \) the mass of a \( \mathrm{^{12}C} \) atom.
Example
The relative isotopic mass of an isotope of oxygen is 17. Explain what this value means.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( 17 \) means that one atom of the \( \mathrm{^{17}O} \) isotope has a mass 17 times greater than \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \), where \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \) is defined by carbon-12.
Example
Calculate the relative molecular mass of \( \mathrm{H_2SO_4} \) and explain the meaning of the value in terms of \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Using periodic table Ar values:
\( \mathrm{M_r(H_2SO_4)} = 2(1.0) + 32.1 + 4(16.0) = 98.1 \)
This means:
\( 1 \) molecule of \( \mathrm{H_2SO_4} \) has a mass \( 98.1 \) times greater than \( 1\,\mathrm{u} \), where \( 1\,\mathrm{u} = \dfrac{1}{12} \) of the mass of a \( \mathrm{^{12}C} \) atom.
