CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 22.1 Infrared spectroscopy Study Notes- 2025-2027 Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 22.1 Infrared spectroscopy Study Notes – New Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 22.1 Infrared spectroscopy Study Notes at IITian Academy focus on specific topic and type of questions asked in actual exam. Study Notes focus on AS/A Level Chemistry latest syllabus with Candidates should be able to:
- analyse an infrared spectrum of a simple molecule to identify functional groups (see the Data section for the functional groups required)
Detailed Analysis of Infrared (IR) Spectra
Infrared spectroscopy is used to identify functional groups present in an organic molecule. It works by measuring the absorption of infrared radiation, which causes bonds to vibrate.
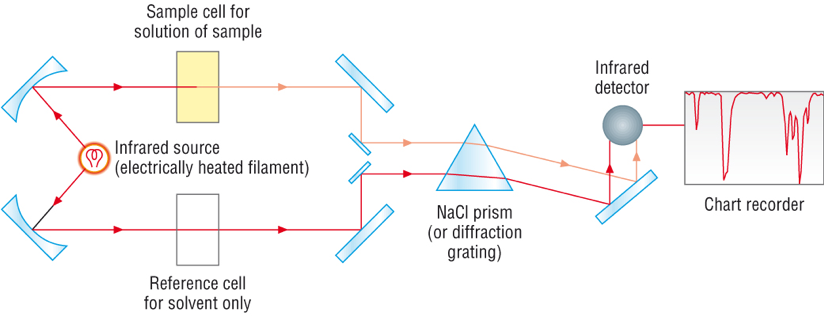
Each type of bond absorbs IR radiation at a characteristic wavenumber, measured in \( \mathrm{cm^{-1}} \).
Key Principles
- Only bond vibrations are detected, not full molecular structures
- Different functional groups absorb at distinct regions of the spectrum
- Peak position, shape, and intensity are all important
Important Regions of an IR Spectrum

- 4000–2500 cm\(^{-1}\) → O–H and N–H stretching
- 2500–2000 cm\(^{-1}\) → triple bonds (C≡C, C≡N)
- 2000–1500 cm\(^{-1}\) → C=O and C=C stretching
- 1500–500 cm\(^{-1}\) → fingerprint region (not analysed at AS)
Functional Groups from the Data Section
- Alcohol O–H: broad peak at 3200–3600 cm\(^{-1}\)
- Carboxylic acid O–H: very broad peak at 2500–3300 cm\(^{-1}\)
- C=O: strong sharp peak at ~1700 cm\(^{-1}\)
- C=C: medium peak at ~1600 cm\(^{-1}\)
- C–H: peaks at 2850–3000 cm\(^{-1}\)
Broad peaks indicate hydrogen bonding, while sharp peaks usually indicate double bonds.
Using Absence of Peaks
The absence of an expected absorption is often as important as its presence.
- No broad O–H peak → not an alcohol or carboxylic acid
- No C=O peak → not an aldehyde, ketone, ester or carboxylic acid
- No C=C peak → molecule is saturated
Exam Technique for IR Questions
- Quote approximate wavenumber values
- Describe peak shape (broad or sharp)
- Link each peak directly to a specific bond
- Use Data Booklet wording
- Avoid guessing the whole structure
Example
An IR spectrum shows a broad absorption between 3200 and 3600 cm\(^{-1}\) and no absorption at 1700 cm\(^{-1}\). Identify one functional group present.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The broad absorption at 3200–3600 cm\(^{-1}\) indicates an O–H bond.
The absence of a peak at 1700 cm\(^{-1}\) shows there is no C=O bond.
This is consistent with an alcohol functional group.
Example
An IR spectrum shows a strong peak at approximately 1700 cm\(^{-1}\) and a very broad absorption between 2500 and 3300 cm\(^{-1}\). Identify the functional group present and explain your reasoning.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The strong peak at approximately 1700 cm\(^{-1}\) indicates a C=O bond.
The very broad absorption from 2500–3300 cm\(^{-1}\) indicates an O–H bond of a carboxylic acid.
Together these peaks confirm the presence of a carboxylic acid functional group.
