CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 23.3 Entropy change, $\Delta S$ Study Notes- 2025-2027 Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 23.3 Entropy change, $\Delta S$ Study Notes – New Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 23.3 Entropy change, $\Delta S$ Study Notes at IITian Academy focus on specific topic and type of questions asked in actual exam. Study Notes focus on AS/A Level Chemistry latest syllabus with Candidates should be able to:
define the term entropy, S, as the number of possible arrangements of the particles and their energy in a given system
predict and explain the sign of the entropy changes that occur:
(a) during a change in state, e.g. melting, boiling and dissolving (and their reverse)
(b) during a temperature change
(c) during a reaction in which there is a change in the number of gaseous moleculescalculate the entropy change for a reaction, ΔS, given the standard entropies, S⦵, of the reactants and
products,ΔS⦵ = ΣS⦵(products) – ΣS⦵(reactants)
(use of ΔS⦵ = ΔSₛᵤᵣᵣ + ΔSₛᵧₛ is not required)
Entropy
Entropy, \( \mathrm{S} \), is a measure of the degree of disorder in a system.
Definition of Entropy, \( \mathrm{S} \)
Entropy is defined as the number of possible arrangements of the particles and their energy in a given system.

A system with more possible arrangements has a higher entropy.
Entropy increases when:
- A solid changes to a liquid or gas
- A liquid changes to a gas
- The number of particles increases
- A gas expands or is formed from solids or liquids
Example
Explain why a gas has a higher entropy than a solid.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Particles in a gas are free to move randomly.
They have many more possible arrangements of position and energy.
A solid has particles fixed in a regular lattice with fewer arrangements.
Example
Using the definition of entropy, explain why entropy increases when ammonium chloride sublimes.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
During sublimation, solid ammonium chloride forms gaseous particles.
The gaseous particles have greater freedom of movement.
There are many more possible arrangements of particles and energy.
This leads to an increase in entropy.
Predicting the Sign of Entropy Changes
The sign of an entropy change, \( \mathrm{\Delta S} \), can be predicted by considering changes in the number of possible arrangements of particles and their energy.
(a) Entropy Change During a Change of State
Entropy increases when matter changes from a more ordered state to a less ordered state.

- Melting (solid → liquid): \( \mathrm{\Delta S > 0} \)
- Boiling (liquid → gas): \( \mathrm{\Delta S > 0} \)
- Dissolving: usually \( \mathrm{\Delta S > 0} \)
In these processes, particles become more free to move and have more possible arrangements.
The reverse processes lead to a decrease in entropy:
- Freezing (liquid → solid): \( \mathrm{\Delta S < 0} \)
- Condensation (gas → liquid): \( \mathrm{\Delta S < 0} \)
- Crystallisation from solution: \( \mathrm{\Delta S < 0} \)
(b) Entropy Change During a Temperature Change
An increase in temperature leads to an increase in entropy.
![]()
Particles have a wider range of possible energy values at higher temperatures, so there are more possible arrangements of energy.
A decrease in temperature results in a decrease in entropy.
(c) Entropy Change in Reactions Involving Gases
Entropy change depends strongly on the number of gaseous molecules.
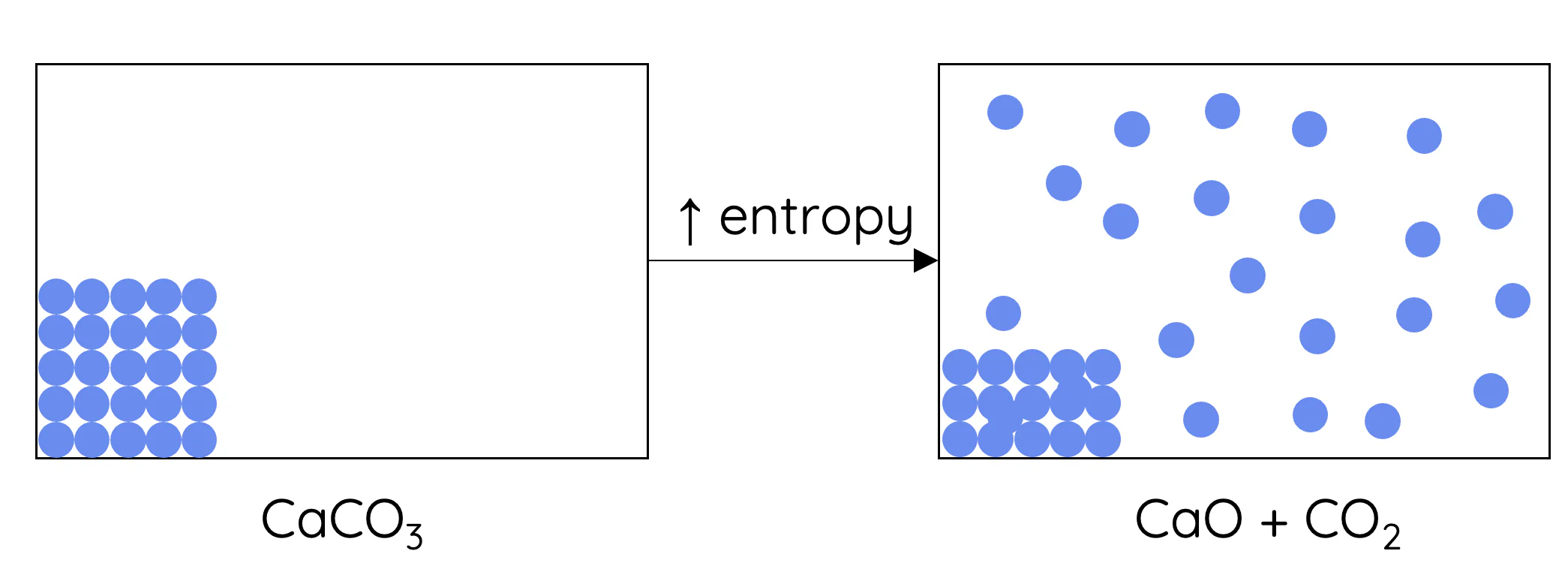
- If the number of gaseous molecules increases, \( \mathrm{\Delta S > 0} \)
- If the number of gaseous molecules decreases, \( \mathrm{\Delta S < 0} \)
- If there is no change, \( \mathrm{\Delta S} \) is likely to be small
More gas particles means more freedom of movement and more possible arrangements.
Example
Predict the sign of the entropy change when liquid ethanol boils.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The entropy change is positive.
Ethanol changes from a liquid to a gas.
Gas particles have more freedom of movement and more possible arrangements.
Example
Predict and explain the sign of the entropy change for the reaction:
\( \mathrm{N_2(g) + 3H_2(g) \rightarrow 2NH_3(g)} \)
▶️ Answer / Explanation
The entropy change is negative.
The number of gaseous molecules decreases from four to two.
This reduces the number of possible arrangements of particles and energy.
Calculating Entropy Change of a Reaction
The entropy change for a reaction can be calculated using standard entropy values, \( \mathrm{S^\circ} \), for reactants and products.
Entropy Change of a Reaction, \( \mathrm{\Delta S^\circ} \)
The standard entropy change of a reaction is given by:
\( \mathrm{\Delta S^\circ = \sum S^\circ(products) – \sum S^\circ(reactants)} \)
Standard entropy values:
- are measured in \( \mathrm{J\,mol^{-1}\,K^{-1}} \)
- apply to substances in their standard states
- must be multiplied by any stoichiometric coefficients in the equation
The sign of \( \mathrm{\Delta S^\circ} \) indicates whether entropy increases (positive) or decreases (negative) during the reaction.
Example
Calculate the entropy change for the reaction:
\( \mathrm{H_2(g) + \tfrac{1}{2}O_2(g) \rightarrow H_2O(l)} \)
\( \mathrm{S^\circ(H_2) = 131\ J\,mol^{-1}\,K^{-1}} \)
\( \mathrm{S^\circ(O_2) = 205\ J\,mol^{-1}\,K^{-1}} \)
\( \mathrm{S^\circ(H_2O(l)) = 70\ J\,mol^{-1}\,K^{-1}} \)
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Calculate total entropy of products:
\( \mathrm{70} \)
Calculate total entropy of reactants:
\( \mathrm{131 + \tfrac{1}{2}(205) = 233.5} \)
Calculate \( \mathrm{\Delta S^\circ} \):
\( \mathrm{\Delta S^\circ = 70 – 233.5 = -163.5\ J\,mol^{-1}\,K^{-1}} \)
The entropy change is negative.
Example
Calculate the entropy change for the reaction:
\( \mathrm{2SO_2(g) + O_2(g) \rightarrow 2SO_3(g)} \)
\( \mathrm{S^\circ(SO_2) = 248\ J\,mol^{-1}\,K^{-1}} \)
\( \mathrm{S^\circ(O_2) = 205\ J\,mol^{-1}\,K^{-1}} \)
\( \mathrm{S^\circ(SO_3) = 257\ J\,mol^{-1}\,K^{-1}} \)
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Calculate total entropy of products:
\( \mathrm{2 \times 257 = 514} \)
Calculate total entropy of reactants:
\( \mathrm{2 \times 248 + 205 = 701} \)
Calculate \( \mathrm{\Delta S^\circ} \):
\( \mathrm{\Delta S^\circ = 514 – 701 = -187\ J\,mol^{-1}\,K^{-1}} \)
The entropy change is negative because the number of gaseous molecules decreases.
