CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 3.3 Metallic bonding Study Notes- 2025-2027 Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 3.3 Metallic bonding Study Notes – New Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 3.3 Metallic bonding Study Notes at IITian Academy focus on specific topic and type of questions asked in actual exam. Study Notes focus on AS/A Level Chemistry latest syllabus with Candidates should be able to:
- define metallic bonding as the electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons
Metallic Bonding
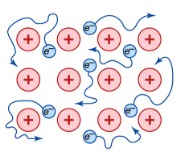
Metallic bonding explains the structure and properties of metals. It arises from the attraction between metal cations and a ‘sea’ of delocalised electrons.
Definition of Metallic Bonding
![]()
Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons.
- Metals lose their outer electrons, forming positive metal ions arranged in layers.
- The electrons become delocalised (free to move throughout the lattice).
- The strong attraction between these electrons and the metal ions is the metallic bond.
Key Points About Metallic Bonding
- Unique to metals.
- Delocalised electrons act as ‘glue’ holding metal ions together.
- Strength of metallic bonding depends on: – number of delocalised electrons – charge on the metal ions – size of the metal ions
- Explains metal properties: conductivity, malleability, ductility, and melting points.
Example
Define metallic bonding.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons.
Example
Describe how metallic bonding forms in sodium metal.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Each sodium atom loses one valence electron to form \( \mathrm{Na^+} \) ions.
The electrons become delocalised and move freely through the lattice.
The attraction between \( \mathrm{Na^+} \) ions and delocalised electrons creates the metallic bond.
Example
Explain why magnesium has stronger metallic bonding than sodium.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Magnesium forms \( \mathrm{Mg^{2+}} \) ions, while sodium forms \( \mathrm{Na^+} \) ions.
Magnesium contributes two delocalised electrons per atom; sodium contributes only one.
More delocalised electrons and a higher ionic charge increase the strength of the electrostatic attraction.
Therefore metallic bonding is stronger in magnesium than in sodium.
