CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 3.7 Dot-and-cross diagrams Study Notes- 2025-2027 Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 3.7 Dot-and-cross diagrams Study Notes – New Syllabus
CIE AS/A Level Chemistry 3.7 Dot-and-cross diagrams Study Notes at IITian Academy focus on specific topic and type of questions asked in actual exam. Study Notes focus on AS/A Level Chemistry latest syllabus with Candidates should be able to:
- use dot-and-cross diagrams to illustrate ionic, covalent and coordinate bonding including the representation of any compounds stated in 3.4 and 3.5 (dot-and-cross diagrams may include species with atoms which have an expanded octet or species with an odd number of electrons)
Dot-and-Cross Diagrams for Ionic, Covalent and Coordinate Bonding
Dot-and-cross diagrams show electrons involved in bonding. Electrons from one atom are drawn as dots, and electrons from the other atom are drawn as crosses. They are used to illustrate:
- Ionic bonding (transfer of electrons)
- Covalent bonding (sharing of electrons)
- Coordinate (dative) bonding (shared pair donated by one atom)
1. Dot-and-Cross Diagrams for Ionic Bonding
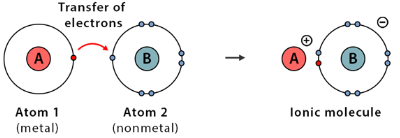
Ionic bonding occurs when electrons are transferred from a metal atom to a non-metal atom, forming oppositely charged ions.
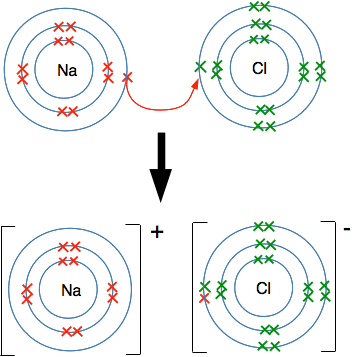
Example: Sodium Chloride, \( \mathrm{NaCl} \)
- Na loses 1 electron → \( \mathrm{Na^+} \)
- Cl gains 1 electron → \( \mathrm{Cl^-} \)
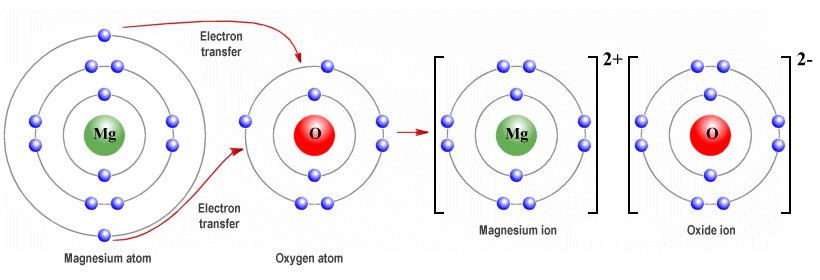
Example: Magnesium Oxide, \( \mathrm{MgO} \)
- Mg loses 2 electrons → \( \mathrm{Mg^{2+}} \)
- O gains 2 electrons → \( \mathrm{O^{2-}} \)
2. Dot-and-Cross Diagrams for Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonds form when atoms share pairs of electrons.
![]()
Example: Water, \( \mathrm{H_2O} \)
- Each H shares 1 electron with O.
- O has 2 lone pairs.
![]()
Example: Carbon Dioxide, \( \mathrm{CO_2} \) (double covalent bonds)
![]()
Example: Nitrogen, \( \mathrm{N_2} \) (triple covalent bond)
![]()
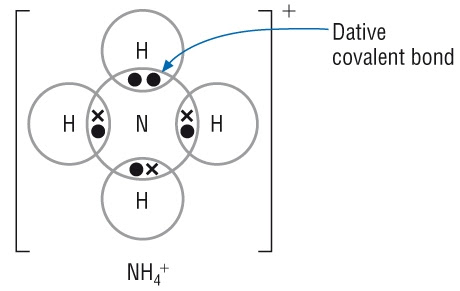
3. Dot-and-Cross Diagrams for Coordinate (Dative) Bonding

A coordinate bond is a covalent bond in which both electrons in the shared pair come from the same atom.
Example: Ammonium ion, \( \mathrm{NH_4^+} \)
Example: Hydronium ion, \( \mathrm{H_3O^+} \)

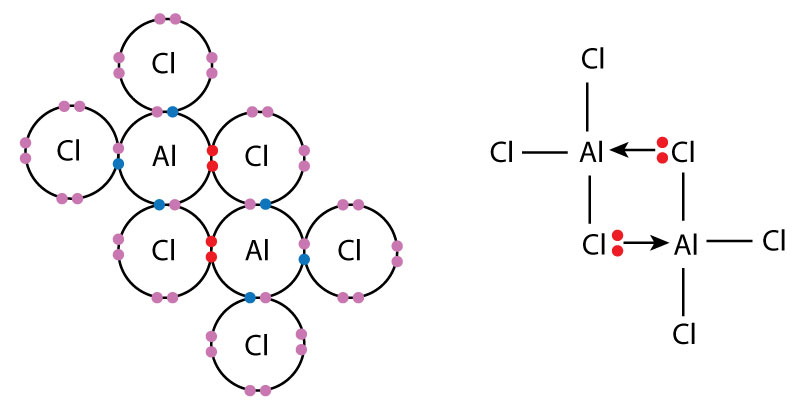
Example: Aluminium Chloride Dimer (\( \mathrm{Al_2Cl_6} \)) — expanded octet
Example
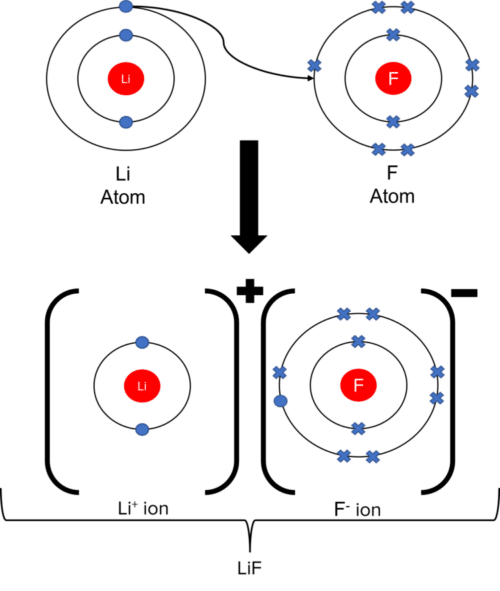
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for \( \mathrm{LiF} \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Example
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for methane, \( \mathrm{CH_4} \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Example
Draw a dot-and-cross diagram for the formation of \( \mathrm{NH_4^+} \).