CIE AS/A Level Maths-6.3 Continuous random variables- Study Notes- New Syllabus - 2026-2027
CIE AS/A Level Maths-6.3 Continuous random variables- Study Notes- New Syllabus
Ace AS/A Level Maths Exam with CIE AS/A Level Maths-6.3 Continuous random variables- Study Notes
Key Concepts:
- Continuous Random Variables and Probability Density Functions (PDFs)
- Using a Probability Density Function (PDF) to Solve Problems
Continuous Random Variables and Probability Density Functions (PDFs)
Continuous Random Variables and Probability Density Functions (PDFs)
Continuous random variable:
- A random variable \(X\) that can take any value within a given interval (finite or infinite) is called continuous.
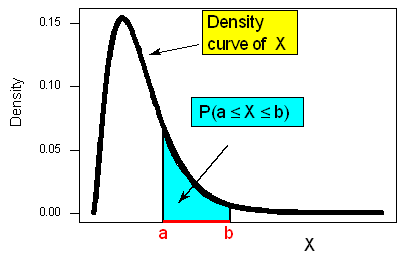
- Unlike discrete variables, the probability of \(X\) taking any exact value is zero: \(P(X = x) = 0\).
Probability density function (PDF):
- A function \(f(x)\) such that the probability that \(X\) lies in an interval \([a, b]\) is given by:
\( P(a \le X \le b) =\displaystyle \int_a^b f(x) \, dx \)
Properties of a PDF \(f(x)\):
- \(f(x) \ge 0\) for all \(x\)
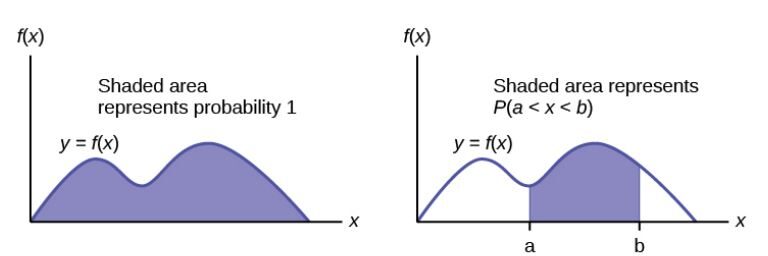
- The total area under the curve is 1: \( \displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f(x) \, dx = 1 \)
- Probabilities are obtained by integrating over intervals, not by evaluating \(f(x)\) at a point.
Expectation (mean) of \(X\):
\( \mathrm{E}(X) = \displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x f(x) \, dx \)
Variance of \(X\):
\( \mathrm{Var}(X) = \displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} (x – \mathrm{E}(X))^2 f(x) \, dx \)
Example:
Let \(X\) be uniformly distributed on \([0, 5]\), so \(f(x) = \dfrac{1}{5}\) for \(0 \le x \le 5\). Find \(P(1 \le X \le 3)\), \(\mathrm{E}(X)\), and \(\mathrm{Var}(X)\).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Probability: \( P(1 \le X \le 3) = \int_1^3 \dfrac{1}{5} \, dx = \dfrac{3-1}{5} = \dfrac{2}{5} \)
Expectation: \( \mathrm{E}(X) = \int_0^5 x \cdot \dfrac{1}{5} \, dx = \dfrac{1}{5} \cdot \dfrac{5^2}{2} = 2.5 \)
Variance: \( \mathrm{Var}(X) = \int_0^5 (x – 2.5)^2 \cdot \dfrac{1}{5} \, dx = \dfrac{25}{12} \approx 2.0833 \)
Final Answer: \(\boxed{P = \frac{2}{5}, \; \mathrm{E}(X) = 2.5, \; \mathrm{Var}(X) \approx 2.083}\)
Example :
Let \(X\) have PDF \( f(x) = \frac{1}{2} e^{-x/2} \), \(x \ge 0\). Find \(P(X > 3)\), \(\mathrm{E}(X)\), and \(\mathrm{Var}(X)\).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Probability: \( P(X > 3) = \int_3^{\infty} \frac{1}{2} e^{-x/2} \, dx = e^{-3/2} \approx 0.2231 \)
Expectation: \( \mathrm{E}(X) = \int_0^{\infty} x \cdot \frac{1}{2} e^{-x/2} \, dx = 2 \)
Variance: \( \mathrm{Var}(X) = \int_0^{\infty} (x-2)^2 \cdot \frac{1}{2} e^{-x/2} \, dx = 4 \)
Final Answer: \(\boxed{P \approx 0.2231, \; \mathrm{E}(X) = 2, \; \mathrm{Var}(X) = 4}\)
Example:
Continuous Random Variable with PDF \( f(x) = \dfrac{3}{x^4}, x \ge 1 \) Verify and find all the parameters
▶️Answer/Explanation
Step 1: Verify PDF
Check that \( \int_1^\infty f(x) \, dx = 1 \)
\( \int_1^\infty \dfrac{3}{x^4} \, dx = 3 \int_1^\infty x^{-4} dx = 3 \left[ \dfrac{x^{-3}}{-3} \right]_1^\infty = 1 \)
Step 2: Find probability \(P(X > 2)\)
\( P(X > 2) = \int_2^\infty f(x) \, dx = \int_2^\infty \dfrac{3}{x^4} dx = 3 \left[ \dfrac{x^{-3}}{-3} \right]_2^\infty = 2^{-3} = \dfrac{1}{8} \)
Step 3: Find expectation \( \mathrm{E}(X) \)
\( \mathrm{E}(X) = \int_1^\infty x f(x) \, dx = \int_1^\infty x \cdot \dfrac{3}{x^4} dx = 3 \int_1^\infty x^{-3} dx = \dfrac{3}{2} \)
Step 4: Find variance \( \mathrm{Var}(X) \)
\( \mathrm{E}(X^2) = \int_1^\infty x^2 f(x) \, dx = \int_1^\infty 3 x^{-2} dx = 3 \)
\( \mathrm{Var}(X) = \mathrm{E}(X^2) – (\mathrm{E}(X))^2 = 3 – \left(\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2 = \dfrac{3}{4} \)
Example:
Let \(X \sim \text{Uniform}(0, 1)\) with PDF \(f(x) = 1\) for \(0 \le x \le 1\). Let \(Y = 3X + 2\). Find \(\mathrm{E}(Y)\) and \(\mathrm{Var}(Y)\).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
\(\mathrm{E}(Y) = \mathrm{E}(3X + 2) = 3 \mathrm{E}(X) + 2 = 3 \cdot 0.5 + 2 = 3.5\)
\(\mathrm{Var}(Y) = \mathrm{Var}(3X + 2) = 3^2 \mathrm{Var}(X) = 9 \cdot \dfrac{1}{12} = 0.75\)
Final Answer: \(\boxed{\mathrm{E}(Y) = 3.5, \; \mathrm{Var}(Y) = 0.75}\)
Using a Probability Density Function (PDF) to Solve Problems
Using a Probability Density Function (PDF) to Solve Problems
A continuous random variable \(X\) has a probability density function \(f(x)\) if the probability that \(X\) lies in an interval \([a, b]\) is given by:
\( P(a \le X \le b) =\displaystyle \int_a^b f(x) \, dx \)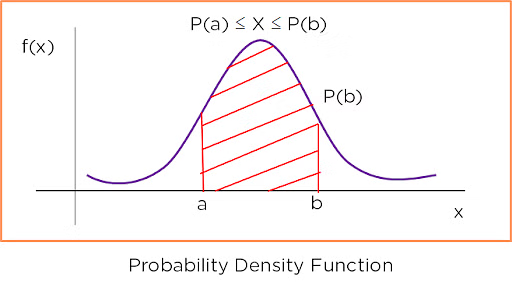
Properties of PDF:
- \(f(x) \ge 0\) for all \(x\)
- \(\displaystyle \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f(x) \, dx = 1 \)
Expectation (mean) and variance:
Expectation: \( \mathrm{E}(X) = \displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x f(x) \, dx \)
Variance: \( \mathrm{Var}(X) = \displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} (x – \mathrm{E}(X))^2 f(x) \, dx \)
Median and percentiles:
The median \(m\) is the value for which half the area under the PDF lies to the left: \( \displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^{m} f(x) \, dx = 0.5 \)
Percentiles are found similarly: the \(p\)th percentile \(x_p\) satisfies \( \displaystyle\int_{-\infty}^{x_p} f(x) \, dx = p/100 \)
Example:
Let \(X\) have PDF \( f(x) = \dfrac{3}{x^4} \) for \( x \ge 1 \). Find \(P(X > 2)\), \(\mathrm{E}(X)\), and \(\mathrm{Var}(X)\).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Probability: \( P(X > 2) = \int_2^{\infty} \dfrac{3}{x^4} dx = 3 \left[ \dfrac{x^{-3}}{-3} \right]_2^\infty = 2^{-3} = \dfrac{1}{8} \)
Expectation: \( \mathrm{E}(X) = \int_1^\infty x \cdot \dfrac{3}{x^4} dx = \dfrac{3}{2} \)
Variance: \( \mathrm{Var}(X) = \int_1^\infty x^2 \cdot \dfrac{3}{x^4} dx – (\mathrm{E}(X))^2 = 3 – \left(\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2 = \dfrac{3}{4} \)
Final Answer: \(\boxed{P(X>2) = \frac{1}{8}, \; \mathrm{E}(X) = \frac{3}{2}, \; \mathrm{Var}(X) = \frac{3}{4}}\)
Example:
Find the median \(m\) of \(X\) with PDF \( f(x) = \dfrac{3}{x^4} \), \(x \ge 1\).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The median satisfies \( \int_1^m \dfrac{3}{x^4} dx = 0.5 \)
Compute the integral: \( 3 \left[ \dfrac{x^{-3}}{-3} \right]_1^m = 0.5 \Rightarrow -(m^{-3} – 1) = 0.5 \Rightarrow 1 – m^{-3} = 0.5 \Rightarrow m^{-3} = 0.5 \)
So \( m = 0.5^{-1/3} = 2^{1/3} \approx 1.26 \)
Final Answer: \(\boxed{m \approx 1.26}\)
Example:
Find the 75th percentile \(x_{0.75}\) of \(X\) with the same PDF.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
75th percentile satisfies \( \int_1^{x_{0.75}} \dfrac{3}{x^4} dx = 0.75 \)
Compute: \( 1 – x_{0.75}^{-3} = 0.75 \Rightarrow x_{0.75}^{-3} = 0.25 \Rightarrow x_{0.75} = 0.25^{-1/3} = 4^{1/3} \approx 1.587 \)
Final Answer: \(\boxed{x_{0.75} \approx 1.587}\)
