CIE AS/A level Physics Paper 1 Prediction - 2025
CIE AS/A level Physics Paper 1 Prediction- 2025
To excel in A level Physics Exam, consistent practice with CIE AS & A Level Revision resources is key. CIE AS/A level Physics Paper 1 Prediction will guide you for exam pattern.
IITian Academy offers a vast collection of questions that can aid your understanding of specific topics and solidify your concepts. By practicing regularly and focusing on these key areas, you’ll be well-prepared for the AS/A level Physics exam
Question 1
What must be included in a record of a physical quantity?
(A) an integer value for the quantity
(B) an SI unit
(C) a numerical value for the quantity
(D) a unit expressed in base units
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans : C
Question 2
Which equation, representing uniformly accelerated motion in a straight line, can be determined using only the definition of acceleration?
(A) $s=ut+\frac{1}{2}at^{^{^{2}}}$
(B)$s=\frac{1}{2}\left ( u+v\right )t$
(C) v = u + at
(D) $v^{2}=u^{2}+2as$
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 3
A rock is launched vertically upwards from the surface of the Earth and an identical rock is launched vertically upwards from the surface of Mars. Each rock is launched with an initial velocity of $12 m s^{–1}$.
Each rock then reaches its maximum height above the surface before returning back down to the surface. The velocity–time graph for each rock is shown. In both cases, air resistance is negligible.
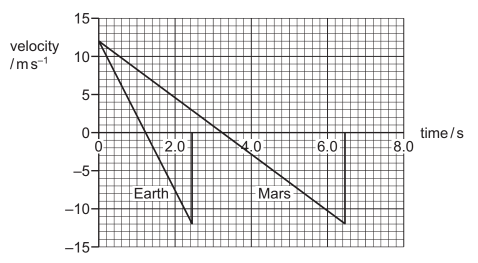
What is the difference in the maximum heights of the two rocks?
(A) 12 m
(B) 15 m
(C) 19 m
(D) 24 m
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 4
A submarine of total mass 3200 kg is at rest underwater.
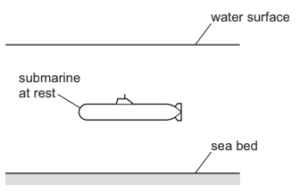
The total mass of the submarine is suddenly decreased by 200 kg by pumping water out of the submarine horizontally in a negligible time. The upthrust acting on the submarine is unchanged.
The change in the total weight of the submarine causes it to accelerate vertically upwards.
What is the initial upwards acceleration of the submarine?
(A) $0.613 m s^{–2}$
(B) $0.654 m s^{–2}$
(C) $9.81 m s^{–2}$
(D) $10.5 m s^{–2}$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 5
An object is falling at a constant speed through a viscous liquid. F$_{u}$ is the upthrust on the object due to the liquid.
W$_{L}$ is the weight of the liquid displaced by the object. W$_{o}$ is the weight of the object.
Which equation must be correct?
(A)$F_{u}=W_{L}$
(B) $F_{u}=W_{L}-W_{L}$
(C) $F_{u}=W_{o}$
(D) $F_{u}=W_{o}-W_{L}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 6
What is not a requirement for two forces to act as a couple?
(A) The two forces act in opposite directions.
(B) The two forces act through the same point.
(C) The two forces combine to produce zero resultant force.
(D) The two forces have equal magnitude.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 7
A rod is pivoted at point O.
A force F is applied to the rod at point W, as shown.

What is the moment of the force F about O?
A F$\times$ distance OX
B F $\times$ distance OY
C F $\times$ distance WO
D F $\times$ distance WX
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 8
Two balls of identical shape and size but different masses are falling through the same liquid. The sum of the drag force and upthrust acting on each ball is equal to its weight.
Which statement about the two balls is correct?
(A The heavier ball has a larger acceleration than the lighter ball.
(B) The heavier ball has a smaller deceleration than the lighter ball.
(C) The heavier ball is falling at the same speed as the lighter ball.
(D) The heavier ball is falling at a larger speed than the lighter ball.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 9
A car moves along a horizontal road with a constant velocity v against a resistive force F. The engine of the car has an efficiency of 25%.
What is the input power to the engine?
(A) $\frac{Fv}{4.0}$
(B) $\frac{4.0}{Fv}$
(C) $4.0F{v}$
(D)$\frac{4.0F}{v}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 10
A man sits on a buggy that is pulled along by a wire attached to a kite. The wire is at an angle of 40 to the horizontal and has a constant tension of 200N. The man and buggy travel a distance of 20m along a straight horizontal path. The wire and the path of the buggy are in the same vertical plane.
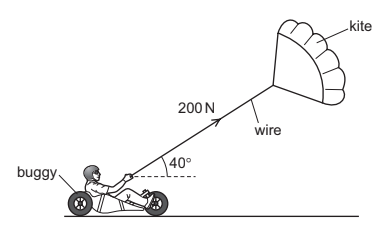
What is the work done by the tension force on the man and buggy?
(A) 2.6kJ
(B) 3.1kJ
(C) 3.4kJ
(D) 4.0kJ
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 11
A volume of 1.5 $m^{3}$ of water is mixed with 0.50 $m^{3}$ of alcohol. The density of water is 1000 kg $m^{-3}$ and the density of alcohol is 800 kg $m^{-3}$. The volume of the mixture is 2.0 $m^{3}$ .
What is the density of the mixture?
(A) 850 kg $m^{-3}$
(B) 900 kg $m^{-3}$
(C) 940 kg $m^{-3}$
(D) 950 kg $m^{-3}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 12
A U-shaped glass tube contains liquid of density$ 2000 kgm^{–3}$, as shown.
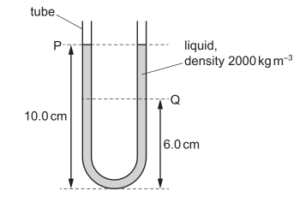
What is the difference in pressure due to the liquid between levels P and Q?
(A) 780Pa
(B) 1200Pa
(C) 1600Pa
(D) 2000Pa
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 13
A metal wire is connected between the terminals of a cell so that there is a current in the wire.
Which statement is correct?
(A) Negatively charged electrons in the wire move from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
(B) Negatively charged nuclei in the wire move from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
(C) Positively charged electrons in the wire move from the positive terminal to the negative terminal.
(D) Positively charged nuclei in the wire move from the positive terminal to the negative terminal.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 14
A metal wire has length 5.2 m and diameter 1.0 mm. The metal has Young modulus 360 GPa. The wire is fixed at one end and a force is applied to the other end. The force extends the wire by 7.2 mm. The wire obeys Hooke’s law.
What is the force applied to the wire?
(A) $1.2 × 10^{2}N$
(B) $3.9 × 10^{2}N$
(C) $5.0 × 10^{2}N$
(D) $1.6 × 10^{3}N$
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 15
The graph shows how the length of a spring varies with the force applied to it.

The spring has unstretched length $L_{0}$. When a force F is applied, the spring has length L1.
What is the work done in stretching the spring to length $L_{1}$?
(A) $\frac{1}{2}FL_{1}$
(B) $\frac{1}{2}F$($L_{1}-L_{0}$)
(C) $FL_{1}$
(D) F$L_{1}-L_{0}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 16
A stone sinks in water.
What is a possible value for the density of the stone?
(A) $ 8\times 10^{2}kgm^{-3}$
(B) $ 2\times 10^{3}kgm^{-3}$
(C) $ 8\times 10^{3}Nm^{-3}$
(D) $ 2\times 10^{4}Nm^{-3}$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 17
Graph 1 shows the variation with time of displacement at a fixed distance along a progressive wave.
Graph 2 represents the same wave and shows the variation with distance of displacement at an instant in time.

What is the speed of the wave?
(A) 5.0cm$s^{-1}$
(B) 48cm$s^{-1}$
(C) 150cm$s^{-1}$
(D) 300cm$s^{-1}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 18
A progressive wave of frequency 1.5 kHz travels in a medium at a speed of 340 m $s^{-1}$.
What is the minimum distance between two points on the wave that have a phase difference of 70$\circ$ ?
(A) 4.4 cm
(B) 8.8 cm
(C) 18 cm
(D) 23 cm
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 19
A microphone detects a sound wave. The microphone is connected to a cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO).

The shape of the trace on the screen of the CRO is shown.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 20
The graph shows the variation with time of the displacement of a particle in a progressive wave.

Two measurements, x and y, are labelled on the graph. What do x and y represent?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 21
An electromagnetic wave has a wavelength of 2.1 cm in a vacuum.
Which region of the electromagnetic spectrum contains this wave?
(A) infrared
(B) microwave
(C) radio wave
(D) visible light
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 22
A beam of visible light is in a vacuum.
What could be the frequency of the light?
(A) $5.0 × 10^{5}Hz$
(B) $5.0 × 10^{8}Hz$
(C) $5.0 × 10^{11}Hz$
(D) $5.0 × 10^{14}Hz$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 23
In an experiment, a student uses a microphone and a cathode-ray oscilloscope (CRO) to analyse a sound wave. The diagram shows the trace on the screen of the CRO.
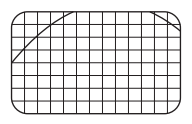
The student is expecting a sinusoidal waveform to be shown on the screen.
Which changes should the student make to the time-base and the y-gain of the CRO so that the screen shows a continuous trace for one complete cycle of the waveform?
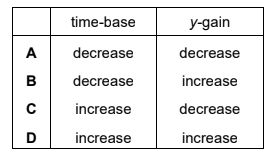
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 24
A battery with internal resistance is connected to a parallel arrangement of two resistors and a switch S, as shown.

Initially, switch S is open.
What happens to the voltmeter and ammeter readings when switch S is closed?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 25
Which charge can be carried by a charge carrier?
(A) $1.1 × 10^{–19}C$
(B) $4.0 × 10^{–19}C$
(C) $4.8 × 10^{–19}C$
(D) $9.1 × 10^{–19}C$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 26
A cell of negligible internal resistance is connected in series with a thermistor, a fixed resistor and an ammeter.
The thermistor is placed in a beaker of water and the temperature of the water is slowly increased.
A graph of current I against the temperature T of the thermistor is plotted.
Which graph could show the variation of I with T?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 27
A boat moves at a constant velocity v through still water. A constant drag force F acts on the boat. What is the power used by the boat to move through the water?
A \(\frac{1}{2}Fv\)
B Fv
C \(\frac{1}{2}Fv^2\)
D \(Fv^2\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans B
Question 28
A wire has a length of 3.0 m and is made of metal of resistivity 4.9 × $10^{-7}\Omega m$.
A potential difference (p.d.) of 12V is applied across the wire so that it has a current of 1.4A.
What is the cross-sectional area of the wire?
(A) 1.2 × $10^{-7}m^{2}$
(B) 1.7 × $10^{-7}m^{2}$
(C) 1.1 × $10^{-6}m^{2}$
(D) 1.3 × $10^{-6}m^{2}$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 29
Two resistors have a combined resistance of 34Ω when connected in series. The same resistors have a combined resistance of 7.4Ω when connected in parallel. What is the resistance of one of the resistors?
(A) 15Ω
(B) 17Ω
(C) 23Ω
(D) 27Ω
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 30
A student assembles the circuit shown.

Which row describes the state of the two lamps?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 31
The charge carriers in a metal wire are free electrons. Which statement about the charge of each free electron is correct?
A The magnitude of the charge increases with the potential difference across the wire.
B The magnitude of the charge is zero unless there is a potential difference across the wire.
C The sign and magnitude of the charge do not depend on the potential difference across the wire.
D The sign of the charge depends on the potential difference across the wire.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Question 32
The diagram shows a circuit that includes a cell with internal resistance.
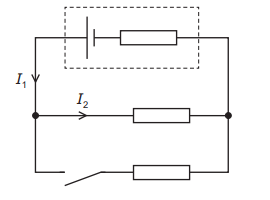
The switch is initially open. Which row describes the effects on currents \(I_1\) and \(I_2\) of closing the switch? 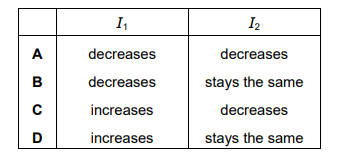
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Question 33
A cell with internal resistance is connected to a variable resistor R as shown.
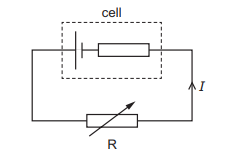 The resistance of R is gradually decreased. How do the current I and the terminal potential difference (p.d.) across the cell change?
The resistance of R is gradually decreased. How do the current I and the terminal potential difference (p.d.) across the cell change?
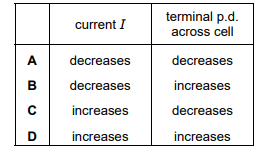
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans C
Question 34
Which statement about β${-}$ decay is correct?
(A) A neutron changes to a proton in the nucleus and an electron and an antineutrino are emitted.
(B) A neutron changes to a proton in the nucleus and an electron and a neutrino are emitted.
(C) A proton changes to a neutron in the nucleus and an electron and an antineutrino are emitted.
(D) A proton changes to a neutron in the nucleus and an electron and a neutrino are emitted.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 35
The table contains data for four different nuclei P, Q, R and S.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 36
A neutron $_{0}^{1}\textrm{n}$is fired at a $_{92}^{235}\textrm{U}$ nucleus. The neutron is absorbed by the nucleus which then splits
to form nuclei of $_{56}^{141}\textrm{Ba}$and $_{36}^{92}\textrm{Kr}$.
What is the number of free neutrons emitted when the $_{92}^{235}\textrm{U}$ nucleus splits?
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 3
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 37
What are isotopes?
(A) nuclei of different elements with the same number of neutrons
(B) nuclei of different elements with the same number of nucleons
(C) nuclei of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
(D) nuclei of the same element with different numbers of protons
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 38
What is the quark composition of a hydrogen-3 nucleus, $\frac{3}{1}H$?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 39
A $π^{+}$ meson has a charge of +e, where e is the elementary charge. It consists of an up quark and one other quark.
What could be the other quark in the $π^{+}$meson?
(A) anti-down
(B) anti-up
(C) bottom
(D) charm
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 40
Which flavours of quark have charge \(+\frac{2}{3}e ?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans A
