AP Biology 1.2 Elements of Life Study Notes - New Syllabus Effective 2025
AP Biology 1.2 Elements of Life Study Notes- New syllabus
AP Biology 1.2 Elements of Life Study Notes – AP Biology – per latest AP Biology Syllabus.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Describe the composition of macromolecules required by living organisms.
Key Concepts:
- Elements of Life
1.2.A – Elements of Life
🧱 What are Living Things Made Of?
Living organisms are made of a few essential elements and 4 main types of macromolecules (large biological molecules). These molecules are built from smaller subunits and are necessary for life functions like growth, repair, energy, and reproduction.
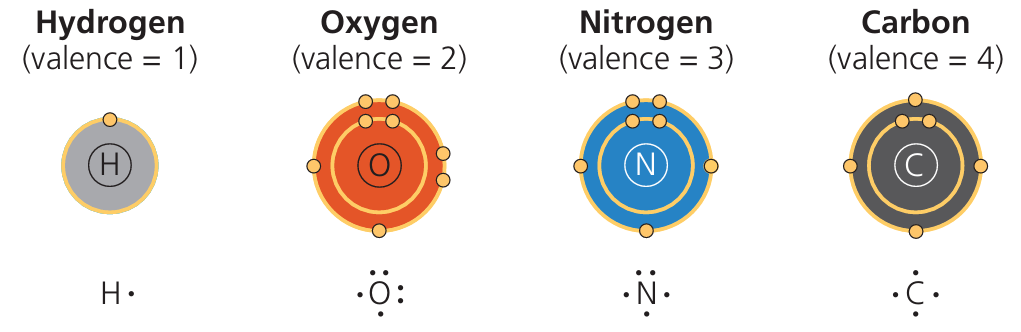
⚛️ Key Elements in Life
These are the most abundant elements in biological systems (CHNOPS):
| Element | Role |
|---|---|
| C – Carbon | Backbone of all macromolecules; forms 4 bonds |
| H – Hydrogen | Part of water, organic molecules |
| N – Nitrogen | Found in proteins (amino acids) and nucleic acids |
| O – Oxygen | In water, needed for cellular respiration |
| P – Phosphorus | In DNA, RNA, ATP (energy) |
| S – Sulfur | In some amino acids and proteins |
🧬 The 4 Biological Macromolecules
| Macromolecule | Monomer (Building Block) | Key Elements | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | Monosaccharides (e.g., glucose) | C, H, O | Quick energy, structure (cell wall) |
| Lipids | Fatty acids + glycerol | C, H, O | Long-term energy, insulation, membranes |
| Proteins | Amino acids | C, H, O, N, (S) | Enzymes, structure, communication |
| Nucleic Acids | Nucleotides (A, T, C, G, U) | C, H, O, N, P | Store and transmit genetic info (DNA/RNA) |
🧠 Summary:
- All life depends on a few elements (mainly CHNOPS).
- Living organisms are made of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
- These macromolecules have specific structures and functions.
- Their composition reflects the elements needed for life.
🧪 1.2.A.1 – Elements Required to Build Macromolecules
🌍 Where Do Living Things Get Their Building Blocks?
Atoms & molecules from the environment are used by organisms to build larger, complex biological molecules (a.k.a. macromolecules).
🔑 Main Elements in Macromolecules
| Element | Role in Macromolecules |
| Carbon (C) | Backbone of all organic molecules (forms 4 bonds very versatile!) |
| Hydrogen (H) | Part of almost all biological compounds |
| Oxygen (O) | Found in carbs, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, key for energy and structure |
🧬 Other Essential Elements & Their Functions
- Nitrogen (N) → Needed for nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and proteins (found in amino group)
- Phosphorus (P) → Found in phospholipids (cell membranes) & nucleic acids (DNA/RNA backbone)
- Sulfur (S) → Found in proteins, especially in some amino acids (like cysteine); helps form disulfide bridges (important for protein folding)
🧠 Why It Matters
- Without these key elements, cells can’t grow, reproduce, or maintain structure.
- All biomolecules – carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids are assembled using these elements from food or environment.
