Question
Lectin is a molecule commonly found in legumes. Colchicine is a molecule that inhibits the formation of spindle fibers. An experiment was performed to observe the effects of lectin and colchicine on dividing cells. A total of 300 cells were observed for each treatment.
Partial results of the experiment are shown in the following table.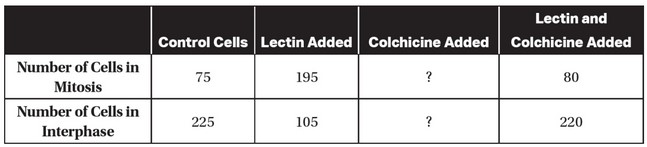
(a) Describe the effect of adding lectin to the cells.
(b) Identify the independent variable and the dependent variable in
this experiment.
(c) Based on the data presented, predict the most likely effect of
adding only colchicine to the cells.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) Lectin stimulates cell division, as shown by the increased number
of cells in mitosis for the treatment with only lectin added
(compared to the number of control cells in mitosis).
(b) The independent variable is the presence or absence of lectin and/or
colchicine. The dependent variable is the number of cells in mitosis
or interphase.
(c) The most likely effects of adding only colchicine to the cells would
be that the number of cells in mitosis would be less than that of the
control group and the number of cells in interphase would be more
than that of the control group.
(d) The addition of lectin alone increased the number of cells in
mitosis (compared to that of the control group). The addition of
both lectin and colchicine resulted in a number of cells in mitosis
that was much closer to that of the control group than it was to that
of the group with only lectin added. So colchicine most likely
reduces the number of cells in mitosis, and thus a group with only
colchicine added would have even fewer cells in mitosis than the
control group had.
Question
The following figure represents the concentrations of two different molecules (cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase) during the cell cycle,
and the arrow indicates the start of mitosis.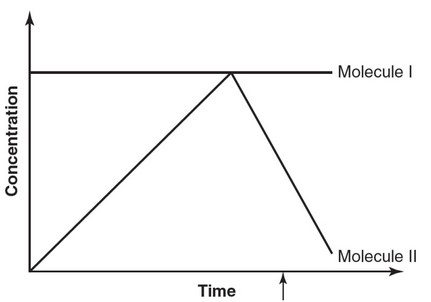
(a) Cell division can be described as having three major events:
replication of chromosomes, alignment of chromosomes, and
separation of chromosomes. Describe the stages of the cell cycle
during which each of these three major events occurs.
(b) In the figure, which molecule (cyclin or cyclin-dependent kinase)
is represented by the line labeled “Molecule I”? Which molecule
(cyclin or cyclin-dependent kinase) is represented by the line
labeled “Molecule II”?
(c) Explain why mitosis starts at the point indicated by the arrow in
the figure.
(d) A cancer cell has a mutation that results in the constant production
of Molecule II. Explain how the process of mitosis might be
affected by this mutation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) Replication of chromosomes occurs during the S stage of
interphase. Alignment of chromosomes occurs during metaphase of
mitosis. Separation of chromosomes occurs during anaphase of
mitosis.
(b) Molecule I represents the concentration of cyclin-dependent kinase
because it is at a constant level throughout the cell cycle. Molecule
II represents the concentration of cyclins because its level peaks
just before the start of mitosis and then falls off rapidly during
mitosis.
(c) Mitosis-promoting factor (MPF) triggers the start of mitosis.
Mitosis-promoting factor forms when cyclins bind to cyclin-
dependent kinases. The arrow shows the point at which there is enough cyclin to form the MPF needed to trigger the start of
mitosis.
(d) If a cancer cell had a mutation that resulted in the constant high
production of cyclins (Molecule II), there would be constantly high
levels of MPF in the cell. Mitosis would constantly be stimulated,
and the cell would divide uncontrollably.
Question
Plants have indeterminate growth; they continue to grow for their entire life. Animals have determinate growth, meaning they grow
until they reach a particular size and then remain at that size for the rest of their life.
State one advantage and one disadvantage of both determinate and indeterminate growth and development.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Determinate growth:
• Advantage: greater complexity of development can be achieved
because a more complex sequence of events can unfold for a longer
period of time. Limited size means limited energy requirements.
• Disadvantage: many structures cannot be regenerated if lost during
life.
Indeterminate growth:
• Advantage: The rate of growth can change in response to the
environment. However, increased growth requires increased energy,
and nutrient and water requirements for both the initial growth and
maintenance of the larger body size. In plants, a larger body size can
translate into the increased capacity to make energy if the right
proportion of the growth is photosynthetic surface. The ability to
grow continuously allows certain plants to “take over” an area. In
addition, plants can generate and regenerate many parts of their
bodies because they retain stem cells at meristems.
• Disadvantage: Growth can incur requirements for energy, nutrients,
and water that may be lacking after growth has already occurred.
