Question
R. C. Punnett conducted experiments on the inheritance of traits in the sweet pea, Lathyrus odoratus. In one experiment, he crossed two different true-breeding sweet pea plant strains, one with erect petals and long pollen, and the other with hooded petals and round pollen. All the offspring (\(F_1\) generation) had erect petals and long pollen (Figure 1).

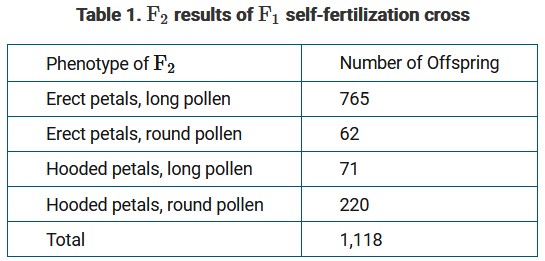
Sweet pea plants have a diploid (2n)
chromosome number of 14.
Which of the following best explains how the sweet pea plants in the parental generation produce \(F_1\) offspring with 14 chromosomes?
A. Meiosis I and II lead to the formation of cells with 14 chromosomes. When two cells combine during fertilization, extra chromosomes are randomly broken down, leading to offspring with 14 chromosomes.
B. Meiosis I and II lead to the formation of cells with 14 chromosomes. When two cells combine during fertilization, extra chromosomes with recessive traits are broken down, leading to offspring with 14 chromosomes.
C. Meiosis I and II lead to the formation of cells with 7 chromosomes. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate. During meiosis II, sister chromatids separate. Two cells combine during fertilization to produce offspring with 14 chromosomes.
D. Meiosis I and II lead to the formation of cells with 7 chromosomes. During meiosis I, sister chromatids separate. During meiosis II, homologous chromosomes separate. Two cells combine during fertilization to produce offspring with 14 chromosomes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Meiosis produces haploid cells with half the number of chromosomes of the parent. When cells combine during fertilization, the diploid chromosome number is restored. Before meiosis, chromosomes replicate, forming duplicated chromosomes, each made of two sister chromatids. During meiosis I, homologous duplicated chromosomes line up in pairs, forming a set of 4 chromatids. The homologous chromosomes separate, forming cells with half the normal number of chromosomes, but the chromosomes are still duplicated. In meiosis II, the sister chromatids separate, forming cells with half the normal number of unduplicated chromosomes.
Question
For sexually reproducing diploid parent cells, which of the following statements best explains the production of haploid cells that occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
A. Separation of chromatids occurs once, and there is one round of cell division in meiosis.
B. Separation of chromatids occurs twice, and there are two rounds of cell division in mitosis.
C. Separation of chromatids occurs once, and there are two rounds of cell division in meiosis.
D. Separation of chromatids occurs twice, and there is one round of cell division in mitosis.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Separation of chromatids occurs once in meiosis, and there are two rounds of cell division, which ensures that haploid gamete cells are formed in sexually reproducing diploid organisms.
Question
Which of the following best explains a distinction between metaphase I and metaphase II?
A. The nuclear membrane breaks down during metaphase I but not during metaphase II.
B. Chromosomes align at the equator of the cell during metaphase II but not during metaphase I.
C. The meiotic spindle is needed during metaphase I but not during metaphase II.
D. Homologous pairs of chromosomes are aligned during metaphase I, but individual chromosomes are aligned during metaphase II.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
During metaphase I, tetrads (homologous pairs of chromosomes) are aligned along the metaphase plate. During metaphase II, however, single chromosomes (each composed of two chromatids) are aligned along the metaphase plate.
Question
Table 1 shows the stage and number of cells and chromosomes per cell at the end of the stage in a 2n=24 organism.
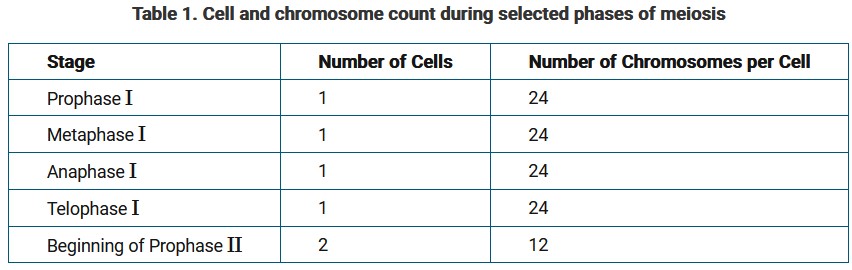
Which of the following statements correctly describes the chromosomes in each daughter cell at the end of meiosis I?
A. Each daughter cell contains 12 chromatids. Each chromatid is one of two from a single chromosome with the other one of the pair found in the other daughter cell.
B. Each daughter cell contains 12 chromosomes, each composed of two chromatids. Since the chromosomes were randomly divided, one daughter cell may contain both of a pair of homologous chromosomes, while the other cell contains both of another pair of homologous chromosomes.
C. Each daughter cell contains 12 chromosomes, each composed of two chromatids. Each chromosome is one of a pair of homologous chromosomes from the parent cell, with the other homologue found in the other daughter cell.
D. Each daughter cell contains 24 separate chromatids. Since every two chromatids were originally joined, forming one homologous chromosome, the number of chromatids is divided by two to determine the number of chromosomes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The described distribution of chromosomes ensures that each daughter cell contains a complete haploid genome. Each chromosome still consists of two chromatids, formed during the S phase of the cell cycle. Chromatids will separate into two daughter cells during meiosis II.
Question
Both mitosis and meiosis begin with a parent cell that is diploid. Which of the following best describes how mitosis and meiosis result in daughter cells with different numbers of chromosomes?
A. In mitosis, the chromosomes consist of a single chromatid, which is passed to two haploid daughter cells. In meiosis, the chromosomes consist of two chromatids during the first round of division and one chromatid during the second round of division, resulting in two haploid daughter cells.
B. In mitosis, synapsis of homologous chromosomes results in four haploid daughter cells after one division. In meiosis, synapsis of homologous chromosomes occurs during the second division and results in four diploid daughter cells.
C. Mitosis produces one identical daughter cell after one round of division. Meiosis has two rounds of division and doubles the number of chromosomes in the second round of division, producing four diploid cells.
D. Mitosis produces two identical diploid daughter cells after one round of division. Meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells after two rounds of division.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The function of mitosis is to produce identical daughter cells, while the function of meiosis is to produce gametes. Meiosis I reduces the chromosome number, and meiosis II separates the sister chromatids in the remaining chromosomes.
Question
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a diploid yeast species that can reproduce either sexually or asexually. An experiment was performed to induce mitotically dividing S. cerevisiae cells in \(G_2\) to undergo meiosis. Which of the following best describes the steps these cells will follow to form gametes?
A. The first division will result in crossing over between homologous chromosomes, and the second division will reduce the original number of chromosomes by half in the daughter cells.
B. The first division will reduce the number of chromosomes by half for each daughter cell, and the second division will result in each daughter cell having one-fourth of the original number of chromosomes.
C. The first division will move single chromatids to each daughter cell, and the second division will double the number of chromosomes in each daughter cell.
D. The first division will reduce the number of chromosomes by half for each daughter cell, and the second division will move single chromatids to each daughter cell.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The homologous pairs of chromosomes separate in meiosis I, resulting in two haploid daughter cells. The chromosomes had replicated prior to \(G_2\) and consist of two sister chromatids. The chromatids separate during meiosis II, resulting in a total of four haploid cells.
