Question.
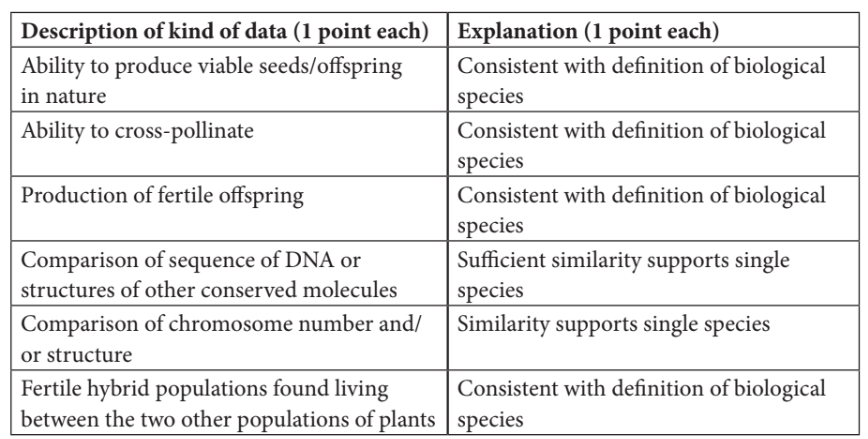
Populations of a plant species have been found growing in the mountains at altitudes above 2,500 meters. Populations of a plant that appears similar, with slight differences, have been found in the same mountains at altitudes below 2,300 meters.
(a) Describe TWO kinds of data that could be collected to provide a direct answer to the question, do the populations growing above 2,500 meters and the populations growing below 2,300 meters represent a single species?
(b) Explain how the data you suggested in part (a) would provide a direct answer to the question.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Question
Information flow in cells can be regulated by various mechanisms.
(a) Describe the role of THREE of the following in the regulation of protein synthesis:
- RNA splicing
- repressor proteins
- methylation
- siRNA
(b) Information flow can be altered by mutation. Describe THREE different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis.
(c) Identify TWO environmental factors that increase the mutation rate in an organism, and discuss their effect on the genome of the organism.
(d) Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in the phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the DNA sequence. Describe ONE example of epigenetic inheritance.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
When a segment of DNA is transcribed into RNA, the RNA can undergo slicing within the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. A complex called a spliceosome cuts segments out of the RNA strand and joins others together. The cut segment, called introns, do not leave the nucleus and aren’t expressed. The remaining segments called exons leave the nucleus to be translated into protein. Two identical RNA molecules can be spliced in different ways and translated into or become different functional products. Repressor proteins can bind to the promoter region of an operon in DNA preventing the attachment of RNA polymerase and / or transcription factors and preventing the expression of that gone, Repressor proteins may be always present. but capable of being activated or deactivated, making the affected operon repressible or inducible, respectively. Methylation of DNA is the attachment of methyl groups to DNA preventing its transcription by inhibiting RNA polymerase.
Missense mutations occur when the nucleotide sequence of a gene is changed at a point in such a way that the functional product of the gene changes in composition. Nonsense mutations occur when a codon within a gene is replaced with a stop codon that ends translation before the rest of the gene is expressed. A frameshift mutation occurs when a number of nucleotides that is not divisible by three is deleted or inserted from / into the gene, altering the way each codon of 3 nucleotides is read. This sort of mutation changes the functional product completely in most cases.
Exposure to radiation as the intake of certain chemicals such as heavy metals increase the rate of mutation in an organism. This potentially changes the DNA permanently, affecting the products of any affected gones;
The acetylation of histone tails in the nucleosomes of a chromosome is an example of epigenetic inheritance. The acetylation of histone proteins loosens the structure of a chromosome increasing the rate of expression of the more exposed genes.
