Question
Himalayan rabbits are a breed of rabbits with highly variable fur color. If genetically similar rabbits are raised in environments that have different temperature conditions, the rabbits can have different color patterns.
Which of the following statements best explains how the fur color can be different in Himalayan rabbits raised under different temperature conditions?
A. The genotype does not contribute to coat color in Himalayan rabbits.
B. The phenotype determines the genotype of coat color in Himalayan rabbits.
C. Different environments cause specific mutations in the genes controlling pigment production.
D. The environment determines how the genotype is expressed.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The environment influences gene activity, which leads to a change in the phenotype of fur color. Temperature is the most significant environmental factor in determining the coat color of these rabbits.
Question
The tadpoles of Mexican spadefoot toads are known to exhibit phenotypic plasticity depending on food availability. Tadpole mouthparts can vary significantly, prompting researchers to categorize them as either omnivore-morph or carnivore-morph. Carnivore-morph tadpoles are larger and have mouthparts that are better suited for predation. Remarkably, carnivore-morph tadpoles can change into omnivore-morph tadpoles when the food supply changes.
Which of the following best describes an advantage of the phenotypic plasticity displayed by the tadpoles?
A. It allows the tadpoles to change their genome in response to environmental pressures.
B. It enables the tadpoles to develop into a distinct species of toads.
C. It gives the tadpoles increased versatility with respect to diet.
D. It allows the tadpoles to delay metamorphosis until there is maximal food available for the adults.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Phenotypic plasticity during development is an adaptation in Mexican spadefoot toads that allows the tadpoles to best exploit the available resources in different environments.
Question
When a mustard plant seedling is transferred to an environment with higher levels of carbon dioxide, the new leaves have a lower stomata-to-surface-area ratio than do the seedling’s original leaves.
Which of the following best explains how the leaves from the same plant can have different stomatal densities when exposed to an elevated carbon dioxide level?
A. Increased photosynthesis leads to larger leaves that need more stomata for photosynthesis, leading to an increase in stomatal density.
B. Leaf growth is promoted through increased photosynthesis, but the genetically regulated rate of stomatal production is not altered, leading to a decrease in stomatal density.
C. Leaf growth is inhibited by decreased photosynthesis, and the genetically regulated rate of stomatal production remains the same, leading to an increase in stomatal density.
D. Leaf growth is inhibited by decreased photosynthesis, and the genetically regulated rate of stomatal production remains the same, leading to a decrease in stomatal density.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Elevated carbon dioxide levels promote leaf growth due to increased photosynthetic activity. If the number of stomata produced remains the same as the leaves grow larger, the stomatal density decreases. This is an example of phenotypic plasticity, which is an adaptive trait.
Question
An African violet grower observes that genetically identical African violet plants growing near the walls of the greenhouse have white flowers, that plants growing farther away from the walls have pale blue flowers, and that plants growing nearest the center of the greenhouse have dark blue flowers.
Which of the following best explains the differences in flower color of the African violets in the greenhouse?
A. Warmer temperatures result in genotypic alterations, which result in flower color differences.
B. The plants along the walls of the greenhouse are homozygous recessive and therefore have white flowers.
C. An enzyme responsible for flower color does not fold correctly in cooler temperatures, and the greenhouse is warmest in the center.
D. More light is available along the walls of the greenhouse, so the flowers need less pigment to absorb sunlight for photosynthesis
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
If an enzyme responsible for pigment production does not fold correctly in cooler temperatures, then the enzyme’s active site will not be in the correct shape and it will not be able to catalyze the required reaction effectively. If temperatures are cooler along the walls of the green house, then the flowers of plants along the walls will have less pigment.
Question
A scientist studying phenotypic variation in a species of butterfly observed that genetically identical caterpillars grown in similar cages but exposed to different colored lights developed into butterflies with differences in wing color and body size, as shown in Table 1.
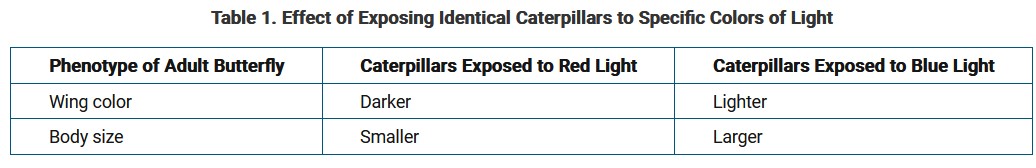
Which of the following best explains the cause of the phenotypic variation observed in the butterflies?
A. Different mutations occurred in the caterpillars that were exposed to different colors of light.
B. The energy used to grow a larger body results in butterflies with lighter colored wings.
C. Individual caterpillars evolved adaptations to survive in each of the light conditions they were exposed to.
D. There was differential gene expression of wing color and body size in response to the colors of light the caterpillars were exposed to.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Phenotype is a product of both genes and environment. Since the butterflies are genetically identical, their phenotype differences must be a product of the environment interacting with the genotype.
