Question
Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme that makes a complementary DNA copy of RNA in retroviruses. This DNA copy can then insert itself into
the genome of the host cell. Reverse transcriptase has a higher error rate than DNA polymerase, which results in more mutations in the DNA copy of the RNA. Reverse transcriptase is not typically used by eukaryotic cells for any function.
(a) Describe which nucleotides you would expect to find in the genome of a virus that uses reverse transcriptase.
(b) The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) contains RNA as its genetic material. Reverse transcriptase inhibitors have been shown to be effective in slowing the replication of HIV. Explain why reverse transcriptase inhibitors have few side effects in eukaryotic cells.
(c) Predict the rate of mutation in a retrovirus compared to that of a DNA virus.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) A virus that uses reverse transcriptase would have RNA as its
genetic material, so its genome would contain the nucleotides
adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil. (Thymine is not found in
RNA.)
(b) Eukaryotic cells contain DNA as their genetic material and do not
need to use reverse transcriptase to make a DNA copy of their
genetic material. Therefore, eukaryotic cells do not contain reverse
transcriptase. A reverse transcriptase inhibitor would have few, if
any, side effects on eukaryotic cells.
(c) Retroviruses would be expected to have a higher mutation rate than
that of DNA viruses.
(d) One reason why a retrovirus would be expected to have a higher
mutation rate than that of a DNA virus is because retroviruses use
reverse transcriptase to copy their genome. Reverse transcriptase is
less accurate and generates more mutations than DNA polymerase,
which would lead to a higher mutation rate in retroviruses.
Question
Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme that makes a complementary DNA copy of RNA in retroviruses. This DNA copy can then insert itself into
the genome of the host cell. Reverse transcriptase has a higher error rate than DNA polymerase, which results in more mutations in the DNA copy of the RNA. Reverse transcriptase is not typically used by eukaryotic cells for any function.
(a) Describe which nucleotides you would expect to find in the genome of a virus that uses reverse transcriptase.
(b) The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) contains RNA as its genetic material. Reverse transcriptase inhibitors have been shown to be effective in slowing the replication of HIV. Explain why reverse transcriptase inhibitors have few side effects in eukaryotic cells.
(c) Predict the rate of mutation in a retrovirus compared to that of a DNA virus.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) A virus that uses reverse transcriptase would have RNA as its
genetic material, so its genome would contain the nucleotides
adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil. (Thymine is not found in
RNA.)
(b) Eukaryotic cells contain DNA as their genetic material and do not
need to use reverse transcriptase to make a DNA copy of their
genetic material. Therefore, eukaryotic cells do not contain reverse
transcriptase. A reverse transcriptase inhibitor would have few, if
any, side effects on eukaryotic cells.
(c) Retroviruses would be expected to have a higher mutation rate than
that of DNA viruses.
(d) One reason why a retrovirus would be expected to have a higher
mutation rate than that of a DNA virus is because retroviruses use
reverse transcriptase to copy their genome. Reverse transcriptase is
less accurate and generates more mutations than DNA polymerase,
which would lead to a higher mutation rate in retroviruses.
Question.
Certain human conditions result from changes in the DNA sequence. The following is a segment of the template strand of an open reading frame of a functional gene.
3′ . . . GTT CAT CTA ACC CCT GAG GAG . . . 5′
(a) Using the segment shown above, determine the sequence of the corresponding mRNA sequence. Indicate the 5′ and 3′ ends.
(b) Using the table provided, determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide fragment.
(c) The mutation results in the following sequence:
3′ . . . GTT CAT CTA ACC CCT GTG GAG . . . 5′
Determine the change in the primary structure of the protein due to this mutation, and explain how this change may lead to a change in the function of the protein.
(d) Describe ONE common human genetic condition that is caused by this type of mutation, including the effect of the change in protein function on the health of the affected individual.
(e) Describe TWO techniques that can be used to identify the presence of this type of genetic change.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Certain human conditions result from changes in the DNA sequence. The following is a segment of the template strand of an open reading frame of a functional gene.
3′ . . . GTT CAT CTA ACC CCT GAG GAG . . . 5′
(a) Using the segment shown above, determine the sequence of the corresponding mRNA sequence. Indicate the 5′ and 3′ ends. (2 points maximum: 1 point for correct sequence with a maximum of one error; 1 point for proper orientation of the 5′ and 3′ ends)
5′ . . . CAA GUA GAU UGG GGA CUC CUC . . . 3′
(b) Using the table provided, determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide fragment. (2 points for
correct sequence; only 1 point if sequence contains an error)
gln – val – asp – trp – gly – his – leu
Changed AA may lead to a change in the structure of the protein. Possible elaboration points:
• Change is in the folding into the tertiary or quaternary structure.
• Some AA side groups are more important than others, e.g., cysteine forms disulfide bridges.
• Some AA can be interchanged with no effect on the structure due to lack of interactive side groups.
• Change to enzyme’s active or allosteric site is especially damaging.
• Others as appropriate.
(d)
Common conditions include:
• Tay-sachs
• Sickle-cell anemia
• Increased cancer risk (P53 gene)
• Cystic fibrosis
• Hemophilia
• Others as appropriate
(e)
Techniques include:
• Microarray assays to compare novel and mutant DNA
• DNA sequencing
• RFLP markers
• Presence of diagnostic phenotype
• Specific marker for mutated sequence
• Others as appropriate (Note: VNTR and Karyotyping are not appropriate techniques.)
Question
Scientists seeking to determine which molecule is responsible for the transmission of characteristics from one generation to the next knew that the molecule must (1) copy itself precisely, (2) be stable but able to be changed, and (3) be complex enough to determine the organism’s phenotype.
• Explain how DNA meets each of the three criteria stated above.
• Select one of the criteria stated above and describe experimental evidence used to determine that DNA is the hereditary material.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Essay 1
DNA replicates itself vising semiconservative replication. This means that each -parent strand of DNA will serve as the template for forming -resulting in daughter molecules that are 1/2 old DNA and 1/2 new. The DNA molecule is split down the middle by helicase, which breaks the hordir holding the complementang nucleotides together. Helicase functions in a 3′ to S’ direction, while the next step, synthells, occurs in a 5′ to 3′ direction, with 3° and s’ denoting the ends of the DNA moleate, A new strand is synthesized by DNA polymerase. which catalyzes the adding of new nucleotides to each half of the DNA molecule. Thus, each daughter DNA molecule wildentical to its parent, be of 11. The DNA molecule is held together in the middle by hydrogen hands between the 2 strands and nucleotides are attached to one another lengthwise down the mutecule by phosphodiester bords. Both of these bonds, pluss the coiling of the molecule, contribute to its stability, However, variation is possible due to mutations in the DNA, Mutations may be caused by a number of Sources, but may They all include the changing of the sequence of nucleotides, Hot Nucleotides be inserted into the chain, deleted, or translocated. Each of these mutations corresponds to a change in the structure of the protein that the gene codes for which may or may not have serious effects. adenine, guanine, cytosine, & thymine. DNA consists of 4 nucleotider – Adenine & quanine are purines, and have complementary structures to cytosine + thyming, which are pyrimidines (A pairs with Ti \(\sigma \) C pairs with G) Their four. a Molecule of DNA are responsible nucleotides, arranged in various sequences along for the incredible diversity of proteins that may be produced. Nucleotides code for proteins in triplets, or codons, Each amino acid corresponds to several different codons, (64 codons are possible, and 20 amino acids exist, with 2 codons signalling for “stop”) The phenotype of an organism wa result of the variations in the proteins produced in this way. Messelson & Stahl performed an experiment to prove Watson & Crick’s theory of semiconservative replication of the DNA indecile. They used a centrifuge to Separate DNA from bacteria. The DNA formed a band visible in the tube. When the bacteria were grown in a medium containing heavy nitrogen isotope (“N), the band was in a different place, when they allowed the bacteria to grow in the medium long enough for I generation of replication, the band formed was between the 2 light & heavy bands, suggesting that it consisted of 1/2 light & 1/2 heavy DNA One more replicationin a MN medium would result in only light + medium bands. showing that half of the strands were all new DNA, while the other half were hybrid light & heavy. This proved that each time, half of the DNA served as a template for replication of a new half of the nodewle.
Essay 2 DNA , a double helix shapped molecule composed of alternating base pair sequences, nucleotides consisting of a base phosphate backbone and sumple sugar, and linked in the midd be by hydrogen bonds (as proposed by Watson and Crick), can easily copy itself is fairly Stable, and very complex. By first wandering unzipping itself with the aid of DNA polymerase DNA is able to replicate having the complementary base pairs of ademing, guanine, thyanning and cytosine defach and being joined by other loose DNA strands on the leading 31 and lagging 5′ end. This semi-conservative replication is efficient, quick, and easy. polymerase, and helicase enzymes all aid in the unzipping, rebinding, and finishing of the replicated Strands. DNA is stable, having all the base pairs bound by the hydrogen Jouds and phosphate backbone. It is neither acidic non basic, isn’t radioactive, can be combined with other DNA strands from other sources (such as inking human DNA with bacteria strands during recombination). However, it is susceptible to gruetic #quence housed in the base as mutations change the information the change as pairs can be changed. sequence of the bases. Deletions can remove a base replicating strand, insertions. from a replicating may add an extra Intations, frame st many more. These base, inversions will reverse a sequence, point will e have change no the sequence and effect, but most often do as the change in may bases cause; a change in what amino acid, enzyme, or otherwise, is produced. This, it is stable but can be changed. Finally it is very complex a as Rach facet of one is within the system of bases of the DNA. These bases are them specifically assorted in ways numbering billions upon billions which depending on that assortment, codes for every aspect of the phenotype (physical expression of the genotype-genetic makeup of an organism). A simple shift, addition, deletion or change of in the genotype, and thus, a The complex system of buses and their of Larboring one or more of these bases causes a information was abrange change in He phenotype, and determined by Watson andd Crick whose theories and postulations on bonding the double helix shape of the DNA molecule deduced such information. And, the experiments of Menselson and Stahl deduced the semi-conservative reproductive replicative nature of DNA when they observed. replicating DNA in a liquid CA medhim and studied the effects.
Essay 3 DNA meets each of the criteria because it can copy itself through the process of ANA replication in which each half of the DNA strand serves as a template for a new complementary strand (semiconservative). It also has includes structures such as DNA ligase and helicase which check and fix BNA errors (along with DNA polymerase). The arrangement of hydrogen bonds, phosphates, and nitrogenous bases contribute to its stability. And the varying sequences of the bases allow DNA to be complex enough to determine an organism’s phenotype. The order of the bases dictate which amino-acids are produced therefore determing which phenotype is expressed, To determine that DNA was in fact the hereditary material used to determine the organism’s phenotype, a few scientists used bacteriophages incorporated with \(^{32}P\) and \(^{27}S\) Mixing a bacteria culture with the bacteriophages, the scientists were able to determine whether DNA was the hereditary material by tracing the movement of of the isotopes (\(^{32}P\) and \(^{27}S\)). The 320 was wincorporated into the bacteriophage’s DNA while the \(^{32}S\) combined with another cellular organelle. from the new colonies, produced by the infected bacteria, only \(^{32}P\) was present indicating that the DNA from the “parent bacteria colony was replicated and produced in the “daughter” bacteria colony. Therefore, DNA had to be the genetic material.
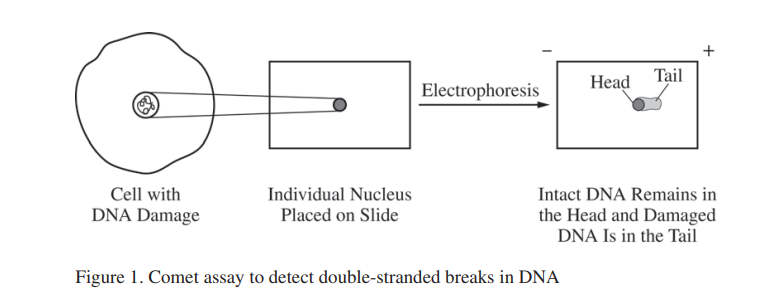
Question:
A comet assay is a technique used to determine the amount of double-strand breaks in DNA (DNA damage) in cells. The nucleus of an individual cell is placed on a microscope slide coated with an agarose gel. An electric current is applied to the gel that causes DNA to move (electrophoresis), and the DNA is stained with a fluorescent dye. When viewed using a microscope, undamaged DNA from the nucleus appears as a round shape (the head), and the fragments of damaged DNA extend out from the head (the tail). The length of the tail corresponds to the amount of the damage in the DNA (see Figure 1).
(a) To explain the movement of DNA fragments in the comet assay, identify one property of DNA and provide reasoning to support how the property contributes to the movement during the comet assay technique.
(b) In a different experiment, cells are treated with a chemical mutagen that causes only nucleotide substitutions in DNA. Predict the likely results of a comet assay for this treatment.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) DNA is negative, therefore when applying an electric current, DNA will move towards a positive charge. Smaller pieces of DNA move through the agarose gel more easily than larger pieces, which is why the smaller, damaged fragments of DNA are drawn out more towards the positive charge (the tail)
(b) All of the DNA will remain in the head (nucleus) because with only nucleotide substitutions, there won’t be any damaged fragments to travel outside as a tail. The nucleotide substitutions will allow the DNA to remain intact, just mutated.

Question:
A comet assay is a technique used to determine the amount of double-strand breaks in DNA (DNA damage) in cells. The nucleus of an individual cell is placed on a microscope slide coated with an agarose gel. An electric current is applied to the gel that causes DNA to move (electrophoresis), and the DNA is stained with a fluorescent dye. When viewed using a microscope, undamaged DNA from the nucleus appears as a round shape (the head), and the fragments of damaged DNA extend out from the head (the tail). The length of the tail corresponds to the amount of the damage in the DNA (see Figure 1).
(a) To explain the movement of DNA fragments in the comet assay, identify one property of DNA and provide reasoning to support how the property contributes to the movement during the comet assay technique.
(b) In a different experiment, cells are treated with a chemical mutagen that causes only nucleotide substitutions in DNA. Predict the likely results of a comet assay for this treatment.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) DNA is negative, therefore when applying an electric current, DNA will move towards a positive charge. Smaller pieces of DNA move through the agarose gel more easily than larger pieces, which is why the smaller, damaged fragments of DNA are drawn out more towards the positive charge (the tail)
(b) All of the DNA will remain in the head (nucleus) because with only nucleotide substitutions, there won’t be any damaged fragments to travel outside as a tail. The nucleotide substitutions will allow the DNA to remain intact, just mutated.
