Question
Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme that makes a complementary DNA copy of RNA in retroviruses. This DNA copy can then insert itself into the genome of the host cell. Reverse transcriptase has a higher error rate than DNA polymerase, which results in more mutations in the DNA copy of the RNA. Reverse transcriptase is not typically used by eukaryotic cells for any function.
(a) Describe which nucleotides you would expect to find in the genome of a virus that uses reverse transcriptase.
(b) The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) contains RNA as its genetic material. Reverse transcriptase inhibitors have been shown to be effective in slowing the replication of HIV. Explain why
reverse transcriptase inhibitors have few side effects in eukaryotic cells.
(c) Predict the rate of mutation in a retrovirus compared to that of a DNA virus.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) A virus that uses reverse transcriptase would have RNA as its
genetic material, so its genome would contain the nucleotides
adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil. (Thymine is not found in
RNA.)
(b) Eukaryotic cells contain DNA as their genetic material and do not
need to use reverse transcriptase to make a DNA copy of their
genetic material. Therefore, eukaryotic cells do not contain reverse
transcriptase. A reverse transcriptase inhibitor would have few, if
any, side effects on eukaryotic cells.
(c) Retroviruses would be expected to have a higher mutation rate than
that of DNA viruses.
(d) One reason why a retrovirus would be expected to have a higher
mutation rate than that of a DNA virus is because retroviruses use
reverse transcriptase to copy their genome. Reverse transcriptase is
less accurate and generates more mutations than DNA polymerase,
which would lead to a higher mutation rate in retroviruses.
Question
An experiment is conducted to study the effect of a ligase inhibitor on
DNA replication.
(a) Describe the function of ligase in DNA replication.
(b) Identify an appropriate control for this experiment.
(c) Predict which strand of the DNA would be most affected by a
ligase inhibitor.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) The function of ligase in DNA replication is to join the fragments
created during replication of the lagging strand in DNA.
(b) An appropriate control would be to conduct replication of the same
DNA sequence without the presence of the ligase inhibitor.
(c) The lagging strand of DNA would be most affected by a ligase
inhibitor.
(d) Replication of the lagging strand of DNA would produce multiple
short fragments that would need to be joined by ligase. An inhibitor
of ligase would prevent this from happening.
Question
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) uses a heat-stable DNA polymerase
and repeated cycles of DNA replication to amplify specific sequences
of DNA. Primers specific to the desired DNA sequences are used to
direct DNA polymerase to the beginning of the sequence to be
amplified. The following table shows the number of copies of the
DNA sequence that exist at the end of each cycle.
| Number of Cycles of DNA Replication | Number of Copies of Desired DNA Sequence |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 8 |
| 4 | 16 |
| 5 | 32 |
| 6 | 64 |
| 7 | 128 |
(a) Explain why a primer is needed to direct DNA polymerase to
copy the desired sequence.
(b) Construct a graph of the data from the table.
(c) Analyze the data, and state the mathematical relationship between
the number of cycles of PCR and the number of copies of the
desired DNA sequence generated.
(d) Predict the minimum number of cycles required to generate 1,000
copies of the desired DNA sequence. Justify your prediction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) DNA polymerase needs a 3′ hydroxyl group to which it can add
new nucleotides, so a primer is necessary to allow DNA
polymerase to add the first new nucleotide.
(b)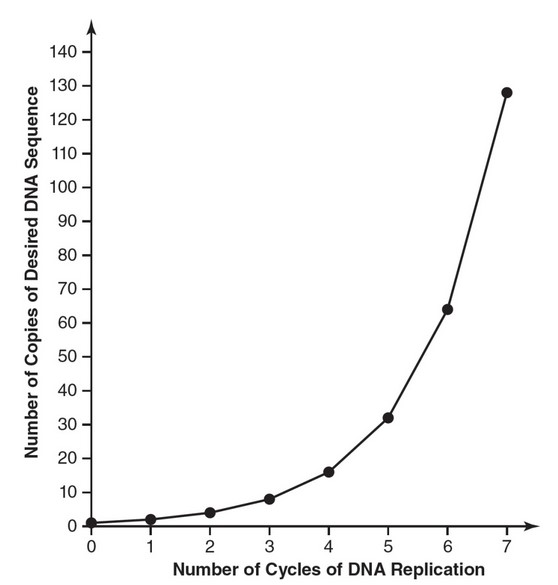
(c) Each cycle of PCR doubles the number of copies of the desired
DNA sequence. In other words, this is an exponential growth
relationship.
(d) Since the number of copies of the desired DNA sequence doubles
with each cycle, a minimum of 10 cycles would be required to
produce at least 1,000 copies. After 8 cycles, 256 copies would be
present. After 9 cycles, 512 copies would be present, and after 10
cycles, 1,024 copies would be present.
