Question
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) type IV is a result of a mutation in the COL3A1 gene, which results in the deletion of one of the exons in the
procollagen transcript.
(a) Describe the location in the cell where the splicing of exons occurs.
(b) Explain the difference between exons and introns.
(c) Predict the effect of the EDS mutation on the structure of the procollagen protein.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) The splicing of exons occurs in the nucleus.
(b) The codons in exons are expressed in the protein and code for
amino acids in the protein. Introns are noncoding sequences and do
not code for amino acids in the protein.
(c) The EDS mutation would result in a shorter, less functional
procollagen protein.
(d) If an exon was deleted, the resulting mRNA transcript would not
contain the complete code for the protein. So the translated protein
would be shorter and likely less functional.
Question
The levels of mRNA and protein produced by three different genes (PDHA1, MBP, and INS) were measured in different tissues of the human body. The levels of mRNA and protein expression from these genes were compared to mRNA and protein expression from the gene POLR2A (RNA polymerase II subunit A, which is expressed in all human tissues). The results are shown in the table. “0” indicates that mRNA or protein were not detected in that tissue, and “+,” “++,” and “+++” indicate relatively low, medium, or high levels of mRNA or protein detected, respectively.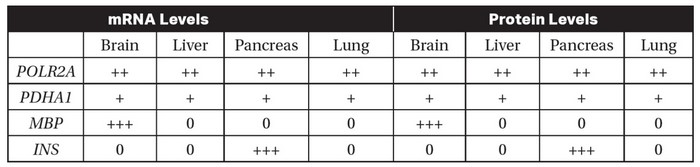
(a) Identify which gene was used as a control in this experiment.
(b) Explain why the gene you selected in part (a) would be an appropriate control for this experiment.
(c) Based on the data in the table, determine which of the genes (PDHA1, MBP, or INS) is most likely involved in glycolysis.
(d) INS is the insulin gene. Insulin is a hormone that is released when blood sugar levels are high. Predict the levels of INS mRNA and protein that would be found in cells in the pancreas when blood sugar levels are low. Justify your prediction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) POLR2A was used as the control because the expression of all the other genes was compared to the expression of POLR2A.
(b) POLR2A would be the best gene to use as a control because it is
known to be expressed in all human tissues, as stated in the
question.
(c) PDHA1 is most likely involved in glycolysis because glycolysis
occurs in the cytoplasm of all living cells, and PDHA1 is expressed
in all the tissues in the experiment.
(d) Since insulin is released when blood sugar levels are high, it is
likely that the levels of insulin would be low when blood sugar
levels are low. Therefore, when blood sugar levels are low, it is
expected that both the INS mRNA and the insulin protein levels
would be low.
Question.
Certain human conditions result from changes in the DNA sequence. The following is a segment of the template strand of an open reading frame of a functional gene.
3′ . . . GTT CAT CTA ACC CCT GAG GAG . . . 5′
(a) Using the segment shown above, determine the sequence of the corresponding mRNA sequence. Indicate the 5′ and 3′ ends.
(b) Using the table provided, determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide fragment.
(c) The mutation results in the following sequence:
3′ . . . GTT CAT CTA ACC CCT GTG GAG . . . 5′
Determine the change in the primary structure of the protein due to this mutation, and explain how this change may lead to a change in the function of the protein.
(d) Describe ONE common human genetic condition that is caused by this type of mutation, including the effect of the change in protein function on the health of the affected individual.
(e) Describe TWO techniques that can be used to identify the presence of this type of genetic change.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Certain human conditions result from changes in the DNA sequence. The following is a segment of the template strand of an open reading frame of a functional gene.
3′ . . . GTT CAT CTA ACC CCT GAG GAG . . . 5′
(a) Using the segment shown above, determine the sequence of the corresponding mRNA sequence. Indicate the 5′ and 3′ ends. (2 points maximum: 1 point for correct sequence with a maximum of one error; 1 point for proper orientation of the 5′ and 3′ ends)
5′ . . . CAA GUA GAU UGG GGA CUC CUC . . . 3′
(b) Using the table provided, determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide fragment. (2 points for
correct sequence; only 1 point if sequence contains an error)
gln – val – asp – trp – gly – his – leu
Changed AA may lead to a change in the structure of the protein. Possible elaboration points:
• Change is in the folding into the tertiary or quaternary structure.
• Some AA side groups are more important than others, e.g., cysteine forms disulfide bridges.
• Some AA can be interchanged with no effect on the structure due to lack of interactive side groups.
• Change to enzyme’s active or allosteric site is especially damaging.
• Others as appropriate.
(d)
Common conditions include:
• Tay-sachs
• Sickle-cell anemia
• Increased cancer risk (P53 gene)
• Cystic fibrosis
• Hemophilia
• Others as appropriate
(e)
Techniques include:
• Microarray assays to compare novel and mutant DNA
• DNA sequencing
• RFLP markers
• Presence of diagnostic phenotype
• Specific marker for mutated sequence
• Others as appropriate (Note: VNTR and Karyotyping are not appropriate techniques.)
