Question
One way that organisms respond to changing environmental conditions is through the regulation of gene expression.
(a) Describe the function of operators and promoters in prokaryotes.
(b) Explain how the operator and repressor interact to control the expression of the inducible lac operon.
(c) Bacteria are placed in an environment that has low levels of glucose and high levels of lactose. Predict the level of expression of the lac operon in this environment.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) Operators serve as binding sites for repressor proteins. Promoters
are binding sites for RNA polymerase.
(b) When the repressor is bound to the operator, it blocks RNA
polymerase’s access to the structural genes, and the operon is shut
down.
(c) The level of expression of the lac operon will be high.
(d) Lactose is the inducer and will bind to the repressor, removing it
from the operator and allowing the operon to be expressed. Low
glucose levels will lead to high levels of cAMP, which will activate
the catabolite activator protein, increasing the expression of the lac
operon even more.
Question
A student conducts an experiment in an effort to determine whether a specific bacterial operon is inducible or repressible. The level of
transcription of the operon was measured after the addition of different molecules to the bacteria’s environment. Data are shown in the table.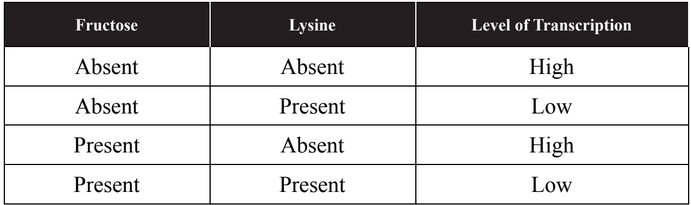
(a) Describe what, if any, effect levels of fructose have on the level of transcription of the operon.
(b) Describe what, if any, effect levels of lysine have on the level of transcription of the operon.
(c) Make a claim about whether this operon is more likely inducible or repressible.
(d) Justify your claim from part (c) using evidence from the experiment and your knowledge of inducible and repressible operons.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) Based on the data in the table, fructose appears to have no effect on
the level of transcription.
(b) The level of transcription is higher when lysine is absent and lower
when lysine is present. Therefore, lysine has a negative effect on
the level of transcription.
(c) This operon is more likely repressible.
(d) Repressible operons have a lower level of expression when the
corepressor is present. Since the presence of lysine decreases the
level of expression of the operon, it is more likely that the operon is
repressible.
Question
The human THY-1 gene (Thy-1 cell surface antigen) codes for a cell surface glycoprotein that is thought to function as a tumor suppressor
in certain types of cancer. In order to find possible locations of enhancer sequences for the THY-1 gene, scientists performed a series
of DNA deletion experiments. In the experiments, different deletions were made in areas that were suspected to function as possible
enhancer sequences, and the levels of THY-1 transcription were measured after each deletion. The following diagram shows the
sequences deleted. A, B, C, D, and E represent different DNA sequences. 1, 2, and 3 represent suspected enhancer sequences. P is the
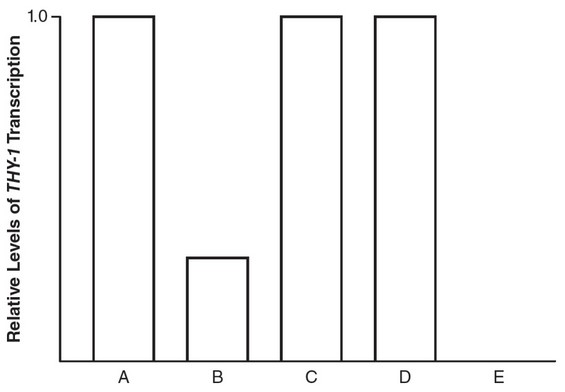
promoter of the THY-1 gene. An X represents the deletion of that portion of the DNA sequence.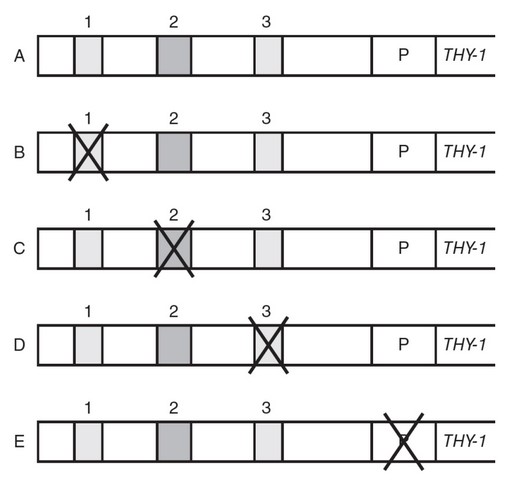
The levels of THY-1 transcription in each part of the experiment are shown in the graph.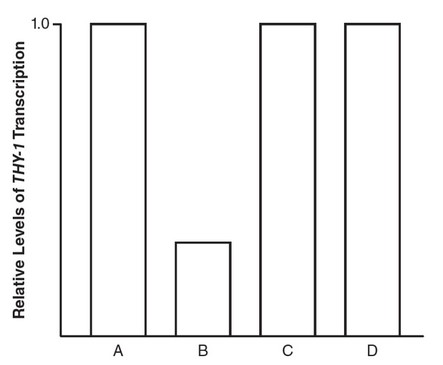
(a) Explain the function of enhancer sequences in eukaryotic gene expression.
(b) Identify which DNA sequence (A, B, C, D, or E) was the control in this experiment.
(c) Which sequence (1, 2, or 3) most likely functions as an enhancer sequence? Support your claim using analysis from the data.
(d) Predict the effects of the deletion of P, as shown in sequence E, and what the relative level of THY-1 transcription would be for E. Justify your prediction with evidence from the data.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) Enhancer sequences function as binding sites for activator proteins
or transcription factors. When an activator or transcription factor
binds to an enhancer site, more transcription of the gene occurs.
(b) DNA sequence A is the control because none of the sequences are
deleted.
(c) Sequence 1 is most likely the enhancer sequence because the
relative levels of THY-1 gene transcription are lower when
sequence 1 is deleted than when sequence 2 or sequence 3 is
deleted.
(d) Promoters serve as binding sites for RNA polymerase. If RNA
polymerase cannot bind, transcription cannot occur. If P were
deleted, no transcription of THY-1 would occur, as shown in the
following figure.