AP Biology 7.3 Artificial Selection Study Notes - New Syllabus Effective 2025
AP Biology 7.3 Artificial Selection Study Notes – New syllabus
AP Biology 7.3 Artificial Selection Study Notes – AP Biology – per latest AP Biology Syllabus.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Explain how humans can affect diversity within a population.
Key Concepts:
- Artificial Selection
7.3.A – Artificial Selection & Human Impact on Diversity
🧠 What Is Artificial Selection?
Artificial selection is when humans intentionally choose which traits get passed on in plants, animals, or other organisms.
📌 Unlike natural selection, which is driven by the environment, artificial selection is driven by human preferences.
🌾 How It Works:
- Humans select individuals with traits they like (e.g., size, color, behavior).
- These individuals are bred together.
- Offspring with the desired traits are kept, others are removed.
- Over generations, the trait becomes more common.
🔁 Real-Life Examples:
| Example | Trait Selected | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Dogs | Temperament, size | Huge variety of dog breeds |
| Corn | Bigger kernels | High-yield crops |
| Cows | Milk production | Cows that produce more milk |
| Strawberries | Sweetness | Sweeter, larger fruits |
| Chickens | Growth rate | Chickens that grow faster |
🌍 Human Impact on Genetic Diversity:
🔻 Reduced Genetic Variation
- Selecting only a few individuals to breed = gene pool gets smaller
- Populations become more genetically uniform
⚠️ Increased Risk
- Less diversity = more vulnerable to diseases, climate change, or pests
- One disease can wipe out a whole population (e.g., bananas 🍌 or potato blight)
🧬 Unintended Consequences
- Traits selected for beauty or productivity may come with health issues
- (e.g., flat-faced dogs with breathing problems)
💡 Summary:
- Artificial selection = human-controlled breeding for certain traits
- Can increase useful traits, but often reduces genetic diversity
- Populations may become less resilient to environmental changes or disease
7.3.A.1 — Artificial Selection & Human Impact on Variation
🌱 What Is Artificial Selection?
Artificial selection is when humans intentionally select which traits should be passed on to the next generation — by choosing specific individuals to breed based on desired characteristics.
📌 Unlike natural selection, it’s not random and not based on survival — it’s driven by human preferences.
🌿 Classic Example: Wild Mustard Plant
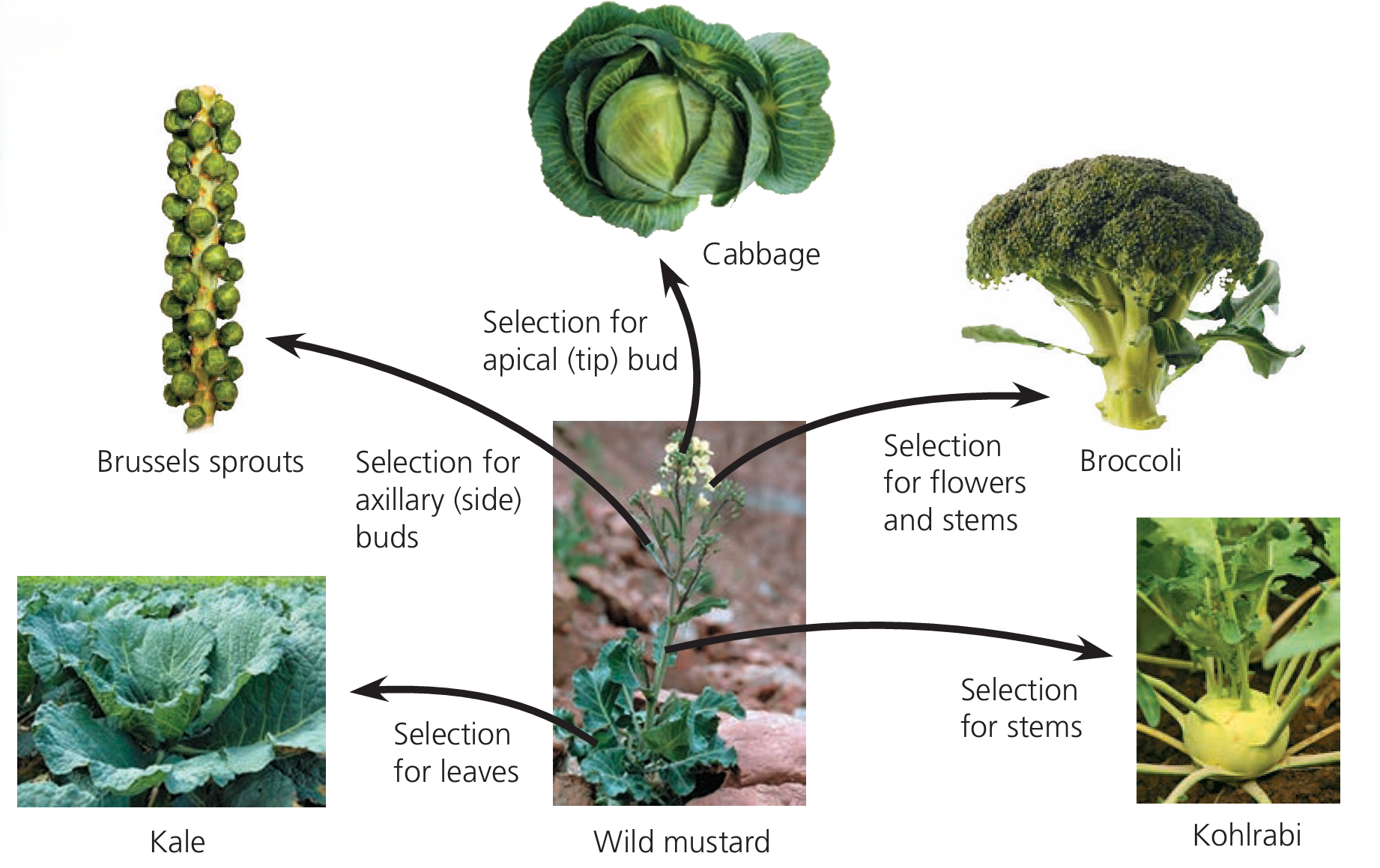 Humans took one species – wild mustard – and created many vegetables by selecting for specific traits:
Humans took one species – wild mustard – and created many vegetables by selecting for specific traits:
| Selected Trait | Resulting Vegetable |
|---|---|
| Enlarged flower buds and stems | Broccoli |
| Large flower clusters | Cauliflower |
| Enlarged leaves | Kale |
| Swollen stems | Kohlrabi |
| Large apical (tip) bud | Cabbage |
| Large axillary (side) buds | Brussels sprouts |
🎯 This shows how artificial selection can create huge diversity from a single species by selecting phenotypic variations.
🔬 Effects of Artificial Selection:
✅ Positive Outcomes:
- Improved crop yields
- Better traits (taste, appearance, size)
- Taming of wild animals into pets
⚠️ Negative Outcomes:
- Reduced genetic diversity – making species more vulnerable
- Health issues – like breathing problems in flat-faced dogs (pugs, bulldogs)
- Traits that may not be adaptive in natural environments
🧬 Key Takeaway:
Artificial selection is a powerful example of how humans directly influence evolution – by shaping the genetic variation within a population based on our needs and preferences.
