AP Biology 7.8 Continuing Evolution Study Notes - New Syllabus Effective 2025
AP Biology 7.8 Continuing Evolution Study Notes- New syllabus
AP Biology 7.8 Continuing Evolution Study Notes – AP Biology – per latest AP Biology Syllabus.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Explain how evolution is an ongoing process in all living organisms.
Key Concepts:
- Continuing Evolution
7.8.A – Evolution is an Ongoing Process in All Living Organisms
🎯 Big Idea:
Evolution isn’t something that only happened in the past – it’s still happening right now in every population, even in humans!
🔁 Why is Evolution Still Happening?
- Populations keep changing over time: As environments shift, so do the selective pressures. New mutations, diseases, or climate conditions force species to adapt or risk extinction.
- Genetic variation never stops: Mutations constantly introduce new traits. Some of these traits increase an organism’s ability to survive and reproduce, and natural selection acts on them.
- Interactions drive evolution: Predators vs. prey, pathogens vs. hosts, and competition between species all push organisms to evolve.
- Example: Bacteria evolving resistance to antibiotics.
🌿 Real-Life Examples of Ongoing Evolution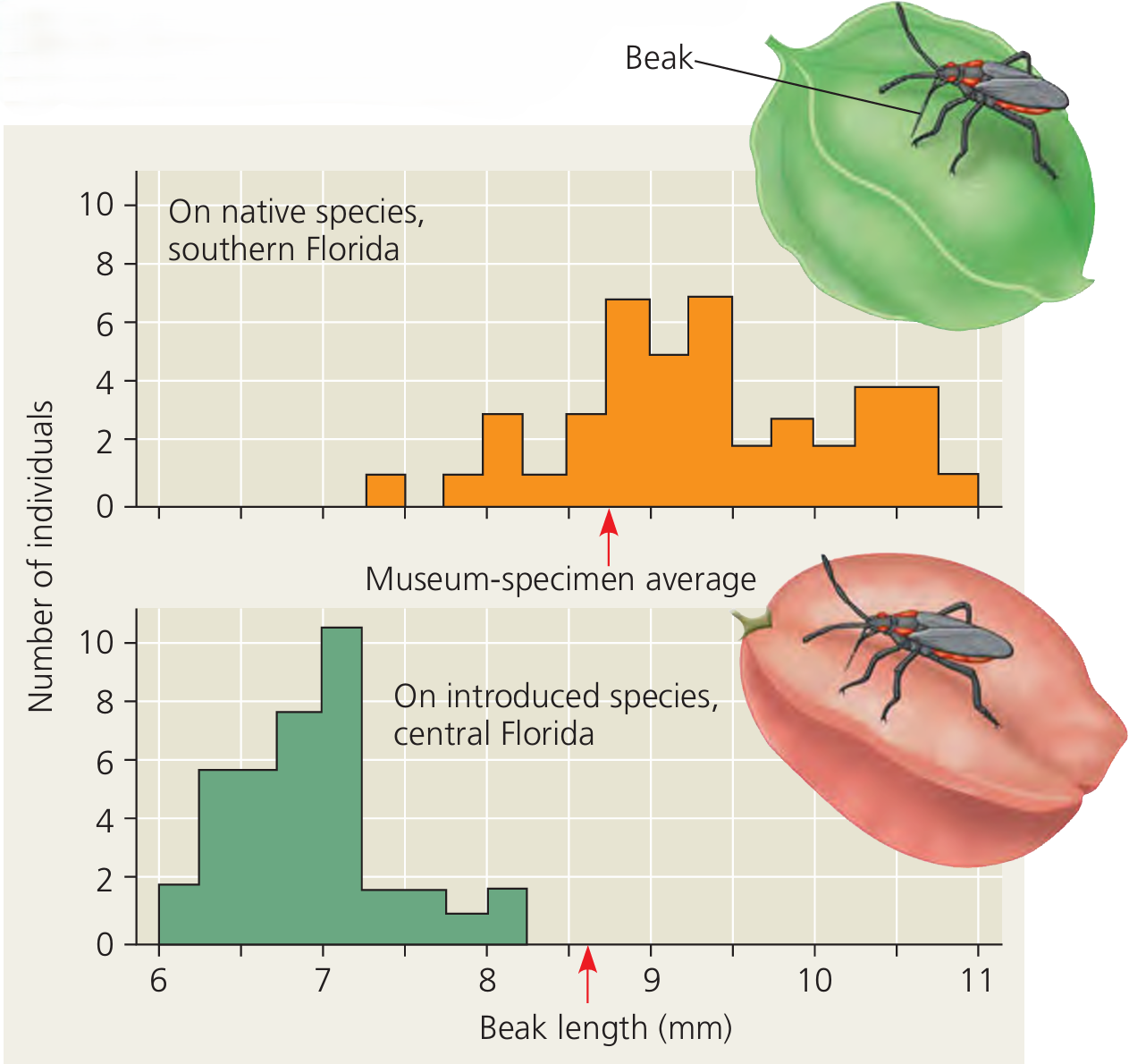
| Example | How It Shows Evolution |
|---|---|
| 🦠 Bacteria and Antibiotics | Bacteria evolve resistance due to overuse of antibiotics. |
| 🐦 Finches in Galápagos | Beak size changes in response to food availability (even observed over a few years!). |
| 🌾 Pesticide Resistance | Insects evolve resistance, requiring stronger or different pesticides. |
| 👨👩👧👦 Humans | Genes related to disease resistance, skin color, and altitude tolerance still evolving. |
🧠 Key Takeaway:
Evolution never stops. Every generation brings new variation, and natural selection, genetic drift, and gene flow continue to shape life on Earth.
7.8.A.1 – Evidence That Evolution Is Ongoing
🎯Main Idea:
All species including humans have evolved and are still evolving. We can actually observe evolution in real time with modern tools and data!
🧪 1. Genomic Changes Over Time
- DNA sequencing helps us compare genomes over generations.
- Small mutations, gene duplications, or chromosomal rearrangements show how populations change.
- These changes can result in:
- New traits 🧬
- Better survival ✅
- Or even new species 🆕
- Example: Comparing ancient human DNA to modern DNA shows how we adapted to things like digesting milk (lactase persistence) or resisting certain viruses.
🦴 2. Continuous Change in the Fossil Record
- Fossils show a timeline of gradual change in organisms over millions of years.
- Transitional fossils show in-between forms (like Tiktaalik between fish and amphibians).
- Newer layers of rock show newer species – proof of long-term evolution.
- Example: Fossils of horses show step-by-step evolution of size, teeth, and hooves over 50 million years.
💊 3. Evolution of Resistance
- Organisms evolve resistance when exposed to strong selection pressures like:
- Antibiotics (for bacteria)
- Pesticides (for insects)
- Herbicides (for plants)
- Chemotherapy (for cancer cells)
- Over time, only the resistant individuals survive and reproduce – making the treatment less effective.
- Example: MRSA (a type of antibiotic-resistant bacteria) evolved in hospitals due to overuse of antibiotics.
🦠 4. Pathogens Causing New Diseases
- Viruses and bacteria mutate quickly.
- These changes can lead to new strains that cause emerging infectious diseases.
- Example:
- SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19 virus) evolved into many variants (Delta, Omicron).
- Flu viruses evolve every year – we need a new vaccine annually.
