Question
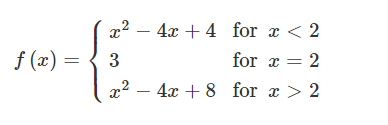
Let f be the piecewise function defined above. The value of \(\lim_{x \to 2^{+}}f(x)\) is
A) 0
B) 3
C) 4
D) non existent
B) 3
C) 4
D) non existent
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution
Correct Answer: C
Solution:
For the right-hand limit (x→2⁺), we use the x > 2 case:
f(x) = x² – 4x + 8
Evaluating the limit:
\(\lim_{x \to 2^{+}} (x^2 – 4x + 8) = 2^2 – 4(2) + 8 = 4 – 8 + 8 = 4\)
Key Concept:
Right-hand limits only consider the function definition for values approaching from above the point.
Question
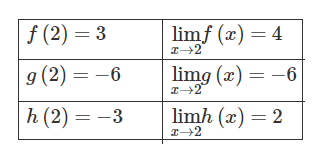
The table above gives selected values and limits of the functions f, g, and h. What is \(\lim_{x \to 2}(h(x)(5f(x)+g(x)))\)?
A) -27
B) -20
C) 28
D) 34
B) -20
C) 28
D) 34
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution
Correct Answer: C
Step-by-Step Solution:
1. Break down the limit using limit laws:
\(\lim_{x \to 2}(h(x)(5f(x)+g(x))) = \lim_{x \to 2}h(x) \times (5\lim_{x \to 2}f(x) + \lim_{x \to 2}g(x))\)
2. Substitute values from the table:
\(= 2 \times (5 \times 4 + (-6))\)
\(= 2 \times (20 – 6)\)
\(= 2 \times 14 = 28\)
Key Concept:
The limit of a product/sum can be evaluated as the product/sum of limits when all individual limits exist. Note that function values (f(2), g(2), h(2)) are irrelevant when the limits exist.
Question
\(\lim_{x \to -3}\left(\frac{x^{2}-9}{x^2-2x-15}\right)\)
A) 0
B) \(\frac{3}{5}\)
C) \(\frac{3}{4}\)
D) 1
E) non existent
B) \(\frac{3}{5}\)
C) \(\frac{3}{4}\)
D) 1
E) non existent
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution
Correct Answer: C
Factor numerator and denominator:
\(\frac{x^{2}-9}{x^2-2x-15} = \frac{(x+3)(x-3)}{(x+3)(x-5)}\)
\(= \frac{x-3}{x-5}\) for x ≠ -3
Evaluate the limit:
\(\lim_{x \to -3} \frac{x-3}{x-5} = \frac{-6}{-8} = \frac{3}{4}\)
Question
If f is the function defined by \(f(x)=\frac{x^{2}-4}{x^2+x-6}\), then \(\lim_{x \to 2}f(x)\) is:
A) 0
B) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
C) \(\frac{4}{5}\)
D) non existent
B) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
C) \(\frac{4}{5}\)
D) non existent
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution
Correct Answer: C
Simplify the function:
\(f(x) = \frac{(x-2)(x+2)}{(x+3)(x-2)}\)
\(= \frac{x+2}{x+3}\) for x ≠ 2
Evaluate the limit:
\(\lim_{x \to 2} \frac{x+2}{x+3} = \frac{4}{5}\)
Key Concept:
Simplifying rational functions before evaluating limits
Question
\(\lim_{x \to -4}{\frac{x+4}{x^3-16x}}\) is
A) 0
B) \(\frac{1}{32}\)
C) 1
D) non existent
B) \(\frac{1}{32}\)
C) 1
D) non existent
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution
Correct Answer: B
Factor the denominator:
\(\frac{x+4}{x^3-16x} = \frac{x+4}{x(x-4)(x+4)}\)
\(= \frac{1}{x(x-4)}\) for x ≠ -4
Evaluate the limit:
\(\lim_{x \to -4} \frac{1}{x(x-4)} = \frac{1}{-4(-4-4)} = \frac{1}{32}\)
