AP Calculus AB 2.6 Derivative Rules: Constant, Sum, Difference, and Constant Multiple - MCQs - Exam Style Questions
No-Calc Question
(B) \(2x^{3}\tan^{2}(2x)+3x^{2}\sec(2x)\)
(C) \(x^{3}\sec(2x)\tan(2x)+3x^{2}\sec(2x)\)
(D) \(2x^{3}\sec(2x)\tan(2x)+3x^{2}\sec(2x)\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Product rule: \((x^{3})’\sec(2x)+x^{3}\,(\sec(2x))’\).
\((x^{3})’=3x^{2}\).
\((\sec(2x))’=\sec(2x)\tan(2x)\cdot 2\).
Combine: \(3x^{2}\sec(2x)+2x^{3}\sec(2x)\tan(2x)\).
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
The graph of the function f, consisting of two line segments, is shown below.
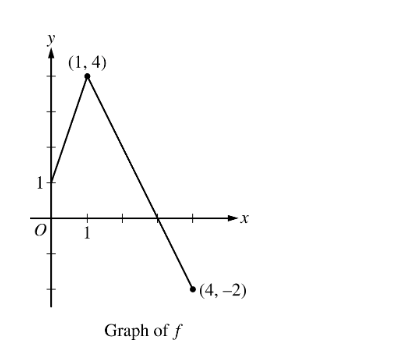
Let \( g(x) = 2x + 1 \), and let \( h(x) = f(g(x)) \). What is the value of \( h'(1) \)?
A) -4
B) -2
C) 4
D) 6
E) nonexistent
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution
Correct Answer: A
Step 1: Use the chain rule: \( h(x) = f(g(x)) \Rightarrow h'(x) = f'(g(x)) \cdot g'(x) \)
Step 2: Evaluate \( g(1) \):
\[ g(1) = 2(1) + 1 = 3 \]
Step 3: Compute the slope of \( f(x) \) at \( x = 3 \). The segment from (1, 4) to (4, -2) has a slope of:
\[ \frac{-2 – 4}{4 – 1} = \frac{-6}{3} = -2 \Rightarrow f'(3) = -2 \]
Step 4: Compute \( h'(1) = f'(g(1)) \cdot g'(1) = f'(3) \cdot 2 = -2 \cdot 2 = -4 \)
