Trapezoidal Rule
Let $f$ be continuous on $[a, b]$. The trapezoidal rule for approximating $\int_a^b f(x) d x$ is given by
$
\int_a^b f(x) d x=\frac{\Delta x}{2}\left[f\left(x_0\right)+2 f\left(x_1\right)+2 f\left(x_2\right)+\cdots+2 f\left(x_{n-1}\right)+f\left(x_n\right)\right],
$
where $x_0=a, x_1=a+\Delta x, x_2=a+2 \Delta x, \ldots, x_{n-1}=a+(n-1) \Delta x, x_n=b$, and $\Delta x=\frac{b-a}{n}$.
Example1
- Use the trapezoidal rule to approximate the integral $\int_1^3 \sqrt{1+x^2} d x$ with four subintervals.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution
$
\begin{aligned}
& \Delta x=\frac{b-a}{n}=\frac{3-1}{4}=\frac{1}{2} \\
& x_0=1, x_1=1+0.5=1.5, x_2=1+2(0.5)=2, x_3=1+3(0.5)=2.5, \\
& \text { and } x_4=1+4(0.5)=3 . \\
& \int_1^3 \sqrt{1+x^2} d x \approx \frac{\Delta x}{2}[f(1)+2 f(1.5)++2 f(2)++2 f(2.5)+f(3)] \\
& =\frac{1}{4}[\sqrt{2}+2 \sqrt{3.25}+2 \sqrt{5}+2 \sqrt{7.25}+\sqrt{10}] \\
& \approx 4.509
\end{aligned}
$
Example2
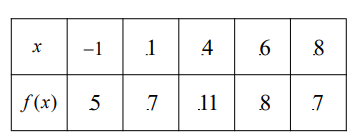
The function $f$ is continuous on the closed interval $[-1,8]$ and has values that are given in the table above. What is the trapezoidal approximation of $\int_{-1}^8 f(x) d x$ ?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution
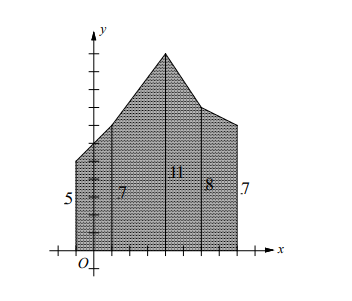
Make a sketch and use the formula for the area of trapezoid.
$
\begin{aligned}
\text { Area } & =\frac{1}{2}(5+7)(2)+\frac{1}{2}(7+11)(3) \\
& +\frac{1}{2}(11+8)(2)+\frac{1}{2}(8+7)(2) \\
& =12+27+19+15=73
\end{aligned}
$
Example3
- If four equal subdivisions on $[0,2]$ are used, what is the trapezoidal approximation of $\int_0^2 e^x d x$ ?
(A) $\frac{1}{4}\left[1+2 \sqrt{e}+2 e+2 e \sqrt{e}+e^2\right]$
(B) $\frac{1}{2}\left[1+2 \sqrt{e}+2 e+2 e \sqrt{e}+e^2\right]$
(C) $\frac{1}{4}\left[1+\sqrt{e}+e+e \sqrt{e}+e^2\right]$
(D) $\frac{1}{2}\left[1+\sqrt{e}+e+e \sqrt{e}+e^2\right]$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Example4
- If three equal subdivisions on $\left[\frac{\pi}{2}, \pi\right]$ are used, what is the trapezoidal approximation of $\int_{\pi / 2}^\pi \sin x d x ?$
(A) $\frac{\pi}{12}\left(\sin \frac{2 \pi}{3}+\sin \frac{5 \pi}{6}+\sin \pi\right)$
(B) $\frac{\pi}{12}\left(\sin \frac{\pi}{2}+\sin \frac{2 \pi}{3}+\sin \frac{5 \pi}{6}+\sin \pi\right)$
(C) $\frac{\pi}{12}\left(\sin \frac{\pi}{2}+2 \sin \frac{2 \pi}{3}+2 \sin \frac{5 \pi}{6}+\sin \pi\right)$
(D) $\frac{\pi}{6}\left(\sin \frac{\pi}{2}+\sin \frac{2 \pi}{3}+\sin \frac{5 \pi}{6}+\sin \pi\right)$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Example5
- If three equal subdivisions on $[0,6]$ are used, what is the trapezoidal approximation of $\int_0^6 \ln (x+1) d x$ ?
(A) $\frac{1}{3}(\ln 1+\ln 9+\ln 25+\ln 7)$
(B) $\frac{1}{2}(\ln 1+\ln 9+\ln 25+\ln 7)$
(C) $\ln 1+\ln 3+\ln 5+\ln 7$
(D) $\ln 1+\ln 9+\ln 25+\ln 7$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D