AP Calculus BC 3.1 The Chain Rule Study Notes - New Syllabus
AP Calculus BC 3.1 The Chain Rule Study Notes- New syllabus
AP Calculus BC 3.1 The Chain Rule Study Notes – AP Calculus BC- per latest AP Calculus BC Syllabus.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Calculate derivatives of compositions of differentiable functions.
Key Concepts:
- The Chain Rule
The Chain Rule: Calculating Derivatives of Compositions of Functions
The Chain Rule: Calculating Derivatives of Compositions of Functions
If \( y = f(g(x)) \), where both \( f \) and \( g \) are differentiable, then the derivative is:
\( \dfrac{dy}{dx} = f'(g(x)) \cdot g'(x) \).

Key Idea: Differentiate the outer function, keep the inside unchanged, then multiply by the derivative of the inside function.
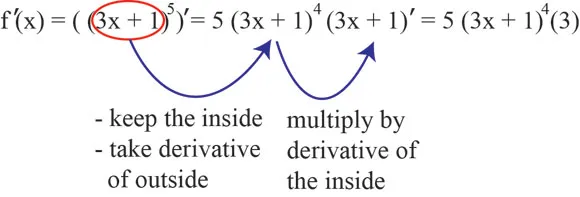
Notation: If \( y = f(u) \) and \( u = g(x) \), then:
\( \dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{dy}{du} \cdot \dfrac{du}{dx} \).
Example:
Find \( \dfrac{d}{dx} \big( (3x^2 + 5)^4 \big) \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Let \( u = 3x^2 + 5 \), then \( y = u^4 \).
\( \dfrac{dy}{du} = 4u^3 \), \( \dfrac{du}{dx} = 6x \).
Apply the chain rule:
\( \dfrac{dy}{dx} = 4u^3 \cdot 6x = 24x(3x^2 + 5)^3 \).
Answer: \( 24x(3x^2 + 5)^3 \).
Example:
Find \( \dfrac{d}{dx} \big( \sin(x^3) \big) \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Outer function: \( \sin(u) \), inner function: \( u = x^3 \).
\( \dfrac{d}{du}(\sin u) = \cos u \), \( \dfrac{du}{dx} = 3x^2 \).
Chain rule:
\( \dfrac{d}{dx}[\sin(x^3)] = \cos(x^3) \cdot 3x^2 \).
Answer: \( 3x^2 \cos(x^3) \).
Example:
Differentiate \( y = \ln(5x^2 + 4) \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Outer function: \( \ln(u) \), inner: \( u = 5x^2 + 4 \).
\( \dfrac{d}{du}[\ln u] = \dfrac{1}{u} \), \( \dfrac{du}{dx} = 10x \).
Apply chain rule:
\( \dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{1}{5x^2 + 4} \cdot 10x = \dfrac{10x}{5x^2 + 4} \).
Answer: \( \dfrac{10x}{5x^2 + 4} \).
Example:
Find \( \dfrac{d}{dx} \big( e^{\sin x} \big) \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Outer function: \( e^u \), inner: \( u = \sin x \).
\( \dfrac{d}{du}[e^u] = e^u \), \( \dfrac{du}{dx} = \cos x \).
Chain rule:
\( \dfrac{d}{dx}[e^{\sin x}] = e^{\sin x} \cdot \cos x \).
Answer: \( e^{\sin x} \cos x \).
