Question
Let f be the function defined by \(f(x)=\frac{3}{2x^{2}-7x+5}.\)
(a) Find the slope of the line tangent to the graph of f at x = 3.
(b) Find the x-coordinate of each critical point of f in the interval 1 < x < 2.5. Classify each critical point as the location of a relative minimum, a relative maximum, or neither. Justify your answers.
(c) Using the identity that \(\frac{3}{2x^{2}-7x+5}=\frac{2}{2x-5}-\frac{1}{x-1}, evaluate\int_{5}^{\infty }f(x)\) or show that the integral diverges.
(d) Determine whether the series \(\sum_{n=5}^{\infty }\frac{3}{2n^{2}-7n+5}\) converges or diverges. State the conditions of the test used for determining convergence or divergence.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) \(f'(x)=\frac{-3(4x-7)}{\left ( 2x^{2}-7x+5 \right )^{2}}\)
\(f'(3)=\frac{-3(5)}{\left ( 18-21+5 \right )^{2}}=-\frac{15}{4}\)
(b) \(f'(x)=\frac{-3(4x-7)}{\left ( 2x^{2}-7x+5 \right )^{2}}=0\Rightarrow x=\frac{7}{4}\)
The only critical point in the interval 1 < x < 2.5 has x-coordinate \(\frac{7}{4}.\) f ′ changes sign from positive to negative at \(x=\frac{7}{4}.\) Therefore, f has a relative maximum at \(x=\frac{7}{4}.\)
(c) \(\int_{5}^{\infty }f(x)dx=\lim_{b\rightarrow \infty }\int_{5}^{b}\frac{3}{2x^{2}-7x+5}dx =\lim_{b\rightarrow \infty }\int_{5}^{b}\left ( \frac{2}{2x-5} -\frac{1}{x-1}\right )dx\)
\(=\lim_{b\rightarrow \infty }\left [ In(2x-5)-In(x-1) \right ]_{5}^{b}=\lim_{b\rightarrow \infty }\left [ In\left ( \frac{2x-5}{x-1} \right ) \right ]_{5}^{b}\)
\(=\lim_{b\rightarrow \infty }\left [ In(\frac{2b-5}{b-1})-In(\frac{5}{4}) \right ]=In 2-In\left ( \frac{5}{4} \right )=In\left ( \frac{8}{5} \right )\)
(d) f is continuous, positive, and decreasing on [5, ∞). The series converges by the integral test since \(\int_{5}^{\infty }\frac{3}{2x^{2}-7x+5}dx\) converges.
-OR –
\(\frac{3}{2n^{2}-7n+5}>0 and \frac{1}{n^{2}}>0 for n\geq 5.\)
Since \(\frac{\frac{3}{2n^{2}-7n+5}}{\frac{1}{n^{2}}} =\frac{3}{2}\) and the series \(\sum_{n=5}^{\infty }\frac{1}{n^{2}}\) converges, the series \(\sum_{n=5}^{\infty }\frac{3}{2n^{2}-7n+5}\) converges by the limit comparison test.
Question
Suppose the Nth partial sum of a series \(\sum_{n=0}^{\infty }a_{n}\) is \(s_{N}=N\tan \left ( \frac{\pi }{N} \right )\)
(A) Find \(a_{4}\).
(B) Find\( \sum_{n=0}^{\infty }a_{n}\).
Answer/Explanation

Question
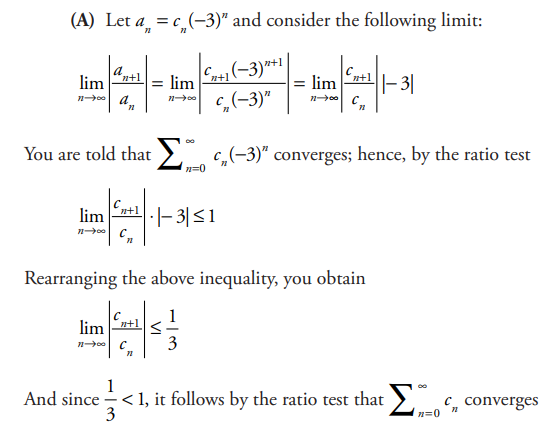
Suppose that \(\sum_{n=0}^{\infty }c_{n}x^{n}\) converges when x = -3 and diverges when x = 5. Using this information, determine whether the following series converge or diverge.
(A)\(\sum_{n=0}^{\infty }c_{n}\)
(B)\(\sum_{n=0}^{\infty }c_{n}6^{n}\)
(C)\(\sum_{n=0}^{\infty }c_{n}(-2)^{n}\)
(D)\(\sum_{n=0}^{\infty }(-1)^{n}c_{n}7^{n}\)
Answer/Explanation